 京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2
京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2
《中国塑料》编辑部 ©2008-2024 版权所有
地址:北京市海淀区阜成路11号 邮编:100048
编辑部:010-68985541 联系信箱:cp@plaschina.com.cn
广告部/发行部:010-68985253 本系统由北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司设计开发

中国塑料 ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (9): 73-81.DOI: 10.19491/j.issn.1001-9278.2024.09.013
宋莎莎1( ), 司星雨1, 郑霓鸣1, 俞盈2, 张扬1(
), 司星雨1, 郑霓鸣1, 俞盈2, 张扬1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-03-10
出版日期:2024-09-26
发布日期:2024-09-27
通讯作者:
张扬(1982—),男,教授,博士,研究方向为聚合物基功能复合材料,绿色包装材料, zhangyang@th.btbu.edu.cn作者简介:宋莎莎(1997—),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为电磁功能复合材料,17855766500@163.com
基金资助:
SONG Shasha1( ), SI Xingyu1, ZHENG Niming1, YU Ying2, ZHANG Yang1(
), SI Xingyu1, ZHENG Niming1, YU Ying2, ZHANG Yang1( )
)
Received:2024-03-10
Online:2024-09-26
Published:2024-09-27
Contact:
ZHANG Yang
E-mail:17855766500@163.com;zhangyang@th.btbu.edu.cn
摘要:
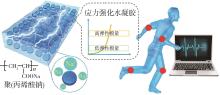
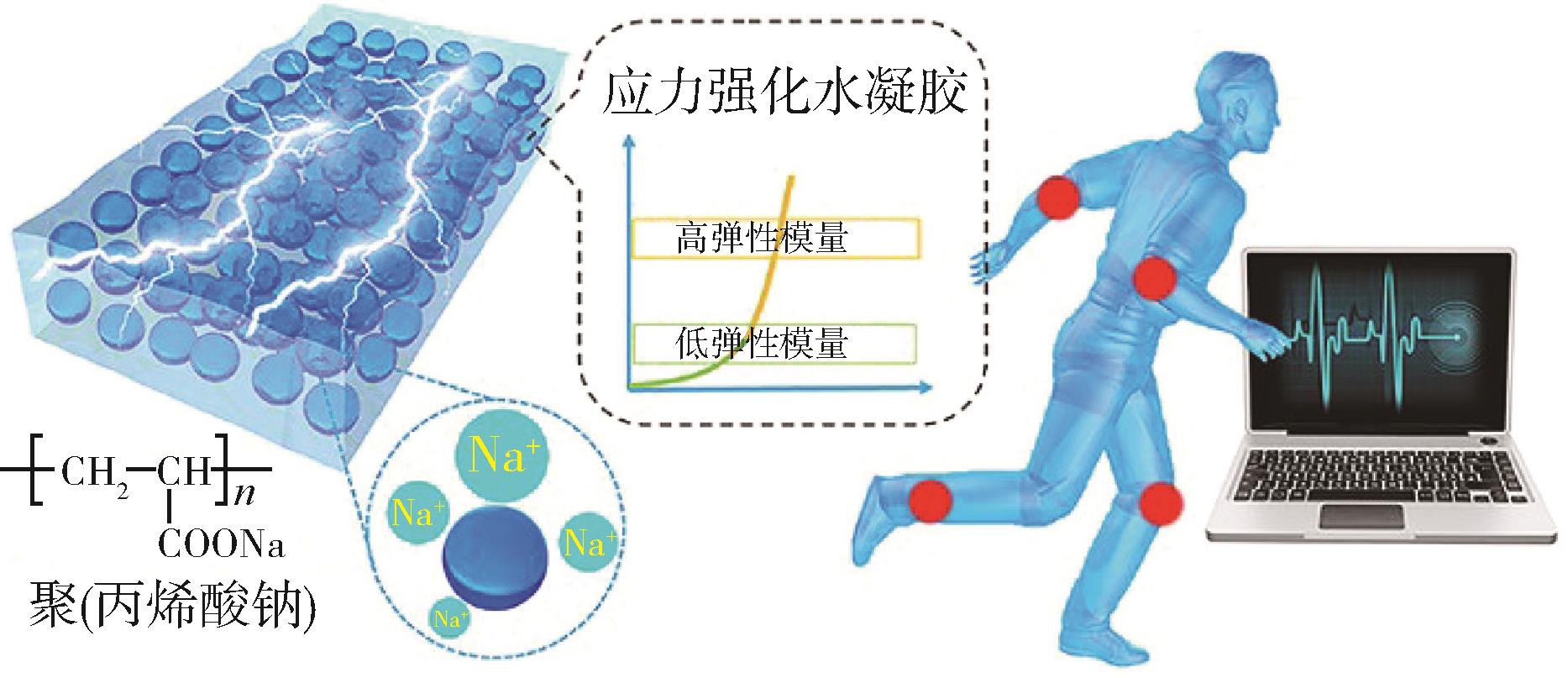
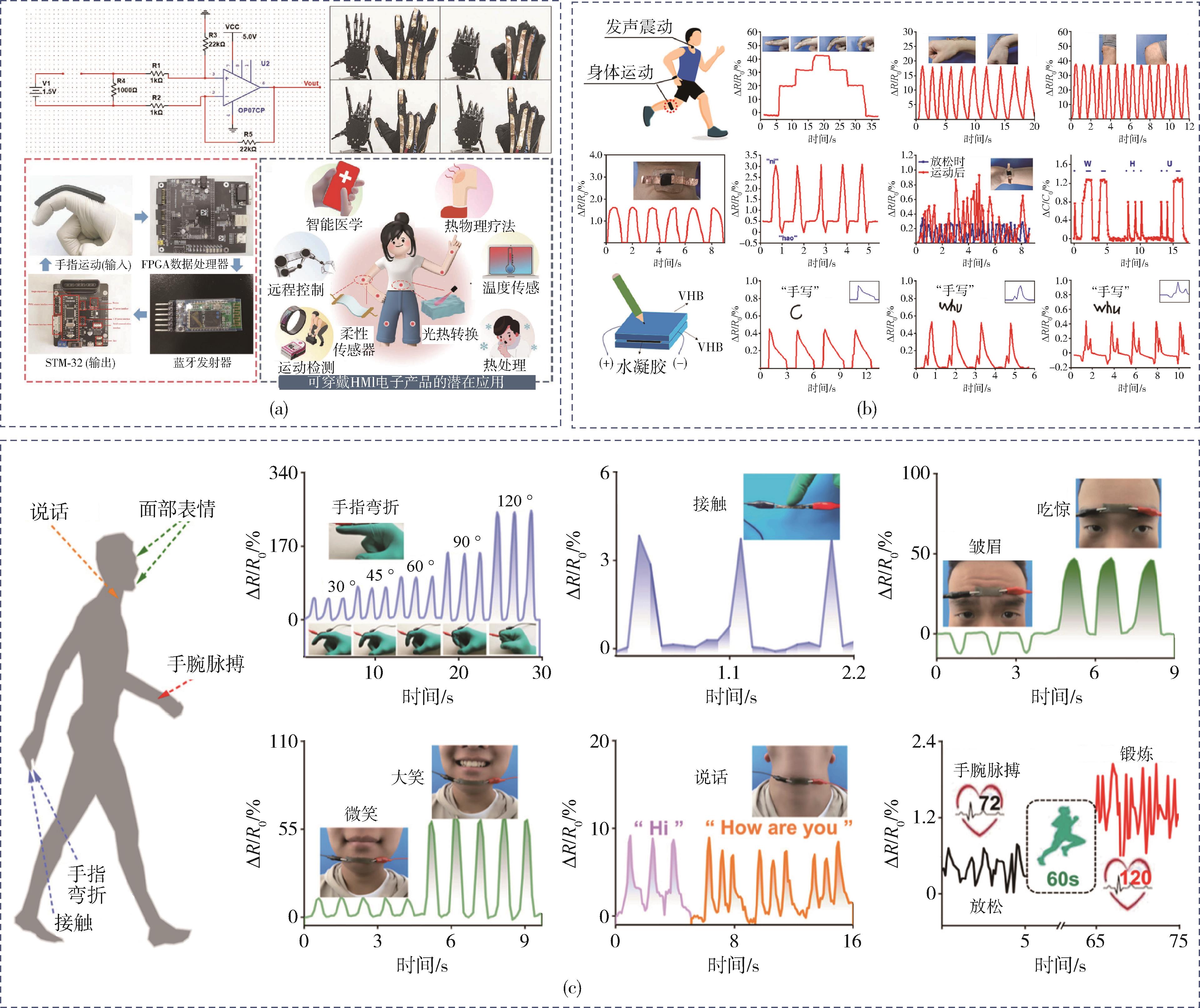
首先综述了压电式、电阻式、摩擦电式以及电容式4种应变传感器的类型的及其传感机理。其次,深入探讨了提升水凝胶应变传感器灵敏度的关键方法。通过选用导电纳米粒子与离子材料等适宜材料,采用微球、锯齿状、多孔等特定结构设计,以及多因素的综合复合等方式,可以赋予水凝胶应变传感器高灵敏度的特征。随后,归纳了此类传感器在智能电子、可穿戴设备和医疗健康领域的应用实例。最后,展望了目前面临的挑战与未来的机遇。
中图分类号:
宋莎莎, 司星雨, 郑霓鸣, 俞盈, 张扬. 水凝胶用于高灵敏度应变传感器的研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2024, 38(9): 73-81.
SONG Shasha, SI Xingyu, ZHENG Niming, YU Ying, ZHANG Yang. Research progress in hydrogels for high⁃sensitivity strain sensors[J]. China Plastics, 2024, 38(9): 73-81.

| 1 | CAO M, SU J, FAN S, et al. Wearable piezoresistive pressure sensors based on 3D graphene [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 406: 126 777⁃126 796. |
| 2 | CUI C, FU Q J, MENG L, et al. Recent progress in natural biopolymers conductive hydrogels for flexible wearable sensors and energy devices: materials, structures, and performance [J]. Acs Applied Bio Materials, 2021, 4(1): 85⁃121. |
| 3 | LI C J. Towards conductive hydrogels in e⁃skins: a review on rational design and recent developments [J]. Rsc Advances, 2021, 11(54): 33 835⁃33 848. |
| 4 | OH J Y, SON D, KATSUMATA T, et al. Stretchable self⁃healable semiconducting polymer film for active⁃matrix strain⁃sensing array [J]. Science Advances, 2019, 5(11): eaav3097. |
| 5 | AJEEV A, JAVAREGOWDA B H, ALI A, et al. Ultrahigh sensitive carbon⁃based conducting rubbers for flexible and wearable human⁃machine intelligence sensing [J]. Advanced Materials Technologies, 2020, 5(12): 2000690. |
| 6 | SUN T, ZHANG J, CHEN Y, et al. Bioinspired, ultra‐sensitive flexible strain sensor based on ceramic fiber paper with superhydrophobic and high‐temperature‐resistant properties [J]. Advanced Materials Technologies, 2022, 8(3): 2200972. |
| 7 | MAN Y, LIU Y, MIAO H, et al. Stretchable and high sensitive ionic conductive hydrogel for the direction recognizable motion detection sensor [J]. Giant, 2023, 16: 100199. |
| 8 | LI G, LI C, LI G, et al. Development of conductive hydrogels for fabricating flexible strain sensors [J]. Small, 2021, 18(5): 2101518. |
| 9 | CHEN K, HU Y P, LIU M X, et al. Highly stretchable, tough, and conductive Ag@Cu nanocomposite hydrogels for flexible wearable sensors and bionic electronic skins [J]. Macromolecular Materials and Engineering, 2021, 306(10): 2100341. |
| 10 | XU J X, GUO Z Y, ZHENG J. Tough, adhesive, self⁃healing, fully physical crosslinked κ⁃CG⁃K+/pHEAA double⁃network ionic conductive hydrogels for wearable sensors [J]. Polymer, 2021, 236: 124 321⁃124 332. |
| 11 | HU Z, LI J, WEI X, et al. Enhancing strain⁃sensing properties of the conductive hydrogel by introducing PVDF⁃TrFE [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(40): 45 853⁃45 868. |
| 12 | FU R, TU L, ZHOU Y, et al. A tough and self⁃powered hydrogel for artificial skin [J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2019, 31(23): 9 850⁃9 860. |
| 13 | ZHOU H, WANG Z, ZHAO W, et al. Robust and sensitive pressure/strain sensors from solution processable composite hydrogels enhanced by hollow⁃structured conducting polymers [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 403: 126 307⁃126 316. |
| 14 | ZHANG H, SHEN H, LAN J, et al. Dual⁃network polyacrylamide/carboxymethyl chitosan⁃grafted⁃polyaniline conductive hydrogels for wearable strain sensors [J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2022, 295: 119 848⁃119 858. |
| 15 | WANG Z, LIU Z R, LI L L. Stretchable unsymmetrical piezoelectric BaTiO3 composite hydrogel for triboelectric nanogenerators and multimodal sensors [J]. Acs Nano, 2022, (16): 1 661⁃1 670. |
| 16 | XU C H, YANG Y R, GAO W. Skin⁃interfaced sensors in digital medicine: from materials to applications [J]. Matter, 2020, 2(6): 1 414⁃1 445. |
| 17 | MO F, HUANG Y, LI Q, et al. A highly stable and durable capacitive strain sensor based on dynamically super‐tough hydro/organo‐gels [J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(28): 2010830. |
| 18 | WANG X D, WANG X Y, PI M H, et al. High⁃strength, highly conductive and woven organic hydrogel fibers for flexible electronics [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 428: 131 172⁃131 182. |
| 19 | WEBER M, KIM J⁃H, LEE J⁃H, et al. High⁃performance nanowire hydrogen sensors by exploiting the synergistic effect of Pd nanoparticles and metal–organic framework membranes [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(40): 34 765⁃34 773. |
| 20 | ZHANG J, WANG Z. Nanoparticle–hydrogel based sensors: synthesis and applications [J]. Catalysts, 2022, 12(10): 1 096. |
| 21 | HE X⁃F, ZENG Z⁃F, NI Q⁃Y, et al. Mechanical robust and highly conductive composite hydrogel reinforced by a combination of cellulose nanofibrils/polypyrrole toward high⁃performance strain sensor [J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2023, 266: 111022. |
| 22 | YOU L, ZHENG Z, XU W, et al. Self⁃healing and adhesive MXene⁃polypyrrole/silk fibroin/polyvinyl alcohol conductive hydrogels as wearable sensor [J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2024, 263: 130439. |
| 23 | ZHAO L, ZHANG H, GUO Z, et al. Natural glycyrrhizic acid⁃tailored homogeneous conductive polyaniline hydrogel as a flexible strain sensor [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(45): 51 394⁃51 403. |
| 24 | LI Y, GONG Q, HAN L, et al. Carboxymethyl cellulose assisted polyaniline in conductive hydrogels for high⁃performance self⁃powered strain sensors [J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2022, 298: 120060. |
| 25 | PENG X, WANG W, YANG W, et al. Stretchable, compressible, and conductive hydrogel for sensitive wearable soft sensors [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2022, 618: 111⁃120. |
| 26 | XU L, LIU S, ZHU L, et al. Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose reinforced conducting polymer hydrogels with ultra⁃stretchability and low hysteresis as highly sensitive strain sensors for wearable health monitoring [J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2023, 236: 123956. |
| 27 | SUN X, QIN Z, YE L, et al. Carbon nanotubes reinforced hydrogel as flexible strain sensor with high stretchability and mechanically toughness [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 382: 122832. |
| 28 | LIU X, HUANG Z, YE C, et al. Graphene‐based hydrogel strain sensors with excellent breathability for motion detection and communication [J]. Macromolecular Materials and Engineering, 2022, 307(8): 2200001. |
| 29 | WANG Y, ZHU L, KONG X, et al. Fabrication of an ion⁃enhanced low⁃temperature tolerant graphene/PAA/KCl hydrogel and its application for skin sensors [J]. Nanoscale, 2023, 15(12): 5 938⁃5 947. |
| 30 | ZHANG L, WANG J, WANG S, et al. Neuron⁃inspired multifunctional conductive hydrogels for flexible wearable sensors [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2022, 10(11): 4 327⁃4 335. |
| 31 | ZHANG W, ZHANG X, ZHAO W, et al. High⁃sensitivity composite dual⁃network hydrogel strain sensor and its application in intelligent recognition and motion monitoring [J]. ACS Applied Polymer Materials, 2023, 5(4): 2 628⁃2 638. |
| 32 | QIN Z, SUN X, YU Q, et al. Carbon nanotubes/hydrophobically associated hydrogels as ultrastretchable, highly sensitive, stable strain, andpressure sensors [J]. Acs Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(4): 4 944⁃4 953. |
| 33 | CUI J, CHEN J, NI Z, et al. High⁃sensitivity flexible sensor based on biomimetic strain⁃stiffening hydrogel [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(41): 47 148⁃47 156. |
| 34 | LI X, LIU Z, LIANG Y, et al. Chitosan⁃based double cross⁃linked ionic hydrogels as a strain and pressure sensor with broad strain⁃range and high sensitivity [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2022, 10(18): 3 434⁃3 443. |
| 35 | NARONGTHONG J, DAS A, LE H H, et al. An efficient highly flexible strain sensor: Enhanced electrical conductivity, piezoresistivity and flexibility of a strongly piezoresistive composite based on conductive carbon black and an ionic liquid [J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2018, 113: 330⁃338. |
| 36 | ZHAI K, WANG H, DING Q, et al. High⁃performance strain sensors based on organohydrogel microsphere film for wearable human⁃computer interfacing [J]. Advanced Science, 2023, 10(6): 2205632. |
| 37 | ZOU J. A stretchable and zigzag structured hydrogel for highly sensitive strain sensors [J]. Materials Letters, 2022, 325: 132835. |
| 38 | CHEN A, ZHANG J, ZHU J, et al. Self⁃adhesive electronic skin for ultra⁃sensitive healthcare monitoring [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2023, 11(10): 4 977⁃4 986. |
| 39 | ZHAO Y, ZHANG B, YAO B, et al. Hierarchically structured stretchable conductive hydrogels for high⁃performance wearable strain sensors and supercapacitors [J]. Matter, 2020, 3(4): 1 196⁃1 210. |
| 40 | FAN K, LI K, HAN L, et al. Multifunctional double⁃network Ti3C2Tx MXene composite hydrogels for strain sensors with effective electromagnetic interference and UV shielding properties [J]. Polymer, 2023, 273: 125865. |
| 41 | HE S, LIU Z, WU X, et al. Novel flexible hydrogels based on carboxymethyl guar gum and polyacrylic acid for ultra⁃highly sensitive and reliable strain and pressure sensors [J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2024, 324: 121515. |
| 42 | WANG W, DENG X, LUO C. Anisotropic hydrogels with high⁃sensitivity and self⁃adhesion for wearable sensors [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2023, 11(1): 196⁃203. |
| 43 | SUN H, ZHAO Y, SHEN C. Environment tolerant conductive nanocomposite organohydrogels as flexible strain sensors and power sources for sustainable electronics [J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(24): 2101696. |
| 44 | WANG J, DAI T, ZHOU Y, et al. Adhesive and high⁃sensitivity modified Ti3C2TX (MXene)⁃based organohydrogels with wide work temperature range for wearable sensors [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2022, 613: 94⁃102. |
| 45 | YANG R, TU Z, CHEN X, et al. Highly stretchable, robust, sensitive and wearable strain sensors based on mesh⁃structured conductive hydrogels [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 480: 148228. |
| 46 | HOU Z, LI X, ZHANG X, et al. A bioinspired, self⁃powered, flytrap⁃based sensor and actuator enabled by voltage triggered hydrogel electrodes [J]. Nano Research, 2023, 16: 10 198–10 205. |
| 47 | BAI Y, LU Y, BI S, et al. Stretchable and photothermal MXene/PAA hydrogel in strain sensor for wearable human‐machine interaction electronics [J]. Advanced Materials Technologies, 2023, 8(9): 2201767. |
| 48 | ROBBY A I, LEE G, LEE K D, et al. GSH⁃responsive self⁃healable conductive hydrogel of highly sensitive strain⁃pressure sensor for cancer cell detection [J]. Nano Today, 2021, 39: 101178. |
| [1] | 曾媛, 李亮, 刘威, 马晶晶, 刘让同. 海藻酸钠/聚丙烯酰胺复合水凝胶的壳聚糖增韧[J]. 中国塑料, 2024, 38(1): 42-48. |
| [2] | 王晓南, 付菁奥, 陈思思, 高海南, 蔡玉东. 水凝胶在油田开采领域的研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2023, 37(10): 101-110. |
| [3] | 周舒毅, 朱敏, 刘忆颖, 曹舒惠, 蔡启轩, 聂慧, 张玉霞, 周洪福. 高分子止血材料研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(7): 74-84. |
| [4] | 刘伟, 吴显, 陈小澄, 成晓琼, 张纯. 羧基化填料对聚乙烯醇/纳米纤维素水凝胶力学、导电和传感性能的影响[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(6): 16-23. |
| [5] | 李海燕, 李爽, 王奇, 崔业翔, 马英杰. 聚丙烯酸/氧化石墨烯自修复水凝胶的合成及性能[J]. 中国塑料, 2016, 30(11): 42-47 . |
| [6] | 孙辉, 胡宇, 杨彪, 许国志. 农林生物质残余物的高值化利用:半纤维素的提取、改性及应用研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2016, 30(04): 12-22 . |
| [7] | 李海燕, 赵志桩, 崔业翔. 聚N异丙基丙烯酰胺/黏土纳米复合自修复水凝胶的制备及性能[J]. 中国塑料, 2015, 29(12): 18-22 . |
| [8] | 舒静, 李小静, 赵大飙. 壳聚糖智能水凝胶研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2010, 24(09): 6-10 . |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2
京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2