 京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2
京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2
《中国塑料》编辑部 ©2008-2024 版权所有
地址:北京市海淀区阜成路11号 邮编:100048
编辑部:010-68985541 联系信箱:cp@plaschina.com.cn
广告部/发行部:010-68985253 本系统由北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司设计开发

中国塑料 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (7): 102-111.DOI: 10.19491/j.issn.1001-9278.2025.07.016
冯硕1, 林小淇2, 朱艳丽2, 高维常3, 翁云宣1, 张彩丽1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-08-09
出版日期:2025-07-26
发布日期:2025-07-22
通讯作者:
张彩丽(1989—),女,副教授,从事生物基与生物降解高分子材料的研究,zhangcaili@btbu.edu.cn作者简介:第一联系人:地址:北京市海淀区阜成路11号《中国塑料》杂志社基金资助:
FENG Shuo1, LIN Xiaoqi2, ZHU Yanli2, GAO Weichang3, WENG Yunxuan1, ZAHNG Caili1( )
)
Received:2024-08-09
Online:2025-07-26
Published:2025-07-22
Contact:
ZAHNG Caili
E-mail:zhangcaili@btbu.edu.cn
摘要:
综述了聚(丁二酸丁二醇酯⁃co⁃对苯二甲酸丁二醇酯)(PBAT)化学回收的现状、面临的挑战以及未来的发展前景。通过水解、醇解、热化学回收和生物催化回收等技术,PBAT废弃物能够转化为基础化学成分,实现资源的循环利用。同时,对PBAT化学回收的生命周期评估(LCA)进行了分析,探讨了不同回收技术的环境和经济效益。此外,讨论了政策与法规在促进PBAT化学回收中的作用,以及当前面临的挑战。最后,文章展望了PBAT化学回收技术的发展潜力,强调了技术创新、市场推动和政策支持对于推动PBAT化学回收产业发展的重要性。
中图分类号:
冯硕, 林小淇, 朱艳丽, 高维常, 翁云宣, 张彩丽. 生物降解塑料PBAT的化学回收与生命周期评价:现状、挑战与前景[J]. 中国塑料, 2025, 39(7): 102-111.
FENG Shuo, LIN Xiaoqi, ZHU Yanli, GAO Weichang, WENG Yunxuan, ZAHNG Caili. Chemical recovery and life cycle assessment of biodegradable plastic PBAT: current situation, challenges and prospects[J]. China Plastics, 2025, 39(7): 102-111.
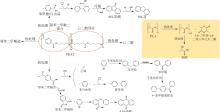
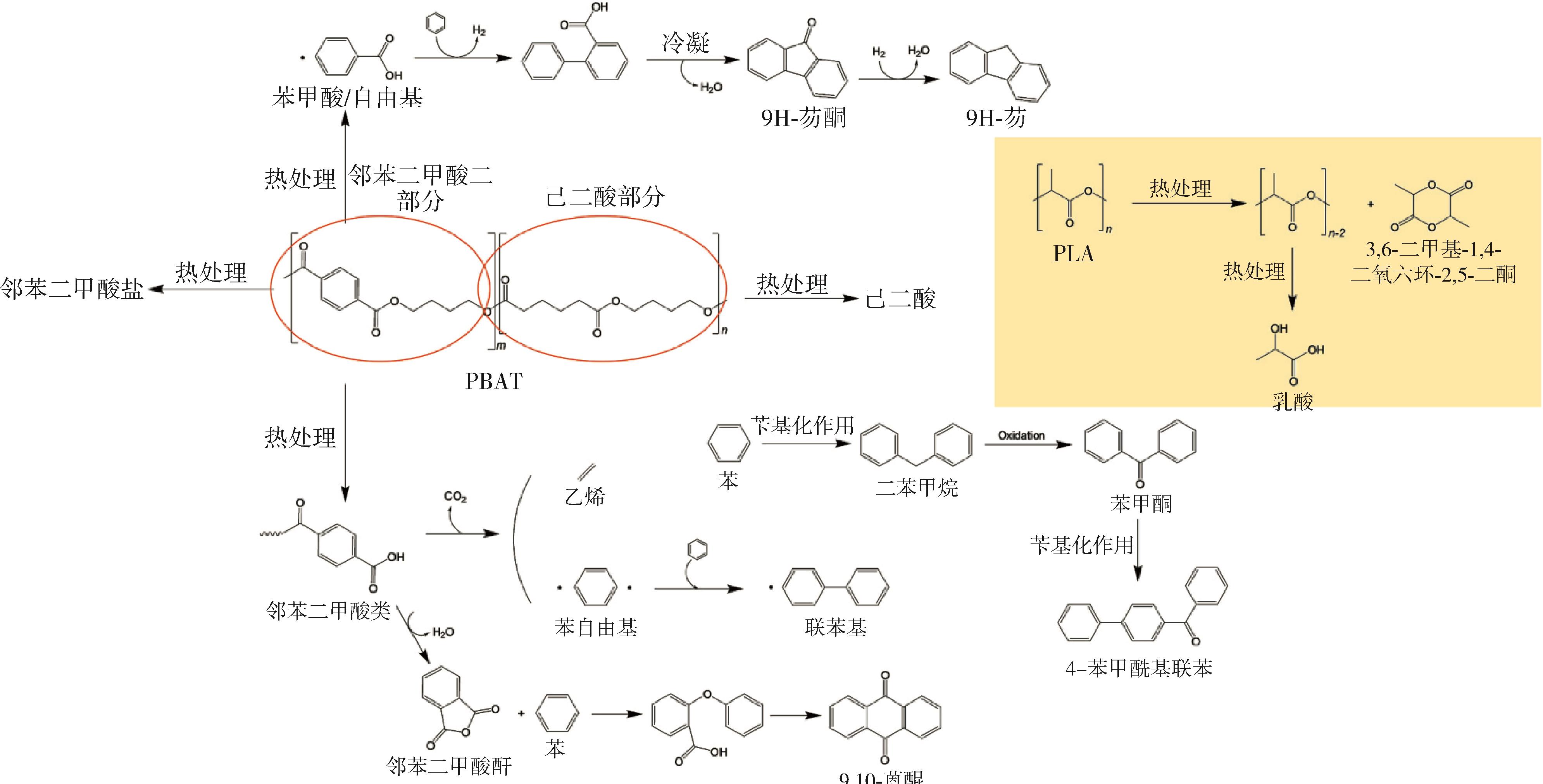
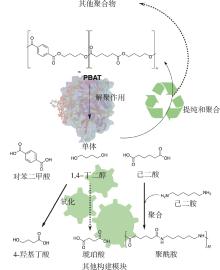
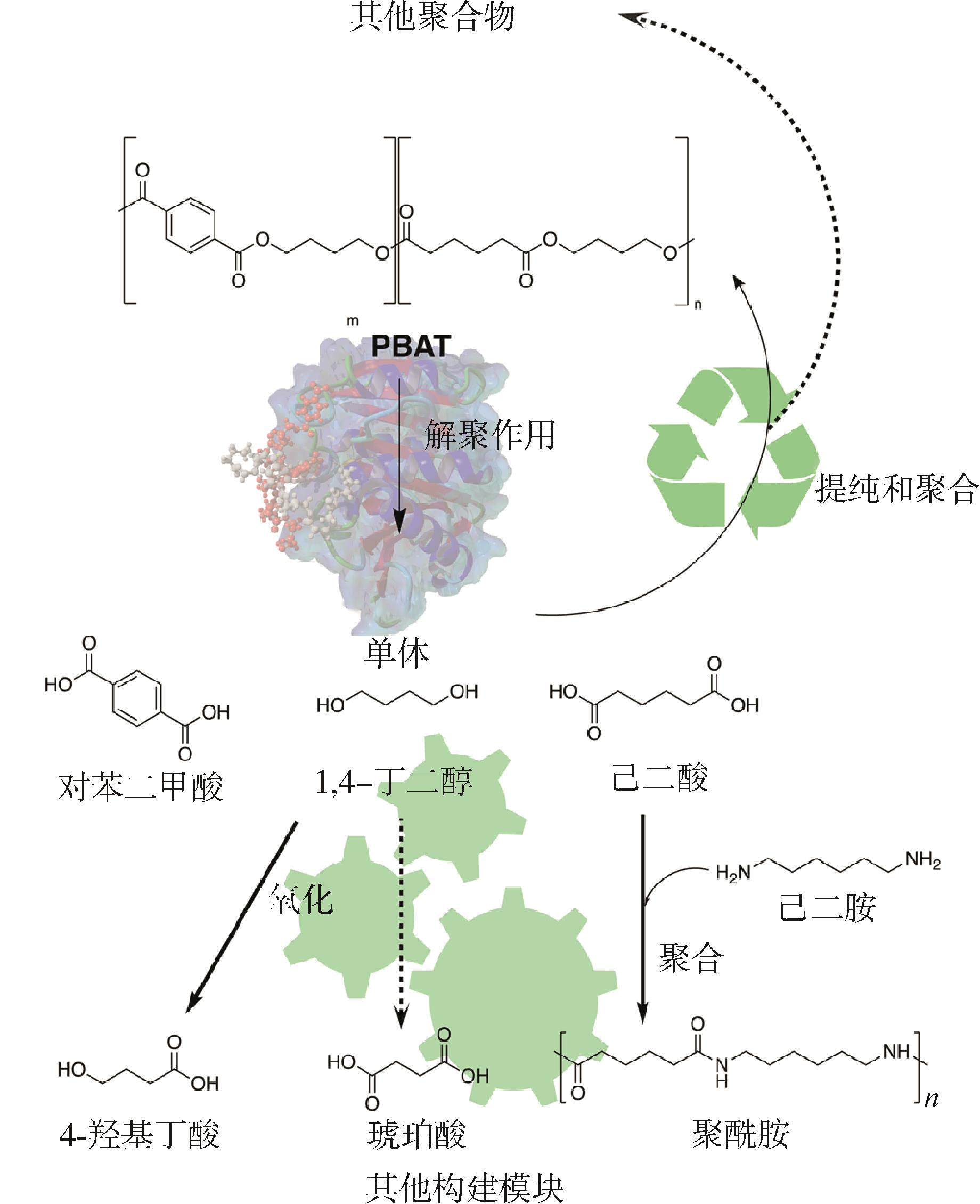
| 回收方式 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|
| ①水解 | (1)水解条件相对容易控制,产物较为纯净; (2)水解产生的单体可以用于重新合成PBAT或其他材料,保持一定的经济价值。 | (1)对设备可能有一定的腐蚀性; (2)存在回收效率不高的情况,导致整体回收效果受到一定影响。 |
| ②醇解 | (1)相对较为成熟,能够有效回收单体或低聚物,可用于再生产; (2)反应条件相对温和。 | (1)可能会产生一些副产物,需要进一步处理; (2)回收过程中可能会有一定的溶剂消耗和排放。 |
| ③热化学 | (1)可实现对 PBAT 的大规模处理,能回收得到有价值的化学品; (2)在回收过程中可回收一部分能量。 | (1)需要较高的温度,能耗较大; (2)可能会产生一些复杂的混合物,后续分离提纯有一定难度。 |
| ④生物催化 | (1)环境友好,减少了化学试剂的使用和潜在污染; (2)具有针对性,提高回收PBAT效率和纯度; (3)常温、常压等,降低能源消耗。 | (1)生物催化剂的开发和应用成本较高; (2)在回收速度和规模上存在一定局限性; (3)生物催化剂可能对环境条件较为敏感,如温度、酸碱度等,稳定性方面有待进一步加强。 |
| 回收方式 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|
| ①水解 | (1)水解条件相对容易控制,产物较为纯净; (2)水解产生的单体可以用于重新合成PBAT或其他材料,保持一定的经济价值。 | (1)对设备可能有一定的腐蚀性; (2)存在回收效率不高的情况,导致整体回收效果受到一定影响。 |
| ②醇解 | (1)相对较为成熟,能够有效回收单体或低聚物,可用于再生产; (2)反应条件相对温和。 | (1)可能会产生一些副产物,需要进一步处理; (2)回收过程中可能会有一定的溶剂消耗和排放。 |
| ③热化学 | (1)可实现对 PBAT 的大规模处理,能回收得到有价值的化学品; (2)在回收过程中可回收一部分能量。 | (1)需要较高的温度,能耗较大; (2)可能会产生一些复杂的混合物,后续分离提纯有一定难度。 |
| ④生物催化 | (1)环境友好,减少了化学试剂的使用和潜在污染; (2)具有针对性,提高回收PBAT效率和纯度; (3)常温、常压等,降低能源消耗。 | (1)生物催化剂的开发和应用成本较高; (2)在回收速度和规模上存在一定局限性; (3)生物催化剂可能对环境条件较为敏感,如温度、酸碱度等,稳定性方面有待进一步加强。 |
| [1] | Omelan M C V, Lachmann K, Meyer H, et al. RETRACTED: bio⁃based thin film coatings using sustainable materials[J]. 2022: 20⁃25. |
| [2] | De Lima L F, Lopes Ferreira A, Martinez de Freitas A S, et al. Biodegradable and flexible thermoplastic composite graphite electrodes: a promising platform for inexpensive and sensitive electrochemical detection of creatine kinase at the point⁃of⁃care[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2023, 15(15): 18 694⁃18 706. |
| [3] | Kim H, Jeon H, Lee M, et al. Enhanced mechanical properties of poly (butylene adipate⁃co⁃terephthalate)/cellulose nanocrystal nanocomposites obtained by in situ polymerization[J]. ACS Applied Polymer Materials, 2022, 5(1): 635⁃643. |
| [4] | Sim J Y, Raj C J, Yu K H. Poly (butylene adipate⁃co⁃terephthalate)(PBAT)/antimony⁃doped tin oxide polymer composite for near infrared absorption coating applications[J]. Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society, 2019, 40(7): 674⁃679. |
| [5] | Ki H C, Park O O. Synthesis, characterization and biodegradability of the biodegradable aliphatic–aromatic random copolyesters[J]. Polymer, 2001, 42(5): 1 849⁃1 861. |
| [6] | Cranston E, Kawada J, Raymond S, et al. Cocrystallization model for synthetic biodegradable poly (butylene adipate⁃co⁃butylene terephthalate)[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2003, 4(4): 995⁃999. |
| [7] | Da Silva J S P, Da Silva J M F, Soares B G, et al. Fully biodegradable composites based on poly (butylene adipate⁃co⁃terephthalate)/peach palm trees fiber[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2017, 129: 117⁃123. |
| [8] | Dedieu I, Peyron S, Gontard N, et al. The thermo⁃mechanical recyclability potential of biodegradable biopolyesters: perspectives and limits for food packaging application[J]. Polymer Testing, 2022, 111: 107620. |
| [9] | Merchan A L, Fischöder T, Hee J, et al. Chemical recycling of bioplastics: technical opportunities to preserve chemical functionality as path towards a circular economy[J]. Green Chemistry, 2022, 24(24): 9 428⁃9 449. |
| [10] | Marinho V A D, Pereira C A B, Vitorino M B C, et al. Degradation and recovery in poly (butylene adipate⁃co⁃terephthalate)/thermoplastic starch blends[J]. Polymer Testing, 2017, 58: 166⁃172. |
| [11] | Šerá J, Kadlečková M, Fayyazbakhsh A, et al. Occurrence and analysis of thermophilic poly (Butylene adipate⁃co⁃terephthalate)⁃degrading microorganisms in temperate zone soils[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2020, 21(21): 7 857. |
| [12] | Álvarez⁃Méndez S J, Ramos⁃Suárez J L, Ritter A, et al. Anaerobic digestion of commercial PLA and PBAT biodegradable plastic bags: potential biogas production and 1H⁃NMR and ATR⁃FTIR assessed biodegradation[J]. Heliyon, 2023, 9(6):e16691. |
| [13] | Wu P, Li Z, Gao J, et al. Characterization of a PBAT degradation carboxylesterase from Thermobacillus composti KWC4[J]. Catalysts, 2023, 13(2): 340. |
| [14] | Gioia C, Giacobazzi G, Vannini M, et al. End of life of biodegradable plastics: composting versus Re/upcycling[J]. ChemSusChem, 2021, 14(19): 4 167⁃4 175. |
| [15] | Wong P C, Kurniawan D, Wu J L, et al. Plasma⁃enabled graphene quantum dot hydrogel–magnesium composites as bioactive scaffolds for in vivo bone defect repair[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2023, 15(38): 44 607⁃44 620. |
| [16] | Lee S, Lee J, Park Y K. Simultaneous upcycling of biodegradable plastic and sea shell wastes through thermocatalytic monomer recovery[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2022, 10(42): 13 972⁃13 979. |
| [17] | Kim S, Lee H S, Yang W, et al. Recovery of lactic acid from biodegradable straw waste through a CO2⁃assisted thermochemical process[J]. Journal of CO2 Utilization, 2022, 64: 102164. |
| [18] | Kim S, Yang W, Lee H S, et al. Effectiveness of CO2⁃mediated pyrolysis for the treatment of biodegradable plastics: A case study of polybutylene adipate terephthalate/polylactic acid mulch film[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 372: 133763. |
| [19] | Arias J J R, Thielemans W. Instantaneous hydrolysis of PET bottles: an efficient pathway for the chemical recycling of condensation polymers[J]. Green Chemistry, 2021, 23(24): 9 945⁃9 956. |
| [20] | Pham D D, Cho J. Low⁃energy catalytic methanolysis of poly (ethyleneterephthalate) Green Chem[J]. 2021,23: 511⁃525. |
| [21] | Wang Q, Geng Y, Lu X, et al. First⁃row transition metal⁃containing ionic liquids as highly active catalysts for the glycolysis of poly (ethylene terephthalate)(PET)[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2015, 3(2): 340⁃348. |
| [22] | Raheem A B, Noor Z Z, Hassan A, et al. Current developments in chemical recycling of post⁃consumer polyethylene terephthalate wastes for new materials production: a review[J]. Journal of cleaner production, 2019, 225: 1 052⁃1 064. |
| [23] | Pang W, Li B, Wu Y, et al. Upgraded recycling of biodegradable PBAT plastic: efficient hydrolysis and electrocatalytic conversion[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 486: 150342. |
| [24] | Ratshoshi B K, Farzad S, Görgens J F. A techno⁃economic study of polybutylene adipate terephthalate (PBAT) production from molasses in an integrated sugarcane biorefinery[J]. Food and Bioproducts Processing, 2024, 145: 11⁃20. |
| [25] | Ma J, Cao Y, Fan L, et al. Degradation characteristics of polybutylene adipate terephthalic acid (PBAT) and its effect on soil physicochemical properties: a comparative study with several polyethylene (PE) mulch films[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2023, 456: 131661. |
| [26] | Shi X Q, Aimi K, Ito H, et al. Characterization on mixed⁃crystal structure of poly (butylene terephthalate/succinate/adipate) biodegradable copolymer fibers[J]. Polymer, 2005, 46(3): 751⁃760. |
| [27] | Shi X Q, Ito H, Kikutani T. Characterization on mixed⁃crystal structure and properties of poly (butylene adipate⁃co⁃terephthalate) biodegradable fibers[J]. Polymer, 2005, 46(25): 11 442⁃11 450. |
| [28] | Niu H, Lyu M, Guo P, et al. Effect of antihydrolysis agents on the structure and properties of PBAT/PGA blend films under artificial accelerated weathering[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2024, 63(8): 3 504⁃3 513. |
| [29] | Wang J H, Tian Y, Zhou B. Degradation and stabilization of poly (butylene adipate⁃co⁃terephthalate)/polyhydroxyalkanoate biodegradable mulch films under different aging tests[J]. Journal of Polymers and the Environment, 2022: 1⁃14. |
| [30] | Xu P Y, Liu T Y, Huang D, et al. Enhanced degradability of novel PBATCL copolyester: study on the performance in different environment and exploration of mechanism[J]. European Polymer Journal, 2023, 186: 111834. |
| [31] | Tseng W S, Lee M J, Wu J A, et al. Poly (butylene adipate⁃co⁃terephthalate) biodegradation by Purpureocillium lilacinum strain BA1S[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2023, 107(19): 6 057⁃6 070. |
| [32] | Kijchavengkul T, Auras R, Rubino M, et al. Biodegradation and hydrolysis rate of aliphatic aromatic polyester[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2010, 95(12): 2 641⁃2 647. |
| [33] | Yang Y, Min J, Xue T, et al. Complete bio⁃degradation of poly (butylene adipate⁃co⁃terephthalate) via engineered cutinases[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 1 645. |
| [34] | Lin W, Zhao Y, Su T, et al. Enzymatic hydrolysis of poly (butylene adipate⁃co⁃terephthalate) by Fusarium solani cutinase[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2023, 211: 110335. |
| [35] | Jiang Z, Hou F, Chen J, et al. Synthesis and properties of biodegradable PBAT prepared from PBT chemically recycled resources[J]. Polymer, 2024, 307: 127326. |
| [36] | Sun C, Wei S, Tan H, et al. Progress in upcycling polylactic acid waste as an alternative carbon source: a review[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 446: 136881. |
| [37] | Czajczyńska D, Anguilano L, Ghazal H, et al. Potential of pyrolysis processes in the waste management sector[J]. Thermal science and engineering progress, 2017, 3: 171⁃197. |
| [38] | Nandakumar A, Chuah J A, Sudesh K. Bioplastics: a boon or bane?[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2021, 147: 111237. |
| [39] | Coralli I, Rombolà A G, Fabbri D. Analytical pyrolysis of the bioplastic PBAT poly (butylene adipate⁃co⁃terephthalate)[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2024, 181: 106577. |
| [40] | Ismail M, Abouhmad A, Warlin N, et al. Closing the loop for poly (butylene⁃adipate⁃co⁃terephthalate) recycling: depolymerization, monomers separation, and upcycling[J]. Green Chemistry, 2024, 26(7): 3 863⁃3 873. |
| [41] | Santos⁃Beneit F, Chen L M, Bordel S, et al. Screening enzymes that can depolymerize commercial biodegradable polymers: heterologous expression of fusarium solani cutinase in Escherichia coli[J]. Microorganisms, 2023, 11 (2):328. |
| [42] | Sharp B E, Miller S A. Potential for integrating diffusion of innovation principles into life cycle assessment of emerging technologies[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(6): 2 771⁃2 781. |
| [43] | Earles J M, Halog A. Consequential life cycle assessment: a review[J]. The International Journal of Life Cycle Assessment, 2011, 16: 445⁃453. |
| [44] | Pauliuk S. Critical appraisal of the circular economy standard BS 8001: 2017 and a dashboard of quantitative system indicators for its implementation in organizations[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2018, 129: 81⁃92. |
| [45] | Lam K L, Zlatanović L, van Der Hoek J P. Life cycle assessment of nutrient recycling from wastewater: a critical review[J]. Water research, 2020, 173: 115519. |
| [46] | He Y, Kiehbadroudinezhad M, Hosseinzadeh⁃Bandbafha H, et al. Driving sustainable circular economy in electronics: a comprehensive review on environmental life cycle assessment of e⁃waste recycling[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2024, 342: 123081. |
| [47] | Sheik A G, Krishna S B N, Patnaik R, et al. Digitalization of phosphorous removal process in biological wastewater treatment systems: challenges, and way forward[J]. Environmental Research, 2024: 119133. |
| [48] | Mohan S V, Hemalatha M, Chakraborty D, et al. Algal biorefinery models with self⁃sustainable closed loop approach: trends and prospective for blue⁃bioeconomy[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 295: 122128. |
| [49] | Mohan S V, Nikhil G N, Chiranjeevi P, et al. Waste biorefinery models towards sustainable circular bioeconomy: critical review and future perspectives[J]. Bioresource technology, 2016, 215: 2⁃12. |
| [50] | Al⁃Sakkari E G, Ragab A, Dagdougui H, et al. Carbon capture, utilization and sequestration systems design and operation optimization: assessment and perspectives of artificial intelligence opportunities[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2024, 917: 170085. |
| [51] | Fonseca A, Ramalho E, Gouveia A, et al. Systematic Insights into a textile industry: reviewing life cycle assessment and eco⁃design[J]. Sustainability, 2023, 15(21): 15267. |
| [52] | Cristofoli N L, Lima A R, Tchonkouang R D N, et al. Advances in the food packaging production from agri⁃food waste and by⁃products: market trends for a sustainable development[J]. Sustainability, 2023, 15(7): 6 153. |
| [53] | Rastogi P, Kandasubramanian B. Breakthrough in the printing tactics for stimuli⁃responsive materials: 4D printing[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 366: 264⁃304. |
| [54] | Abdallah M, Rahmat⁃Ullah Z, Hosny M, et al. Minimizing the environmental impacts of waste valorization systems using multi⁃criteria life cycle optimization[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2024, 449: 141619. |
| [55] | Veksha A, Ahamed A, Wu X Y, et al. Technical and environmental assessment of laboratory scale approach for sustainable management of marine plastic litter[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 421: 126717. |
| [56] | Dong J, Chi Y, Zou D, et al. Energy–environment–economy assessment of waste management systems from a life cycle perspective: Model development and case study[J]. Applied Energy, 2014, 114: 400⁃408. |
| [57] | Parascanu M M, Gamero M P, Sánchez P, et al. Life cycle assessment of olive pomace valorisation through pyrolysis[J]. Renewable Energy, 2018, 122: 589⁃601. |
| [58] | Davidson M G, Furlong R A, McManus M C. Developments in the life cycle assessment of chemical recycling of plastic waste⁃a review[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 293: 126163. |
| [59] | Schrijvers D L, Leroux F, Verney V, et al. Ex⁃ante life cycle assessment of polymer nanocomposites using organo⁃modified layered double hydroxides for potential application in agricultural films[J]. Green Chemistry, 2014, 16(12): 4 969⁃4 984. |
| [60] | Brookes C K. Advancement of biobased products through design, synthesis and engineering of biopolyesters[M]. Michigan State University. Department of Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, 2007. |
| [61] | Saibuatrong W, Cheroennet N, Suwanmanee U. Life cycle assessment focusing on the waste management of conventional and bio⁃based garbage bags[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 158: 319⁃334. |
| [62] | Dunn J B, Adom F, Sather N, et al. Life⁃cycle analysis of bioproducts and their conventional counterparts in GREET[R]. Argonne National Lab.(ANL), Argonne, IL (United States), 2015. |
| [63] | Moutousidi E S, Kookos I K. Life cycle assessment of biobased chemicals from different agricultural feedstocks[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 323: 129201. |
| [64] | Wang B X, Cortes⁃Peña Y, Grady B P, et al. Techno⁃economic analysis and life cycle assessment of the production of biodegradable polyaliphatic–polyaromatic polyesters[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2024, 12(24): 9 156⁃9 167. |
| [65] | Carmona E, Rojo⁃Nieto E, Rummel C D, et al. A dataset of organic pollutants identified and quantified in recycled polyethylene pellets[J]. Data in Brief, 2023, 51: 109740. |
| [1] | 尚云龙, 王东浩, 任志彬. 湿法橡胶沥青存储稳定性研究综述[J]. 中国塑料, 2025, 39(8): 75-82. |
| [2] | 梁永煌, 刘京, 葛冬琦. 我国塑料化学回收产业现状、存在问题及发展趋势[J]. 中国塑料, 2025, 39(7): 112-120. |
| [3] | 殷茂峰, 王晓珂, 孙国华, 张信, 李鹏鹏, 马劲松, 肖军, 侯连龙. 红外光谱快速检测生物降解聚酯的研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2024, 38(9): 94-100. |
| [4] | 焦晓龙, 党开放, 周洋, 马艺涛, 王金领, 谢鹏程. 从德国K展2022看注塑产业发展新趋势[J]. 中国塑料, 2024, 38(1): 49-54. |
| [5] | 全淑苗, 张彦军, 宋小飞, 杜闰萍, 于丹. 废塑料脱氯技术现状及产业化进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(9): 122-130. |
| [6] | 马腾, 刘倩倩, 魏晓丽, 宋海涛, 李明丰. 废塑料热解油中杂质硅、氯的影响及应对策略探讨[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(8): 127-134. |
| [7] | 董少策, 李承高, 张旭锋, 咸贵军. 植物纤维纸蜂窝制备的环境影响评价[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(6): 108-115. |
| [8] | 吴雄杰, 陶强, 朱东波, 程劲松, 储雨, 许磊. 食品接触用生物降解塑料购物袋材质鉴别与总迁移量研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(5): 127-132. |
| [9] | 姚逸, 张尔杰, 卢昌利, 王超军, 焦建, 曾祥斌. 食品接触法规对PBS发展的影响浅析[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(10): 125-130. |
| [10] | 刁晓倩, 翁云宣, 付烨, 周迎鑫. 生物降解塑料应用及性能评价方法综述[J]. 中国塑料, 2021, 35(8): 152-161. |
| [11] | 周迎鑫, 翁云宣, 张彩丽, 刁晓倩, 宋鑫宇. 聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯回收技术和标准现状[J]. 中国塑料, 2021, 35(8): 162-171. |
| [12] | 孙小东, 曹鼎, 胡倩倩, 姚文清, 李景虹, 冯拥军. 废弃塑料的化学回收资源化利用研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2021, 35(8): 44-54. |
| [13] | 李明丰, 蔡志强, 邹亮, 魏晓丽, 习远兵, 王国清, 蔡立乐, 张哲民, 夏国富, 蒋海滨. 中国石化废旧塑料化学回收与化学循环技术探索[J]. 中国塑料, 2021, 35(8): 64-76. |
| [14] | 刘学 刘国清. 三种生物降解塑料改性技术研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2011, 25(11): 1-4 . |
| [15] | 冯彦洪 张叶青 瞿金平 何和智. 植物纤维/生物降解塑料复合材料的纤维表面改性研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2011, 25(10): 50-54 . |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2
京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2