京ICP备13020181号-2
© 《China Plastics》
© 《China Plastics》

China Plastics ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (9): 36-40.DOI: 10.19491/j.issn.1001-9278.2024.09.007
• Materials and Properties • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Gang( ), YAO Cheng, JIA Lei, CHEN Xipeng, CAI Hansheng
), YAO Cheng, JIA Lei, CHEN Xipeng, CAI Hansheng
Received:2023-12-28
Online:2024-09-26
Published:2024-09-27
CLC Number:
LIU Gang, YAO Cheng, JIA Lei, CHEN Xipeng, CAI Hansheng. Study on hot⁃stretching⁃induced structure evolution of isotactic polypropylene used in capacitance films[J]. China Plastics, 2024, 38(9): 36-40.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.plaschina.com.cn/EN/10.19491/j.issn.1001-9278.2024.09.007
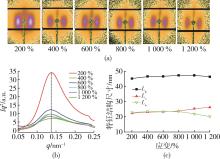
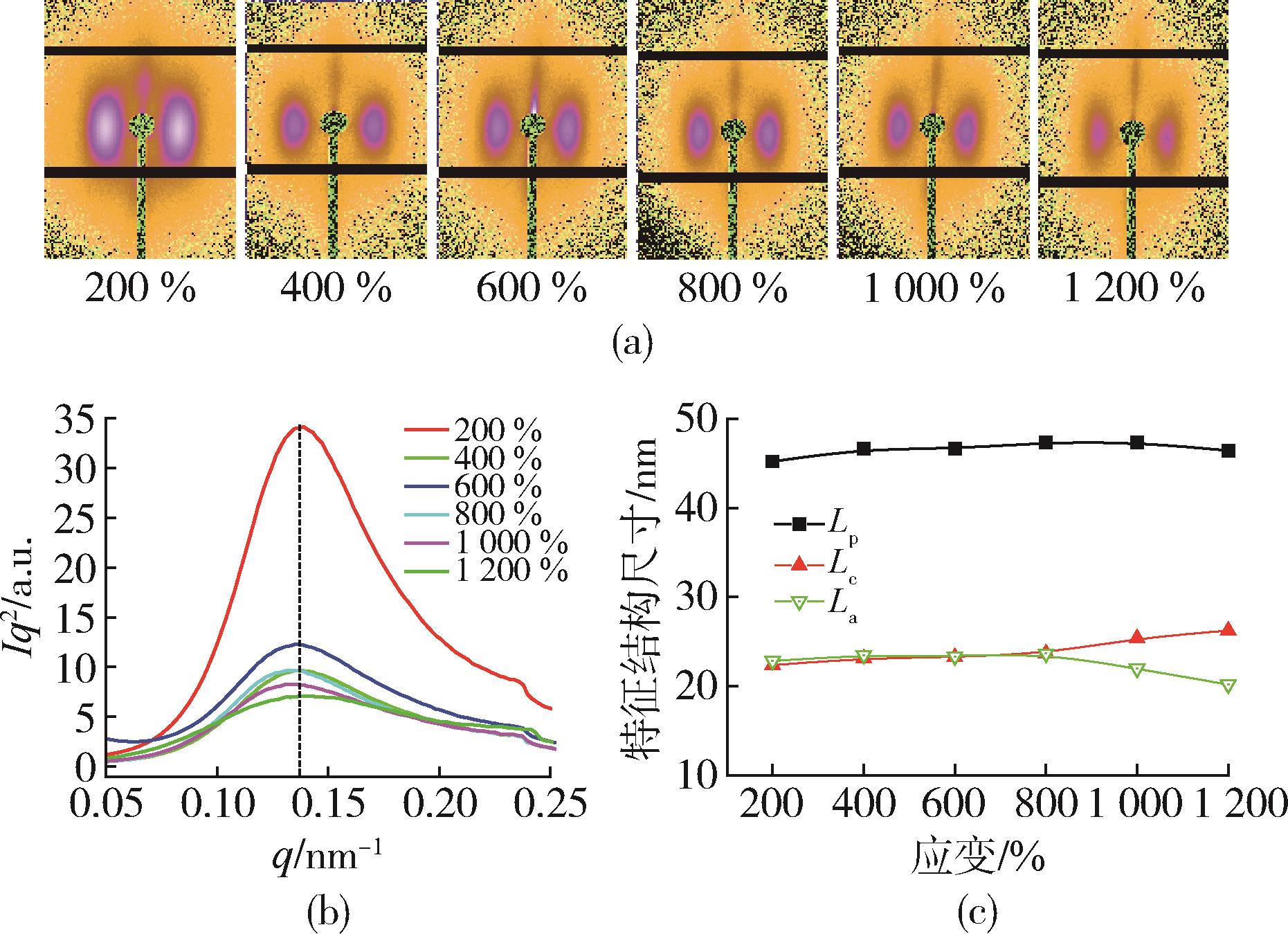
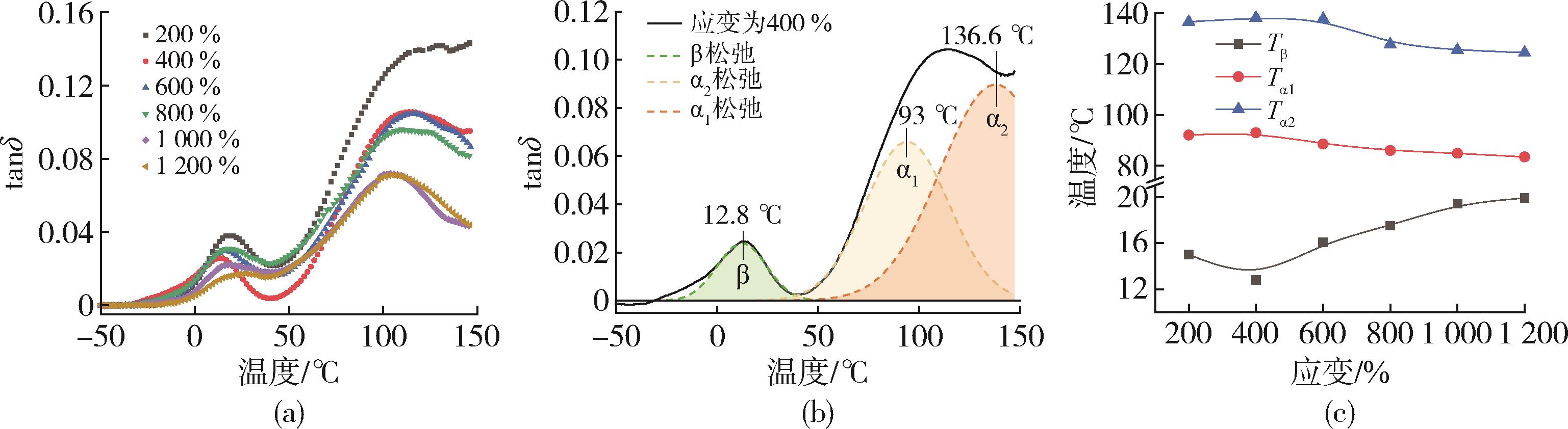
| 1 | 赵燕, 徐典宏, 陈 红, 等. 我国电容膜聚丙烯专用树脂生产现状及其技术进展[J]. 石化技术与应用, 2021, 39(5): 365⁃370. |
| ZHAO Y, XU D H, CHEN H, et al. Production status and technical progress of special polypropylene resin exclusive for capacitor film in China[J]. Petrochemical Technology & Application, 2021, 39(5): 365⁃370. | |
| 2 | 段光伟. 浅析电容器膜用聚丙烯的现状及发展[J]. 当代化工研究, 2020 (14): 8⁃10. |
| DUAN G W. Present situation and development of polypropylene for capacitor film[J]. Modern Chemical Research, 2020 (14): 8⁃10. | |
| 3 | 谌基国, 王 睿, 刘 华, 等. 电容膜专用聚丙烯树脂的性能对比[J]. 石化技术与应用, 2023, 41(4): 288⁃291. |
| SHEN JI G, WANG R, LIU H, et al. Performance comparison of polypropylene resin for capacitor film[J]. Petrochemical Technology & Application, 2023, 41(4): 288⁃291. | |
| 4 | Capt L, Rettenberger S, Munstedt H, et al. Simultaneous Biaxial Stretching of Polypropylene Resins of Varying Tacticity Part II: Film Morphology and Properties[J]. International Polymer Processing, 2022, 20: 369⁃379. |
| 5 | 戴熙瀛, 张 翀, 万彩霞, 等. 影响BOPP 电容膜击穿场强的微观结构及与制备工艺的关系探究[J]. 中国塑料, 2023, 37(12): 29⁃34. |
| DAI X Y, ZHANG C, WAN C X, et al. Microstructure of BOPP capacitor film affecting breakdown field strength and its relationship with preparation process[J]. China Plastics, 2023, 37(12): 29⁃34. | |
| 6 | 马宇威, 程 璐, 刘宏博, 等. 双向拉伸聚丙烯薄膜聚集态结构与击穿特性的关联[J]. 绝缘材料,2023, 56(1): 1⁃7. |
| Ma Y W, Cheng L, Liu H B, et al. Correlation between aggregation structure of biaxially oriented polypropylene and its breakdown property[J]. Insulating Materials,2023, 56(1): 1⁃7. | |
| 7 | Xu S, Zhou J, Pan P. Strain⁃induced multiscale structural evolutions of crystallized polymers: From fundamental studies to recent progresses[J]. Progress in Polymer Science, 2023, 140: 101676. |
| 8 | Dai X, Xing Z, Yang W, et al. The Effect of Annealing on the Structure and Electric Performance of Polypropylene Films[J]. International Journal of Polymer Science, 2022, 5970484: 1⁃12. |
| 9 | Gajzlerova L, Navratilova J, Zenzingerova S, et al. On isotactic polypropylene annealing: Difference in final properties of neat and β⁃nucleated polypropylene[J]. Express Polymer Letters, 2022, 16: 453⁃464. |
| 10 | Wang Y, Chen S, Wu T, et al. Yielding behavior of isotactic polypropylene at elevated temperature understood at the spherulite level[J]. Polymer, 2023, 281: 126150. |
| 11 | Deng B, Chen L, Li X, et al. Influence of Prereserved Shish Crystals on the Structural Evolution of Ultrahigh⁃Molecular Weight Polyethylene Films during the Hot Stretching Process[J]. Macromolecules, 2022, 55: 4 600⁃4 613. |
| 12 | Kida T, Tanaka R, Shiono T, et al. Direct Observation of the Effect of a High⁃Molecular⁃Weight Component on the Deformation Behavior of Polyethylene Solids Using the Rheo⁃Raman Spectroscopic Technique[J]. Macromolecules,2023, 56: 3 073⁃3 082. |
| 13 | Zhang C, Dai X, Xing Z, et al. Investigation on the Structure and Performance of Polypropylene Sheets and Bi⁃axially Oriented Polypropylene Films for Capacitors[J]. Chinese J of Polymer Science, 2022, 40: 1 688⁃1 696. |
| 14 | Sharaf M A, Kloczkowski A. Evolution of the Deformation⁃ and Flow⁃Induced Crystallization and Characterization of the Microstructure of a Single Spherulite, Lamella, and Chain of Isotactic Polypropylene[J]. Macromolecular Chemistry and Physics, 2023, 2300203: 1⁃44. |
| 15 | Wu F Y, Yang S, Lin H, et al. Enhanced melt⁃recrystallization process of propylene⁃ethylene copolymer during the uniaxial stretching with the aid of isotactic polypropylene[J]. Polymer, 2022, 239: 124443. |
| 16 | Chen X, Meng L, Zhang W, et al. Frustrating Strain⁃Induced Crystallization of Natural Rubber with Biaxial Stretch[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11: 47 535⁃47 544. |
| 17 | Men Y. Critical strains determine the tensile deformation mechanism in semicrystalline polymers[J]. Macromolecules, 2020, 53: 9 155⁃9 157. |
| 18 | Deng B, Chen L, Li X, et al. Influence of Prereserved Shish Crystals on the Structural Evolution of Ultrahigh⁃Molecular Weight Polyethylene Films during the Hot Stretching Process[J]. Macromolecules, 2022, 55: 4 600⁃4 613. |
| 19 | Yu L, Bao J, Wang G, et al. Structure and properties of gel⁃spun ultra⁃high molecular weight polyethylene fibers obtained from industrial production line[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2021, 138(44): e51317. |
| 20 | Iqbal O, Guo H, Chen W. Structural Origin of Double Yielding: The Critical Role of Crystallite Aggregate Heterogeneity[J]. Macromolecules, 2021, 54(18): 8 381⁃8 392. |
| [1] | SHAO Haofeng, JIAO Longjie, GONG Weiguang, MENG Xin. Synergistic antioxidant effect of phosphonite P⁃EPQ and hindered phenol in polypropylene [J]. China Plastics, 2024, 38(8): 20-25. |
| [2] | LUO Bofei, XU Chen, XING Jingkai, WANG Bo, ZHANG Yanni. Research on polypropylene carboxylic acid salt [J]. China Plastics, 2024, 38(8): 81-87. |
| [3] | SONG Wenlan, SONG Wenxing, LI Bing, LIU Qian, OUYANG Yuge, TIAN Huafeng, GUO Gaiping. Research progress in BOPP films of capacitors for enhancing dielectric and electric energy storage [J]. China Plastics, 2024, 38(7): 138-143. |
| [4] | SHEN Qiangfeng, LYU Mingfu, XU Yaohui. Study on autoclave foaming properties of metallocene polypropylene [J]. China Plastics, 2024, 38(7): 55-61. |
| [5] | XU Chen, LUO Bofei, LIU Tengteng, XING Jingkai. Research progress in modification of polypropylene with nucleating agent [J]. China Plastics, 2024, 38(7): 79-85. |
| [6] | LIU Ying, SUN Hao, YANG Yong, JIANG Kaiyu, YU Tongmin, MA Sai, ZHU Tieli. Effect of ultrasonic vibration on mechanical properties of injection⁃molded parts of glass⁃fiber⁃reinforced polyamide 6 [J]. China Plastics, 2024, 38(7): 9-14. |
| [7] | YANG Lian, JIANG Jing, JIA Caiyi, XIE Yuehan, WANG Xiaofeng, LI Qian. Preparation of polyamide 6 microfiber reinforced polypropylene composite and its property of chemical foam injection molding [J]. China Plastics, 2024, 38(6): 12-18. |
| [8] | DONG Yapeng, ZHAO Tianjiao, WANG Meizhen, CUI Wenju, LIN Fuhua, WANG Bo. Effect of long chain fatty acid sodium/sodium arylamide fatty acid compounding nucleating agent on properties of polypropylene [J]. China Plastics, 2024, 38(6): 60-65. |
| [9] | XIE Bo, TU Zhigang, ZHOU Xianjin, ZHAG Shangxian, XIONG Ligui, YANG Ting. Development of heat shrinkable BOPP packaging film with low friction coefficient [J]. China Plastics, 2024, 38(6): 78-81. |
| [10] | LEI Jingfa, HU Jibo, LIU Tao, WU Wenqi, Shen Zhaoyang. Study on static and dynamic mechanical properties and constitutive model of PVC/TPU blends [J]. China Plastics, 2024, 38(5): 1-6. |
| [11] | HAO Wenbo, TANG Shi, SU Tingting, WANG Zhanyong. Synthesis and properties of esterified starches with different contents of straight chain [J]. China Plastics, 2024, 38(5): 19-23. |
| [12] | ZHANG Yi, HUANG Yating, WEI Yongbao, TANG Wei, QIAN Lijun. Study on pyrolysis mechanism of intumescent flame⁃retardant system based on reaction force field [J]. China Plastics, 2024, 38(5): 66-72. |
| [13] | GUO Minghai. Studies on structure and properties of high⁃impact copolymerized polypropylene with high melt flow rate [J]. China Plastics, 2024, 38(5): 7-13. |
| [14] | GUO Jiang, XU Mengyi, LI Hui, HUANG Xiang, LIN Hao, JIANG Shengbao, CHEN Shang, CHEN Cheng. Preparation and dielectric properties of polypropylene/ZrO2 composite materials [J]. China Plastics, 2024, 38(3): 44-48. |
| [15] | WANG Peng, YAO Cheng, LIU Gang, CAI Xipeng, JIA Lei, WANG Kai, CHEN Long. Structural characteristics and electrical insulating properties of BOPP films based on different stretching modes [J]. China Plastics, 2024, 38(3): 54-58. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||