 京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2
京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2
《中国塑料》编辑部 ©2008-2024 版权所有
地址:北京市海淀区阜成路11号 邮编:100048
编辑部:010-68985541 联系信箱:cp@plaschina.com.cn
广告部/发行部:010-68985253 本系统由北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司设计开发

中国塑料 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (11): 13-19.DOI: 10.19491/j.issn.1001-9278.2025.11.003
收稿日期:2024-11-27
出版日期:2025-11-26
发布日期:2025-11-21
通讯作者:
李果(1987-),男,助理研究员,博士,主要研究方向为高分子材料成型装备与工艺,gl_119@ecust.edu.cn作者简介:徐成龙(2000-),男,硕士,主要研究方向为高分子材料成型装备与工艺,xcl1526259715@163.com
XU Chenglong( ), WANG Yu, LI Guo(
), WANG Yu, LI Guo( ), XIE Linsheng, MA Yulu
), XIE Linsheng, MA Yulu
Received:2024-11-27
Online:2025-11-26
Published:2025-11-21
Contact:
LI Guo
E-mail:xcl1526259715@163.com;gl_119@ecust.edu.cn
摘要:
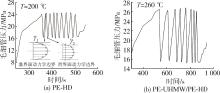
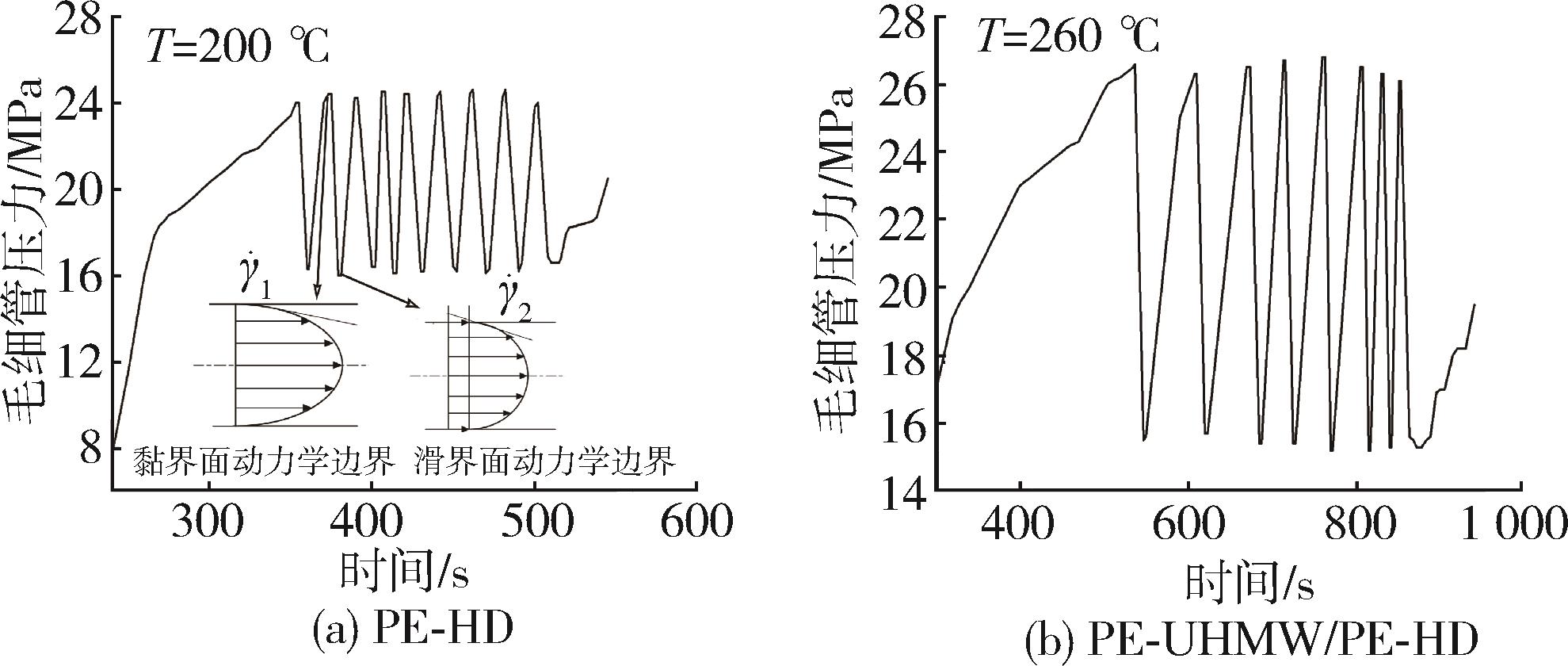
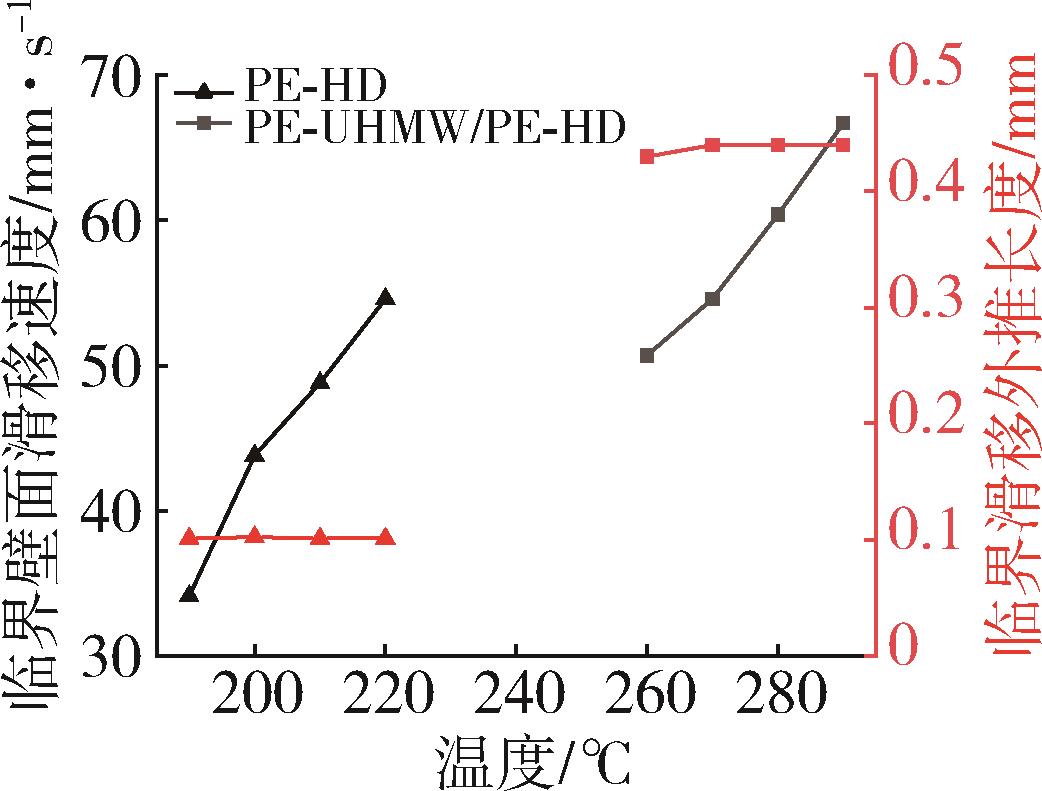
针对超高分子量聚乙烯在熔融挤出过程中容易产生挤出缺陷的问题,借助毛细管流变仪挤出超高分子量聚乙烯(PE⁃UHMW)/高密度聚乙烯(PE⁃HD)共混物,通过观察纯PE⁃UHMW、纯PE⁃HD及共混挤出物的表面形貌,分析了不同挤出温度下共混物的不稳定流动行为,包括挤出过程中发生振荡畸变和熔体破裂现象的临界剪切速率,以及超过临界剪切速率后挤出物的压力振荡行为和壁面滑移现象。结果表明,共混物的挤出形貌经过了鲨鱼皮⁃振荡畸变⁃整体熔体破裂的演变过程。毛细管挤出温度为260 ℃时,当剪切速率达到116 s-1后,挤出压力产生剧烈振荡,熔体与管壁界面存在动态黏⁃滑转变特征,引起挤出物的振荡畸变和壁面滑移现象。同时,挤出温度的升高可以延缓挤出物不稳定流动的发生,引发振荡畸变形貌发生的剪切速率区间从116~522 s-1增加至152~686 s-1。
中图分类号:
徐成龙, 王玉, 李果, 谢林生, 马玉录. 基于毛细管挤出的PE⁃UHMW/PE⁃HD共混物不稳定流动行为分析[J]. 中国塑料, 2025, 39(11): 13-19.
XU Chenglong, WANG Yu, LI Guo, XIE Linsheng, MA Yulu. Analysis of unstable flow behavior in PE⁃UHMW/PE⁃HD blends during capillary extrusion[J]. China Plastics, 2025, 39(11): 13-19.
| 试样 | 零剪切黏度η0/ Pa·s | 松弛时间 λ/s | 非牛顿指数 n |
|---|---|---|---|
| PE⁃HD | 1.76×105 | 16.44 | 0.34 |
| PE⁃UHMW/PE⁃HD | 9.70×105 | 25.72 | 0.30 |
| PE⁃UHMW | 1.51×106 | 27.04 | 0.28 |
| 试样 | 零剪切黏度η0/ Pa·s | 松弛时间 λ/s | 非牛顿指数 n |
|---|---|---|---|
| PE⁃HD | 1.76×105 | 16.44 | 0.34 |
| PE⁃UHMW/PE⁃HD | 9.70×105 | 25.72 | 0.30 |
| PE⁃UHMW | 1.51×106 | 27.04 | 0.28 |
| 试样 | 振荡畸变 | 螺旋熔体破裂 | 总熔体破裂 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
临界剪切 速率/s-1 | 临界剪切 应力/kPa | 临界剪切 速率/s-1 | 临界剪切 速率/s-1 | |
| PE⁃HD | 428 | 272 | 774 | ⁃ |
| PE⁃UHMW/PE⁃HD | 116 | 342 | ⁃ | 522 |
| PE⁃UHMW | 27 | 395 | ⁃ | 450 |
| 试样 | 振荡畸变 | 螺旋熔体破裂 | 总熔体破裂 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
临界剪切 速率/s-1 | 临界剪切 应力/kPa | 临界剪切 速率/s-1 | 临界剪切 速率/s-1 | |
| PE⁃HD | 428 | 272 | 774 | ⁃ |
| PE⁃UHMW/PE⁃HD | 116 | 342 | ⁃ | 522 |
| PE⁃UHMW | 27 | 395 | ⁃ | 450 |
| [1] | Shelly D, Lee S Y, Park S J. Compatibilization of ultra⁃high molecular weight polyethylene (PE⁃UHMW) fibers and their composites for superior mechanical performance: A concise review [J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2024, 275: 111294. |
| [2] | Li W, Li R, Li C, et al. Mechanical properties of surface⁃modified ultra⁃high molecular weight polyethylene fiber reinforced natural rubber composites [J]. Polymer Composites, 2017, 38(6): 1 215⁃1 220. |
| [3] | Shen H, He L, Fan C, et al. Effective dissolution of PE⁃UHMW in PE⁃HD improved by high temperature melting and subsequent shear[J]. Polymer Engineering & Science, 2015, 55(2): 270⁃276. |
| [4] | Kim T, Chae Y. Synthesis and application of novel high light fastness red dyes for ultra high molecular weight polyethylene fibers[J]. Fibers and Polymers, 2014, 15(2): 248⁃253. |
| [5] | Riveiro A, Soto R, Del Val J, et al. Laser surface modification of ultra⁃high⁃molecular⁃weight polyethylene (PE⁃UHMW) for biomedical applications[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2014, 302: 236⁃242. |
| [6] | XIE Y C, QI S B, BAI J Q, et al. Ballistic performance of flexible structures composed of PE⁃UHMW fibers and airbag: Effects of the stacking order [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2024, 191: 105008. |
| [7] | Khasraghi S S, Rezaei M. Preparation and characterization of PE⁃UHMW/PE⁃HD/MWCNT melt⁃blended nanocomposites[J]. Journal of Thermoplastic Composite Materials, 2015, 28(3): 305⁃326. |
| [8] | Yang H, Yilmaz G, Jiang J, et al. Pelletizing ultra⁃high molecular weight polyethylene (PE⁃UHMW) powders with a novel tapered die and addition of high density polyethylene (PE⁃HD): Processing, morphology, and properties [J]. Polymer, 2022, 256: 125171. |
| [9] | Lee H Y, Kim D H, Son Y. Anomalous rheological behavior of polyethylene melts in the gross melt fracture regime in the capillary extrusion [J]. Polymer, 2006, 47(11): 3 929⁃3 934. |
| [10] | Barone J R, Plucktaveesak N, Wang S Q. Interfacial molecular instability mechanism for sharkskin phenomenon in capillary extrusion of linear polyethylenes[J]. Journal of Rheology, 1998, 42(4): 813⁃832. |
| [11] | Delgadillo⁃Velazquez O, Hatzikiriakos S G. Processability of LLDPE/LDPE blends: Capillary extrusion studies. Polymer Engineering and Science, 2007, 47(9): 1 317⁃1 326. |
| [12] | Monchai S, Mieda N, Doan V A, et al. Effect of shear history on flow instability at capillary extrusion for long⁃chain branched polyethylene[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2012, 124(1): 429⁃435. |
| [13] | Ansari M, Inn Y W, Sukhadia A M, et al. Melt fracture of PE⁃HDs: Metallocene versus Ziegler–Natta and broad MWD effects[J]. Polymer, 2012, 53(19): 4 195⁃4 201. |
| [14] | Adesina A A, Nasser M S, Hussein I A. Comparative Analysis of the Effect of Organoclay, Boron Nitride, and Fluoropolymer on the Rheology and Instabilities in the Extrusion of High Density Polyethylene[J]. International Journal of Polymer Science, 2015. |
| [15] | Allal A, Lavernhe A, Vergnes B, et al. Relationships between molecular structure and sharkskin defect for linear polymers[J]. Journal of Non⁃Newtonian Fluid Mechanics, 2006, 134(1⁃3 SPEC. ISS.): 127⁃135. |
| [16] | Ansari M, Derakhshandeh M, Doufas A A, et al. The role of microstructure on melt fracture of linear low density polyethylenes[J]. Polymer Testing, 2018, 67: 266⁃274. |
| [17] | 尹文艳. 不同润滑剂对高密度聚乙烯(PE⁃HD)流变性能影响的研究 [D]. 青岛科技大学, 2006. |
| [18] | Chen J, Yang W, Yu G P, et al. Continuous extrusion and tensile strength of self⁃reinforced PE⁃HD/PE⁃UHMW sheet[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2008, 202(1): 165⁃169. |
| [19] | Shen H, He L, Fan C, et al. Improving the integration of PE⁃HD/PE⁃UHMW blends by high temperature melting and subsequent shear[J]. Materials Letters, 2015, 138: 247⁃250. |
| [20] | 郭浩东, 贾润礼. PE⁃UHMW/PE⁃HD自增强材料研究进展 [J]. 合成材料老化与应用, 2022, 51(02): 95⁃98. |
| GUO H D, JIA R L. Research progress of PE⁃UHMW/PE⁃HD self⁃reinforcing materials[J]. Synthetic Materials Aging and Application, 2022, 51(02): 95⁃98. | |
| [21] | 张强, 王庆昭, 陈勇. 熔纺超高分子量聚乙烯纤维初生丝制备及拉伸工艺 [J]. 工程塑料应用, 2023, 51(05): 81⁃85+97. |
| ZHANG Q, WANG Q Z, CHEN Y. Preparation and drawing process of melt⁃spun ultra high molecular weight polyethylene virgin fibers[J]. Polymer Materials and Engineering, 2023, 51(05): 81⁃85+97. | |
| [22] | 李果, 谢林生, 罗日萍, 等. 叠片式密炼机转子结构对混合特性的影响 [J]. 高分子材料科学与工程, 2014, 30(03): 134⁃138+43. |
| LI G, XIE L S, LUO R P, et al. The influence of rotor structure on mixing characteristics of laminated mixer[J]. Polymer Materials Science and Engineering, 2014, 30(03): 134⁃138+43. | |
| [23] | LIU M, WANG Y, CHEN J, et al. The retarded recovery of disentangled state by blending PE⁃HD with ultra⁃high molecular weight polyethylene [J]. Polymer, 2020, 192: 122329. |
| [24] | 吴其晔, 李 鹏, 王宁, et al. 聚合物熔体挤出畸变的指纹辨识及量化描述 [J]. 现代塑料加工应用, 2013, 25(02): 59⁃63. |
| WU Q Y, LI P, WANG N, et al. The fingerprinting and quantitative descriptions of extrudate distortions of polymer melts[J]. Modern Plastics Processing and Applications[J]. 2013, 25(02): 59⁃63. | |
| [25] | Cogswell F N. Stretching flow instabilities at the exits of extrusion dies[J]. Journal of Non⁃Newtonian Fluid Mechanics, 1977, 2(1): 37⁃47. |
| [26] | 张海琛. 基于拉伸流变的PE⁃UHMW熔融挤出过程及其结构与性能研究 [D].华南理工大学, 2017. |
| [27] | Zhang X, Zhao S, Xin Z. The chain dis⁃entanglement effect of polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes (POSS) on ultra⁃high molecular weight polyethylene (PE⁃UHMW) [J]. Polymer, 2020, 202: 122631. |
| [28] | Joshi Y M, Lele A K, Mashelkar R A. A unified wall slip model[J]. Journal of Non⁃Newtonian Fluid Mechanics, 2000, 94(2): 135⁃149. |
| [29] | 王克俭, 周持兴. 考虑壁面滑移的Z⁃W流变模型及其应用 [J]. 高分子通报, 2003(01): 8⁃17. |
| WANG K J, ZHOU C X. Z⁃W rheological model for polymer melt considering wall slip and its applications[J]. Polymer Bulletin, 2003(01): 8⁃17. | |
| [30] | 刘丽超. 超高分子量聚乙烯改性料流变特性及熔融纺丝研究 [D].北京化工大学, 2020. |
| [31] | 吴其晔,巫静安. 高分子材料流变学 [M]. 北京:高等教育出版社, 2002. |
| [32] | Wang S Q. Molecular transitions and dynamics at polymer / wall interfaces: origins of flow instabilities and wall slip[J]. Advances in Polymer Science, 1999, 138: 227⁃275. |
| [33] | 廖华勇, 谭中欣, 陶国良. 聚合物熔体的壁面滑移行为 [J]. 高分子材料科学与工程, 2009, 25(12): 103⁃106. |
| LIAO H Y, TAN Z X, TAO G L. Wall slip behavior of polymer melt[J]. Polymer Materials Science and Engineering, 2009, 25(12): 103⁃106. |
| [1] | 牛凯, 张润, 刘鸣飞, 傅陈超, 薛平, 吴嘉俊. 热力耦合作用下PE⁃UHMW的黏弹塑性变形性能初探[J]. 中国塑料, 2025, 39(9): 7-11. |
| [2] | 陈天欢, 严成, 蒋干兵, 郭帅, 颜甜甜, 钱坤, 俞科静. 单宁酸表面改性PE⁃UHMW纤维及其界面性能研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2024, 38(8): 26-32. |
| [3] | 严成, 李露露, 陈天欢, 郭帅, 俞科静. 超高分子量聚乙烯纤维表面纳米ZnO可控生长及其界面性能研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2024, 38(5): 47-54. |
| [4] | 宋瑞铭, 吕怀兴, 张文龙, 李斌, 李慧. 锂电池湿法隔膜用超高分子量聚乙烯的降解动力学研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2024, 38(12): 24-28. |
| [5] | 余大荣, 辛勇. 超高分子量聚乙烯改性研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(8): 135-145. |
| [6] | 王轲, 龙春光. PE⁃UHMW/海泡石纤维复合材料的力学性能与摩擦学性能研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(5): 19-23. |
| [7] | 许荣霞, 魏刚, 魏莉岚, 吴洁萃, 蒋雨江. Nano⁃SiO2及PA6复合改性PE⁃UHMW的摩擦磨损性能研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(4): 47-52. |
| [8] | 王非, 刘丽超, 薛平. 熔纺PE⁃UHMW/PE⁃HD共混纤维的力学性能和晶体结构研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(1): 47-52. |
| [9] | 陈欣 沙金 陈涛 谢林生 马玉录. EMAA-Na离聚物对PE-HD/Al2O3复合材料微观结构和流变特性的影响[J]. 中国塑料, 2018, 32(08): 19-24. |
| [10] | 黄安民, 刘婷, 朱志勇, 伍海斌. 铁路桥梁支座耐磨材料的性能研究与优选应用[J]. 中国塑料, 2015, 29(11): 38-42 . |
| [11] | 罗鹏, 刘惠文, 戴文利, 邹晓轩, 敬波. PE-UHMW对聚甲醛力学性能及非等温结晶的影响研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2014, 28(04): 46-51 . |
| [12] | 何振强 薛平 戚晓芸. 无机填料增强改性超高相对分子质量聚乙烯的研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2012, 26(11): 50-55 . |
| [13] | 吕晓雷 倪忠斌 薛花娟 赵军 刘礼华 陈明清. 桥梁缆索PE护套的抗紫外老化性能研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2009, 23(06): 60-64 . |
| [14] | 王新威 吴向阳 张炜 张玉梅 徐静安. 超高分子量聚乙烯的滑动摩擦磨损研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2009, 23(05): 80-85. |
| [15] | 黄英珠, 信春玲, 付中玉, 何亚东. 聚丙烯/超高相对分子质量聚乙烯共混物的结晶动力学及发泡性能研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2009, 23(02): 54-60 . |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2
京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2