 京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2
京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2
《中国塑料》编辑部 ©2008-2024 版权所有
地址:北京市海淀区阜成路11号 邮编:100048
编辑部:010-68985541 联系信箱:cp@plaschina.com.cn
广告部/发行部:010-68985253 本系统由北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司设计开发

中国塑料 ›› 2020, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (8): 113-120.DOI: 10.19491/j.issn.1001-9278.2020.08.017
• 综述 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2020-02-28
出版日期:2020-08-26
发布日期:2020-08-26
基金资助:
Baogou WU1, Piming MA1( ), Pengwu XU1, Yong ZHANG2, Ruyin WANG3
), Pengwu XU1, Yong ZHANG2, Ruyin WANG3
Received:2020-02-28
Online:2020-08-26
Published:2020-08-26
Contact:
Piming MA
E-mail:p.ma@jiangnan.edu.cn
摘要:
综述了近期在聚乳酸(PLA)材料的成核结晶、立构复合、增韧与耐热改性方面的工作,重点探讨了成核剂化学结构、快速立构复合技术、反应性增容和退火等技术对PLA材料力学性能的影响,并对PLA材料的应用和发展方向进行了展望。
中图分类号:
吴保钩, 马丕明, 徐鹏武, 张勇, 王如寅. 聚乳酸增韧及结晶改性研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2020, 34(8): 113-120.
Baogou WU, Piming MA, Pengwu XU, Yong ZHANG, Ruyin WANG. Research Progress in Toughening and Crystalline Modification of Poly(lactic acid)[J]. China Plastics, 2020, 34(8): 113-120.
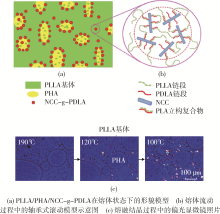
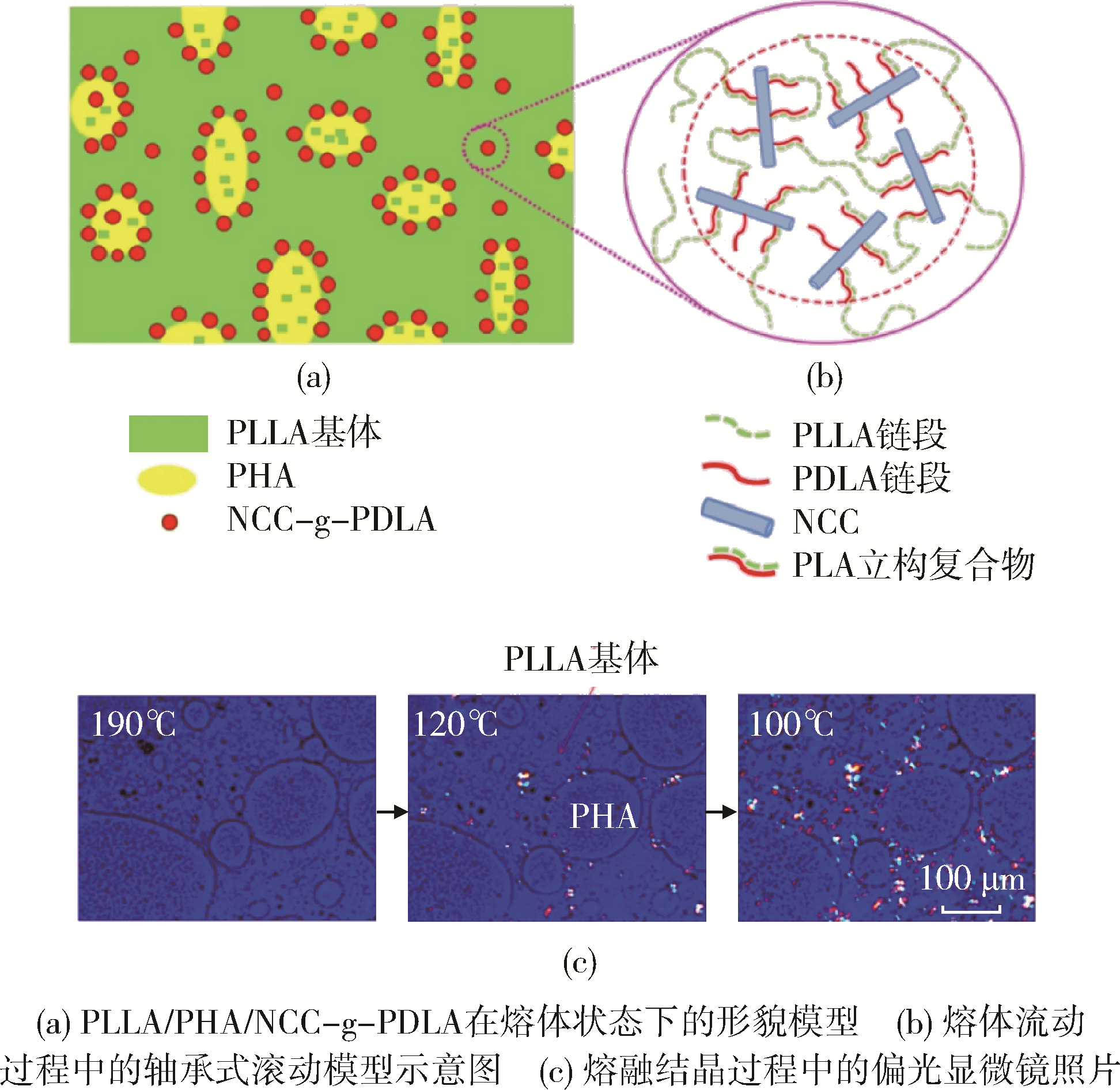
| 1 | 陈学思,陈国强,陶友华,等. 生态环境高分子的研究进展[J].高分子学报,2019,50(10):1 068⁃1 082. |
| CHEN X S, CHEN G Q, TAO Y H, et al. Research Progress in Eco⁃Polymers[J]. Acta Polymerica Sinica, 2019, 50(10): 1 068⁃1 082. | |
| 2 | MICHALSKI A, BRZEZINSKI M, LAPIENIS G, et al. Star⁃Shaped and Branched Polylactides: Synthesis, Characterization, and Properties[J]. Progress in Polymer Science, 2019, 89(2): 159⁃212. |
| 3 | GROSS A R. Biodegradable Polymers for the Environment[J]. Science, 2002, 297(5582): 803⁃807. |
| 4 | RHIM J W, PARK H M, HA C S. Bio⁃Nanocomposites for Food Packaging Applications[J]. Progress in Polymer Science, 2013, 38(10): 1 629⁃1 652. |
| 5 | NAMPOOTHIRI K M, NAIR N R, JOHN R P. An Overview of the Recent Developments in Polylactide (PLA) Research[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2010, 101(22): 8 493⁃8 501. |
| 6 | MA P, SHEN T, XU P, et al. Superior Performance of Fully Biobased Poly(lactide) via Stereocomplexation⁃Induced Phase Separation: Structure Versus Property[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2015, 3(7): 1 470⁃1 478. |
| 7 | LI H, HUNEAULT M A. Effect of Nucleation and Plasticization on the Crystallization of Poly(lactic acid)[J]. Polymer, 2007, 48(23): 6 855⁃6 866. |
| 8 | LIU G, ZHANG X, WANG D. Tailoring Crystallization: Towards High⁃Performance Poly(lactic acid)[J]. Advanced Materials, 2014, 26(40): 6 905⁃6 911. |
| 9 | ZHANG R, ZHA L, HU W. Intramolecular Crystal Nucleation Favored by Polymer Crystallization: Monte Carlo Simulation Evidence[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2016, 120(27): 6 754⁃6 760. |
| 10 | YIN H Y, WEI X F, BAO R Y, et al. High⁃Melting⁃Point Crystals of Poly(l⁃lactic acid) (PLLA): The Most Efficient Nucleating Agent to Enhance the Crystallization of PLLA[J]. CrystEngComm, 2015, 17(11): 2 310⁃2 320. |
| 11 | XIE Q, HAN L, SHAN G, et al. Polymorphic Crystalline Structure and Crystal Morphology of Enantiomeric Poly(lactic acid) Blends Tailored by a Self⁃Assemblable Aryl Amide Nucleator[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2016, 4(5): 2 680⁃2 688. |
| 12 | BAI H, ZHANG W, DENG H, et al. Control of Crystal Morphology in Poly(l⁃lactide) by Adding Nucleating agent[J]. Macromolecules, 2011, 44(6): 1 233⁃1 237. |
| 13 | FAN Y, ZHU J, YAN S, et al. Nucleating Effect and Crystal Morphology Controlling Based on Binary Phase Behavior Between Organic Nucleating Agent and Poly(l⁃lactic acid)[J]. Polymer, 2015, 67(12): 63⁃71. |
| 14 | MA P, XU Y, WANG D, et al. Rapid Crystallization of Poly(lactic acid) by Using Tailor⁃Made Oxalamide Derivatives as Novel Soluble⁃Type Nucleating Agents[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2014, 53(32): 12 888⁃12 892. |
| 15 | MA P, DESHMUKH Y S, WILSENS C H, et al. Self⁃Assembling Process of Oxalamide Compounds and Their Nucleation Efficiency in Bio⁃Degradable Poly(hydroxyalkanoate)s[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5(1): 13280. |
| 16 | MA P, XU Y, SHEN T, et al. Tailoring the Crystallization Behavior of Poly(l⁃lactide) with Self⁃Assembly⁃Type Oxalamide Compounds as Nucleators: 1. Effect of Terminal Configuration of the Nucleators[J]. European Polymer Journal, 2015, 70(9): 400⁃411. |
| 17 | SHEN T, XU Y, CAI X, et al. Enhanced Crystallization Kinetics of Poly(lactide) with Oxalamide Compounds as Nucleators: Effect of Spacer Length Between the Oxalamide Moieties[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(54): 48 365⁃48 374. |
| 18 | MA P, YU Q, SHEN T, et al. Strong Synergetic Effect of Fibril⁃Like Nucleator and Shear Flow on the Melt Crystallization of Poly(l⁃lactide)[J]. European Polymer Journal, 2017, 87(2): 221⁃230. |
| 19 | IKADA Y, JAMSHIDI K, TSUJI H, et al. Stereocomplex Formation Between Enantiomeric Poly(lactides)[J]. Macromolecules, 1987, 20(4): 904⁃906. |
| 20 | TSUJI H, IKADA Y. Stereocomplex Formation Between Enantiomeric Poly(lactic acids). 9. Stereocomplexation from the Melt[J]. Macromolecules, 1993, 26(25): 6 918⁃6 926. |
| 21 | HAN L, SHAN G, BAO Y, et al. Exclusive Stereocomplex Crystallization of Linear and Multiarm Star⁃Shaped High⁃Molecular⁃Weight Stereo Diblock Poly (lactic acid)s[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2015, 119(44): 14 270⁃14 279. |
| 22 | MA P, LV P, XU P, et al. Design of Bio⁃Based Conductive and Fast Crystallizing Nanocomposites with Controllable Distribution of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes via Interfacial Stereocomplexation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 336(6): 223⁃232. |
| 23 | MA P, JIANG L, XU P, et al. Rapid Stereocomplexation Between Enantiomeric Comb⁃Shaped Cellulose⁃g⁃Poly(l⁃lactide) Nanohybrids and Poly(d⁃lactide) from the Melt[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2015, 16(11): 3 723⁃3 729. |
| 24 | XIONG Z, ZHANG X, WANG R, et al. Favorable Formation of Stereocomplex Crystals in Poly(l⁃lactide)/Poly(d⁃lactide) Blends by Selective Nucleation[J]. Polymer, 2015, 76(26): 98⁃104. |
| 25 | JIANG L, LV P, MA P, et al. Stereocomplexation Kinetics of Enantiomeric Poly(l⁃lactide)/Poly(d⁃lactide) Blends Seeded by Nanocrystalline Cellulose[J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(87): 71 115⁃71 119. |
| 26 | MA P, SHEN T, LIN L, et al. Cellulose⁃g⁃Poly(d⁃lactide) Nanohybrids Induced Significant Low Melt Viscosity and Fast Crystallization of Fully Bio⁃based Nanocomposites[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2017, 155(1): 498⁃506. |
| 27 | XU P, LV P, WU B, et al. Smart Design of Rapid Crystallizing and Nonleaching Antibacterial Poly(lactide) Nanocomposites by Sustainable Aminolysis Grafting and in Situ Interfacial Stereocomplexation[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018, 6(10): 13 367⁃13 377. |
| 28 | WANG R, WANG S, ZHANG Y, et al. Toughening Modification of PLLA/PBS Blends via in Situ Compatibilization[J]. Polymer Engineering and Science, 2009, 49(1): 26⁃33. |
| 29 | 丁正亚,王 蕾,王标兵. 酯交换反应对PLA/PBS共混物性能的影响[J].工程塑料应用,2018,46(3):128⁃131. |
| DING Z Y, WANG L, WANG B B. Influences of Transesterification on Properties of PLA/PBS Blends[J]. Engineering Plastics Application, 2018, 46(3): 128⁃131. | |
| 30 | MA P, CAI X, ZHANG Y, et al. In⁃Situ Compatibilization of Poly(lactic acid) and Poly(butylene adipate⁃co⁃terephthalate) Blends by Using Dicumyl Peroxide as a Free⁃Radical Initiator[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2014, 102(4): 145⁃151. |
| 31 | MA P, HRISTOVA B D, GOOSSENS J, et al. Toughening of Poly(lactic acid) by Ethylene⁃co⁃Vinyl Acetate Copolymer with Different Vinyl Acetate Contents[J]. European Polymer Journal, 2012, 48(1): 146⁃154. |
| 32 | WU B, XU P, YANG W, et al. Super‐Toughened Heat⁃Resistant Poly(lactic acid) Alloys by Tailoring the Phase Morphology and the Crystallization Behaviors[J]. Journal of Polymer Science, 2020, 58: 500⁃509. |
| 33 | CHEN Y, CHEN K, WANG Y, et al. Biobased Heat⁃Triggered Shape⁃Memory Polymers Based on Polylactide/Epoxidized Natural Rubber Blend System Fabricated via Peroxide⁃Induced Dynamic Vulcanization: Co⁃Continuous Phase Structure, Shape Memory Behavior, and Interfacial Compatibilization[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2015, 54(35): 8 723⁃8 731. |
| 34 | CHEN Y, YUAN D, XU C. Dynamically Vulcanized Biobased Polylactide/Natural Rubber Blend Material with Continuous Cross⁃Linked Rubber Phase[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(6): 3 811⁃3 816. |
| 35 | XU P, MA P, CAI X, et al. Selectively Cross⁃Linked Poly(lactide)/Ethylene⁃Glycidyl Methacrylate⁃Vinyl Acetate Thermoplastic Elastomers with Partial Dual⁃Continuous Network⁃Like Structures and Shape Memory Performances[J]. European Polymer Journal, 2016, 84(11): 1⁃12. |
| 36 | MA P, XU P, ZHAI Y, et al. Biobased Poly(lactide)/Ethylene⁃co⁃Vinyl Acetate Thermoplastic Vulcanizates: Morphology Evolution, Superior Properties, and Partial Degradability[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2015, 3(9): 2 211⁃2 219. |
| 37 | MA P, XU P, LIU W, et al. Bio⁃based Poly(lactide)/Ethylene⁃co⁃Vinyl Acetate Thermoplastic Vulcanizates by Dynamic Crosslinking: Structure Vs. Property[J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(21): 15 962⁃15 968. |
| 38 | WANG Y, CHIAO S, HUNG T. F,et al. Improvement in Toughness and Heat Resistance of Poly(lactic acid)/Polycarbonate Blend Through Twin⁃Screw Blending: Influence of Compatibilizer Type[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2012, 125(2): 1 402⁃1 412. |
| 39 | DENG L, XU C, WANG X, et al. Supertoughened Polylactide Binary Blend with High Heat Deflection Temperature Achieved By Thermal Annealing Above the Glass Transition Temperature[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018, 6(1): 480⁃490. |
| 40 | WU B, ZENG Q, NIU D, et al. Design of Supertoughened and Heat⁃Resistant PLLA/Elastomer Blends by Controlling the Distribution of Stereocomplex Crystallites and the Morphology[J]. Macromolecules, 2019, 52(3): 1 092⁃1 103. |
| 41 | DENG S, BAI H, LIU Z, et al. Toward Supertough and Heat⁃Resistant Stereocomplex⁃Type Polylactide/Elastomer Blends with Impressive Melt Stability via in Situ Formation of Graft Copolymer During One⁃Pot Reactive Melt Blending[J]. Macromolecules, 2019, 52(4): 1 718⁃1 730. |
| 42 | 肖云超,刘淑强,吴改红,等. 聚乳酸纤维吸湿排汗运动面料的制备与性能研究[J].丝绸,2015,52(5):6⁃10. |
| XIAO Y C, LIU S Q, WU G H, et al. Preparation and Properties of PLA Fiber Sportswear Fabric with Moisture Absorption and Sweat Discharging Properties[J]. Joural of Silk, 2015, 52(5): 6⁃10. | |
| 43 | LOU C, YAO C, CHEN Y, et al. Manufacturing and Properties of PLA Absorbable Surgical Suture[J]. Textile Research Journal, 2008, 78(11): 958⁃965. |
| 44 | 宋树鑫,梁 敏,王治洲,等. 改性聚乳酸薄膜对阿拉善双峰驼肉的自发气调保鲜[J].食品工业,2017,38(5):81⁃86. |
| SONG S X, LIANG M, WANG Z Z, et al. Preservation Effect of Modified Poly(l⁃lactic acid) Film on the Alxa Bactrian Camel Meat in Equilibrium Modified Atmosphere Packaging[J]. The Food Industry, 2017, 38(5): 81⁃86. | |
| 45 | 付田霞,战孟娇,王新现. 聚乳酸的改性及其在食品包装领域的应用研究进展[J].包装工程,2009,30(12):111⁃123. |
| FU T X, ZHAN M J, WANG X X. Research Progress of Modification of Poly(lactic acid) and Its Application in Food Packaging Field[J]. Packaging Engineering, 2009, 30(12): 111⁃123. |
| [1] | 沈雪梅, 朱小龙, 胡燕超, 宋任远, 张现峰, 李席. 静电喷雾法制备聚乳酸/布洛芬微球及其性能研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(7): 61-67. |
| [2] | 周舒毅, 朱敏, 刘忆颖, 曹舒惠, 蔡启轩, 聂慧, 张玉霞, 周洪福. 高分子止血材料研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(7): 74-84. |
| [3] | 邵琳颖, 郗悦玮, 翁云宣. 可降解聚乳酸复合材料研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(6): 155-164. |
| [4] | 王镕琛, 张恒, 孙焕惟, 段书霞, 秦子轩, 李晗, 朱斐超, 张一风. 医疗卫生用聚乳酸非织造材料的制备及其亲水改性研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(5): 158-166. |
| [5] | 李梦琪, 陈雅君. 纳米材料阻燃聚乳酸的研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(4): 102-114. |
| [6] | 孙滔, 杨青, 胡健, 王洋样, 刘博, 云雪艳, 董同力嘎. 聚(乳酸⁃乙醇酸)薄膜制备及其性能研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(2): 33-40. |
| [7] | 毛晨, 刘番, 鄂毅, 邹姝燕, 龚兴厚. 纳米CoFe2O4的制备及其对PLA结晶性能的影响[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(1): 9-14. |
| [8] | 韦宗辰, 郗悦玮, 翁云宣. 聚乳酸基复合骨组织修复材料的研究现状及进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2021, 35(9): 136-146. |
| [9] | 唐于婧, 王亚桥, 倪敬越, 王从龙, 王向东. 立构复合晶对聚乳酸发泡行为的影响[J]. 中国塑料, 2021, 35(8): 117-124. |
| [10] | 李玉竹, 姚利辉, 叶世强, 吕国永, 刘盼盼, 徐龙飞, 仇丹. 生物降解材料在水环境中降解性能的研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2021, 35(7): 103-114. |
| [11] | 段续远, 郑红娟. 改性聚乳酸发泡技术研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2021, 35(7): 134-139. |
| [12] | 蔡小芳, 袁航, 刁晓倩, 李字义, 封棣. 食品接触聚乳酸杯盖中的滑石粉迁移分析[J]. 中国塑料, 2021, 35(7): 91-96. |
| [13] | 杨文杰, 何佳文, 朱寒宾, 王思思, 李熹平. 石墨烯增强聚乳酸力学性能及其发泡行为研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2021, 35(6): 26-32. |
| [14] | 孙东宝, 路琴, 陆鑫禹, 贾王一, 曹尚. PLA/稻壳粉复合材料界面改性方法及性能研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2021, 35(6): 80-84. |
| [15] | 张博, 王小峰, 郭萌, 白志媛, 任翠红, 韩文娟, 宇山浩, 李倩. 聚乳酸表面羧基化改性及细胞相容性研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2021, 35(5): 17-23. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2
京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2