 京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2
京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2
《中国塑料》编辑部 ©2008-2024 版权所有
地址:北京市海淀区阜成路11号 邮编:100048
编辑部:010-68985541 联系信箱:cp@plaschina.com.cn
广告部/发行部:010-68985253 本系统由北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司设计开发

中国塑料 ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (6): 155-164.DOI: 10.19491/j.issn.1001-9278.2022.06.024
收稿日期:2022-01-05
出版日期:2022-06-26
发布日期:2022-06-27
通讯作者:
郗悦玮(1990—),女,讲师,生物医用高分子材料及生物基材料,xiyuewei@btbu.edu.cn基金资助:
SHAO Linying1, XI Yuewei1,2( ), WENG Yunxuan1,2(
), WENG Yunxuan1,2( )
)
Received:2022-01-05
Online:2022-06-26
Published:2022-06-27
Contact:
XI Yuewei, WENG Yunxuan
E-mail:xiyuewei@btbu.edu.cn;wyxuan@th.btbu.edu.cn;xiyuewei@btbu.edu.cn
摘要:
对聚乳酸(PLA)复合材料的生物降解性能进行综述,总结PLA与有机物(如木质素、纤维素等)、无机物(如碳酸钙、纳米银颗粒等)复合后力学性能、热性能、生物相容性、抗菌性的变化及在不同环境条件下生物降解速率的变化,梳理了PLA复合材料结构、组成与降解性能的相互关系,对降解性能可控的PLA复合材料应用前景进行了展望。
中图分类号:
邵琳颖, 郗悦玮, 翁云宣. 可降解聚乳酸复合材料研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(6): 155-164.
SHAO Linying, XI Yuewei, WENG Yunxuan. Research progress in degradation characteristics of poly(lactic acid) composites[J]. China Plastics, 2022, 36(6): 155-164.
| 复合材料添加剂 | 木质素 | 木质纤维素、 碳二亚胺 | 木质纤维 | 玄武岩 纤维 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 降解效果 | 促进降解 | 抑制降解 | 促进降解 | 抑制降解 |
| 力学性能 | 降低 | 含量较少时略有提高 | 降低 | 增强 |
| 热性能 | 没有变化 | 先增加后下降 | ⁃⁃⁃⁃ | ⁃⁃⁃⁃ |
| 结晶度 | 降低 | 降低 | ⁃⁃⁃⁃ | ⁃⁃⁃⁃ |
| 复合材料添加剂 | 木质素 | 木质纤维素、 碳二亚胺 | 木质纤维 | 玄武岩 纤维 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 降解效果 | 促进降解 | 抑制降解 | 促进降解 | 抑制降解 |
| 力学性能 | 降低 | 含量较少时略有提高 | 降低 | 增强 |
| 热性能 | 没有变化 | 先增加后下降 | ⁃⁃⁃⁃ | ⁃⁃⁃⁃ |
| 结晶度 | 降低 | 降低 | ⁃⁃⁃⁃ | ⁃⁃⁃⁃ |
| 样品名称 | 添加剂 | 添加量/ % | 第二次热循环 | 参考文献 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tm/℃ | Tc/℃ | Xc/% | |||||
| PLA | 无 | 0 | 177 | 113 | 54.3 | [ | |
| PLA/lignin | lignin | 5 | 177 | 112 | 45.4 | [ | |
| PLA/lignin | lignin | 10 | 174 | 101 | 42.5 | [ | |
| PLA/lignin | lignin | 15 | 174 | 92 | 30.3 | [ | |
| PLA | 无 | 0 | 177 | 98 | 13.80 | [ | |
| PLA/WF | WF | 7.5 | 177 | 96 | 16.65 | [ | |
| PLA/WF | WF | 15 | 178 | 94 | 16.34 | [ | |
| PLA/BF | BF | 7.5 | 176 | 97 | 14.22 | [ | |
| PLA/BF | BF | 15 | 178 | 95 | 13.24 | [ | |
| 样品名称 | 添加剂 | 添加量/ % | 第二次热循环 | 参考文献 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tm/℃ | Tc/℃ | Xc/% | |||||
| PLA | 无 | 0 | 177 | 113 | 54.3 | [ | |
| PLA/lignin | lignin | 5 | 177 | 112 | 45.4 | [ | |
| PLA/lignin | lignin | 10 | 174 | 101 | 42.5 | [ | |
| PLA/lignin | lignin | 15 | 174 | 92 | 30.3 | [ | |
| PLA | 无 | 0 | 177 | 98 | 13.80 | [ | |
| PLA/WF | WF | 7.5 | 177 | 96 | 16.65 | [ | |
| PLA/WF | WF | 15 | 178 | 94 | 16.34 | [ | |
| PLA/BF | BF | 7.5 | 176 | 97 | 14.22 | [ | |
| PLA/BF | BF | 15 | 178 | 95 | 13.24 | [ | |
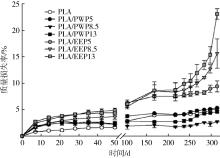
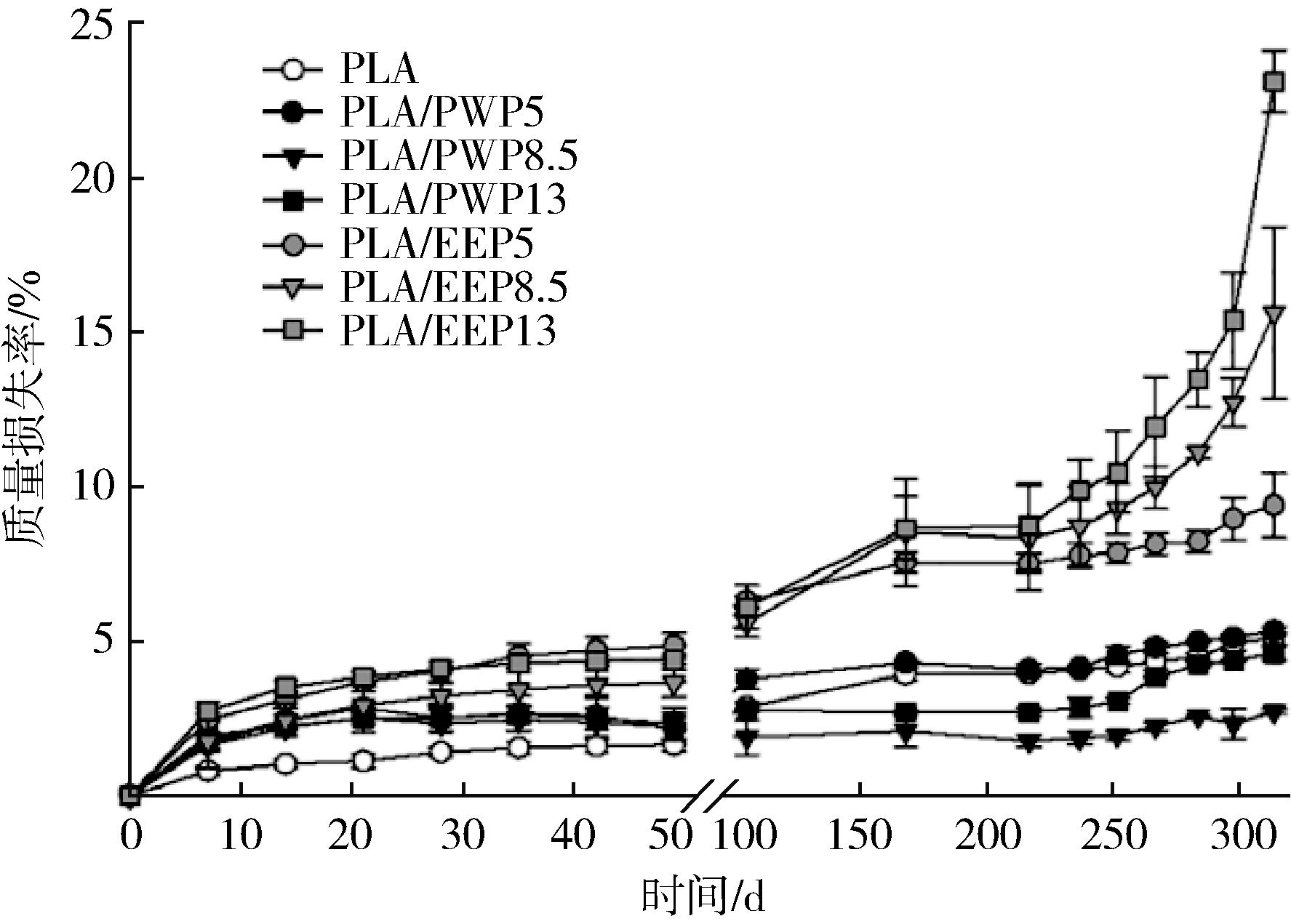
| 薄膜种类 | 添加量/ % | 热性能 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tg/℃ | Tm/℃ | ΔHm/J•g-1 | ||
| PLA | 0 | 50.1±7.5 | 150.4±0.4 | 22.4±3.1 |
| PLA/PWP5 | 5 | 48.3±5.4 | 148.1±3.8 | 21.3±8.9 |
| PLA/PWP8.5 | 8.5 | 43.4±6.7 | 148.3±3.6 | 19.4±0.4 |
| PLA/PWP13 | 13 | 38.6±7.4 | 149.8±3.2 | 18.7±0.4 |
| PLA/EEP5 | 5 | 46.7±2.4 | 151.2±1.4 | 24.2±2.4 |
| PLA/EEP8.5 | 8.5 | 43.7±3.4 | 149.7±0.9 | 21.6±4.7 |
| PLA/EEP13 | 13 | 49.8±4.8 | 146.8±1.4 | 11.4±6.5 |
| 薄膜种类 | 添加量/ % | 热性能 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tg/℃ | Tm/℃ | ΔHm/J•g-1 | ||
| PLA | 0 | 50.1±7.5 | 150.4±0.4 | 22.4±3.1 |
| PLA/PWP5 | 5 | 48.3±5.4 | 148.1±3.8 | 21.3±8.9 |
| PLA/PWP8.5 | 8.5 | 43.4±6.7 | 148.3±3.6 | 19.4±0.4 |
| PLA/PWP13 | 13 | 38.6±7.4 | 149.8±3.2 | 18.7±0.4 |
| PLA/EEP5 | 5 | 46.7±2.4 | 151.2±1.4 | 24.2±2.4 |
| PLA/EEP8.5 | 8.5 | 43.7±3.4 | 149.7±0.9 | 21.6±4.7 |
| PLA/EEP13 | 13 | 49.8±4.8 | 146.8±1.4 | 11.4±6.5 |
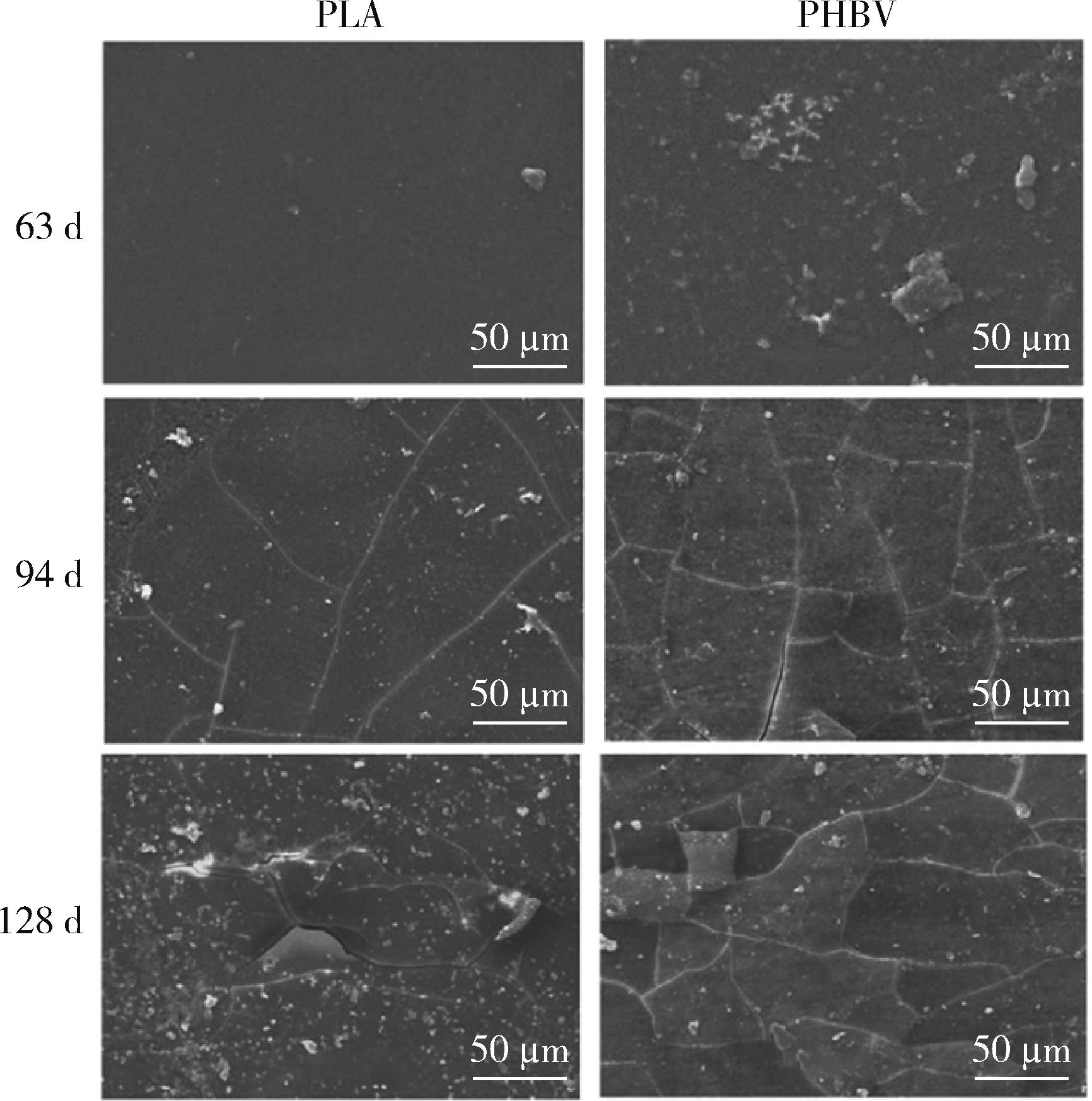
| 1 | Qin M, Chen C, Song B, et al. A review of biodegradable plastics to biodegradable microplastics: another ecological threat to soil environments? [J]. J Clean Prod, 2021, 312. |
| 2 | Rezvani Ghomi E, Khosravi F, Saedi Ardahaei A, et al. The life cycle assessment for polylactic acid (PLA) to make it a low⁃carbon material [J]. Polymers, 2021, 13(11). |
| 3 | Kliem S, Kreutzbruck M, Bonten C. Review on the biological degradation of polymers in various environments [J]. Materials, 2020, 13(20). |
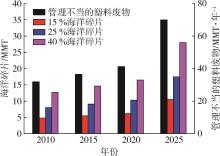
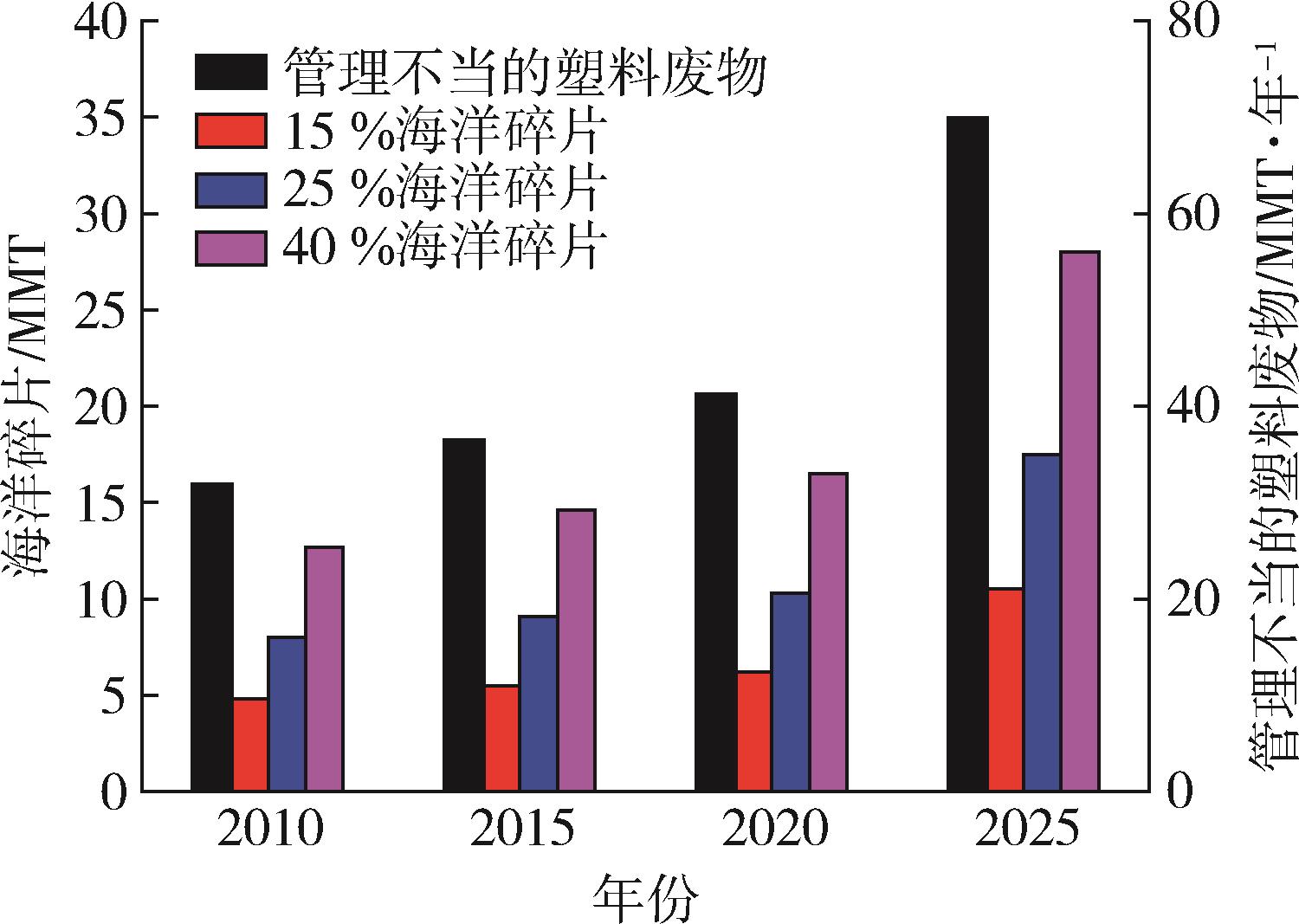
| 4 | Jambeck J R, Geyer R, Wilcox C, et al. Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean [J]. Science, 2015, 347(6223): 768⁃771. |
| 5 | Zaaba N F, Jaafar M. A Review on degradation mechanisms of polylactic acid: hydrolytic, photodegradative, microbial, and enzymatic degradation [J]. Polym Eng Sci, 2020, 60(9): 2 061⁃2 075. |
| 6 | Haider T P, Volker C, Kramm J, et al. Plastics of the future? the impact of biodegradable polymers on the environment and on society [J]. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl, 2019, 58(1): 50⁃62. |
| 7 | Armentano I, Bitinis N, Fortunati E, et al. Multifunctional nanostructured PLA materials for packaging and tissue engineering [J]. Prog Polym Sci, 2013, 38(10⁃11): 1 720⁃1 747. |
| 8 | Rajeshkumar G, Arvindh Seshadri S, Devnani G L, et al. Environment friendly, renewable and sustainable poly lactic acid (PLA) based natural fiber reinforced composites⁃a comprehensive review [J]. J Clean Prod, 2021, 310. |
| 9 | Ramesh P, Vinodh S. State of art review on life cycle assessment of polymers [J]. Int J Sustain Eng, 2020, 13(6): 411⁃422. |
| 10 | Rasal R M, Janorkar A V, Hirt D E. Poly(lactic acid) modifications [J]. Prog Polym Sci, 2010, 35(3): 338⁃356. |
| 11 | Rosli N A, Karamanlioglu M, Kargarzadeh H, et al. Comprehensive exploration of natural degradation of poly(lactic acid) blends in various degradation media: a review [J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2021, 187: 732⁃741. |
| 12 | Andrzejewska A. One year evaluation of material properties changes of polylactide parts in various hydrolytic degradation conditions [J]. Polymers, 2019, 11(9). |
| 13 | Sednickova M, Pekarova S, Kucharczyk P, et al. Changes of physical properties of pla⁃based blends during early stage of biodegradation in compost [J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2018, 113: 434⁃442. |
| 14 | Madhavan Nampoothiri K, Nair N R, John R P. An overview of the recent developments in polylactide research [J]. Bioresour Technol, 2010, 101(22): 8 493⁃8 501. |
| 15 | Karamanlioglu M, Preziosi R, Robson G D. Abiotic and biotic environmental degradation of the bioplastic polymer poly(lactic acid): a review [J]. Polym Degradation Stab, 2017, 137: 122⁃130. |
| 16 | Larrañaga A, Lizundia E. A review on the thermomechanical properties and biodegradation behaviour of polyesters [J]. Eur Polym J, 2019, 121. |
| 17 | Da Silva S A, Hinkel E W, Lisboa T C, et al. A biostimulation⁃based accelerated method for evaluating the biodegradability of polymers [J]. Polym Test, 2020, 91. |
| 18 | Mayekar P C, Castro⁃Aguirre E, Auras R, et al. Effect of nano⁃clay and surfactant on the biodegradation of poly(lactic acid) films [J]. Polymers, 2020, 12(2). |
| 19 | Saadi Z, Rasmont A, Cesar G, et al. Fungal degradation of poly(l⁃lactide) in soil and in compost [J]. J Polym Environ, 2011, 20(2): 273⁃282. |
| 20 | Longieras A, J⁃B Tanchette, Erre D, et al. Compostability of poly(lactide): degradation in an inert solid medium [J]. J Polym Environ, 2007, 15(3): 200⁃206. |
| 21 | Wang H, Pu Y, Ragauskas A, et al. From lignin to valuable products⁃strategies, challenges, and prospects [J]. Bioresour Technol, 2019, 271: 449⁃461. |
| 22 | Sugiarto S, Leow Y, Tan C L, et al. How far is lignin from being a biomedical material? [J]. Bioact Mater, 2022, 8: 71⁃94. |
| 23 | Silva T F D, Menezes F, Montagna L S, et al. Effect of lignin as accelerator of the biodegradation process of poly(lactic acid)/lignin composites [J]. Mater Sci Eng, B, 2019, 251. |
| 24 | Wang Y, Liu S, Wang Q, et al. Strong, ductile and biodegradable polylactic acid/lignin⁃containing cellulose nanofibril composites with improved thermal and barrier properties [J]. Ind Crops Prod, 2021, 171. |
| 25 | Sun C, Huang Z, Liu Y, et al. The effect of carbodiimide on the stability of wood fiber/poly(lactic acid) composites during soil degradation [J]. J Polym Environ, 2020, 28(4): 1 315⁃1 325. |
| 26 | Kuciel S, Mazur K, Hebda M. The influence of wood and basalt fibres on mechanical, thermal and hydrothermal properties of PLA composites [J]. J Polym Environ, 2020, 28(4): 1 204⁃1 215. |
| 27 | Quitadamo A, Massardier V, Iovine V, et al. Effect of cellulosic waste derived filler on the biodegradation and thermal properties of hdpe and PLA composites [J]. Processes, 2019, 7(10). |
| 28 | E⁃R Radu, Panaitescu D M, C⁃A Nicolae, et al. The soil biodegradability of structured composites based on cellulose cardboard and blends of polylactic acid and polyhydroxybutyrate [J]. J Polym Environ, 2021, 29(7): 2 310⁃2 320. |
| 29 | Ilyas R A, Sapuan S M, Harussani M M, et al. Polylactic acid (PLA) biocomposite: processing, additive manufacturing and advanced applications [J]. Polymers, 2021, 13(8). |
| 30 | Hegyesi N, Zhang Y, Kohári A, et al. Enzymatic degradation of PLA/cellulose nanocrystal composites [J]. Ind Crops Prod, 2019, 141. |
| 31 | Zhao X P, Hu H, Wang X, et al. Super tough poly(lactic acid) blends: a comprehensive review [J]. Rsc Advances, 2020, 10(22): 13 316⁃13 368. |
| 32 | Coiai S, Di Lorenzo M L, Cinelli P, et al. Binary green blends of poly(lactic acid) with poly(butylene adipate⁃co⁃butylene terephthalate) and poly(butylene succinate⁃co⁃butylene adipate) and their nanocomposites [J]. Polymers, 2021, 13(15). |
| 33 | Qiu S, Zhou Y, Waterhouse G I N, et al. Optimizing interfacial adhesion in PBAT/PLA nanocomposite for biodegradable packaging films [J]. Food Chem, 2021, 334: 127487. |
| 34 | Correa⁃Pacheco Z N, Black⁃Solis J D, Ortega⁃Gudino P, et al. Preparation and characterization of bio⁃based PLA/PBAT and cinnamon essential oil polymer fibers and life⁃cycle assessment from hydrolytic degradation [J]. Polymers, 2019, 12(1). |
| 35 | Jian J, Xiangbin Z, Xianbo H. An overview on synthesis, properties and applications of poly(butylene⁃adipate⁃co⁃terephthalate)–PBAT [J]. Advanced Industrial and Engineering Polymer Research, 2020, 3(1): 19⁃26. |
| 36 | Rameshkumar S, Shaiju P, O'connor K E, et al. Bio⁃based and biodegradable polymers ⁃ state⁃of⁃the⁃art, challenges and emerging trends [J]. Current Opinion in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, 2020, 21: 75⁃81. |
| 37 | Gao X, Xie D, Yang C. Effects of a PLA/PBAT biodegradable film mulch as a replacement of polyethylene film and their residues on crop and soil environment [J]. Agric Water Manage, 2021, 255. |
| 38 | Ren Y, Hu J, Yang M, et al. Biodegradation behavior of poly (lactic acid) (PLA), poly (butylene adipate⁃co⁃terephthalate) (PBAT), and their blends under digested sludge conditions [J]. J Polym Environ, 2019, 27(12): 2 784⁃2 792. |
| 39 | Fu Y, Wu G, Bian X, et al. Biodegradation behavior of poly(butylene adipate⁃co⁃terephthalate) (PBAT), poly(lactic acid) (PLA), and their blend in freshwater with sediment [J]. Molecules, 2020, 25(17). |
| 40 | Jia H, Zhang M, Weng Y, et al. Degradation of polylactic acid/polybutylene adipate⁃co⁃terephthalate by coculture of pseudomonas mendocina and actinomucor elegans [J]. J Hazard Mater, 2021, 403: 123679. |
| 41 | Rocha D B, Souza De Carvalho J, De Oliveira S A, et al. A new approach for flexible PBAT/PLA/CaCO3 films into agriculture [J]. J Appl Polym Sci, 2018, 135(35). |
| 42 | Kim H⁃S, Park B H, Choi J H, et al. Mechanical properties and thermal stability of poly(l⁃lactide)/calcium carbonate composites [J]. J Appl Polym Sci, 2008, 109(5): 3 087⁃3 092. |
| 43 | Ulloa P A, Vidal J, Dicastillo C, et al. Development of poly(lactic acid) films with propolis as a source of active compounds: biodegradability, physical, and functional properties [J]. J Appl Polym Sci, 2018, 136(8). |
| 44 | Srimalanon P, Prapagdee B, Sombatsompop N. Soil inoculation with pseudomonas geniculata ws3 for accelerating the biodegradation process of in situ compatibilized Pbs/PLA blends doped with hpqm [J]. J Polym Environ, 2020, 28(4): 1 138⁃1 149. |
| 45 | Brdlik P, Boruvka M, Behalek L, et al. Biodegradation of poly(lactic acid) biocomposites under controlled composting conditions and freshwater biotope [J]. Polymers, 2021, 13(4). |
| 46 | Mazur K, Singh R, Friedrich R P, et al. The effect of antibacterial particle incorporation on the mechanical properties, biodegradability, and biocompatibility of PLA and PHBV composites [J]. Macromol Mater Eng, 2020, 305(9). |
| 47 | Ramos M, Fortunati E, Beltran A, et al. Controlled release, disintegration, antioxidant, and antimicrobial properties of poly (lactic acid)/thymol/nanoclay composites [J]. Polymers, 2020, 12(9). |
| 48 | Siakeng R, Jawaid M, Asim M, et al. Accelerated weathering and soil burial effect on biodegradability, colour and textureof coir/pineapple leaf fibres/PLA biocomposites [J]. Polymers, 2020, 12(2). |
| 49 | Boonluksiri Y, Prapagdee B, Sombatsompop N. Promotion of polylactic acid biodegradation by a combined addition of PLA⁃degrading bacterium and nitrogen source under submerged and soil burial conditions [J]. Polym Degradation Stab, 2021, 188. |
| 50 | Stoleru E, Vasile C, Oprica L, et al. Influence of the chitosan and rosemary extract on fungal biodegradation of some plasticized PLA⁃based materials [J]. Polymers, 2020, 12(2). |
| 51 | Pantani R, Sorrentino A. Influence of crystallinity on the biodegradation rate of injection⁃moulded poly(lactic acid) samples in controlled composting conditions [J]. Polym Degradation Stab, 2013, 98(5): 1 089⁃1 096. |
| 52 | De Jong S J, Arias E R, Rijkers D T S, et al. New insights into the hydrolytic degradation of poly(lactic acid): participation of the alcohol terminus [J]. Polymer, 2001, 42(7): 2 795⁃2 802. |
| 53 | Valentina I, Haroutioun A, Fabrice L, et al. Poly(lactic acid)⁃based nanobiocomposites with modulated degradation rates [J]. Materials, 2018, 11(10). |
| 54 | Mai F, Tu W, Bilotti E, et al. Preparation and properties of self⁃reinforced poly(lactic acid) composites based on oriented tapes [J]. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf, 2015, 76: 145⁃153. |
| 55 | Alcock B, Peijs T. Technology and development of self⁃reinforced polymer composites [J]. Polymer Composites ⁃ Polyolefin Fractionation ⁃ Polymeric Peptidomimetics ⁃ Collagens, 2013, 251: 1⁃76. |
| 56 | Gil⁃Castell O, Badia J D, Ingles⁃Mascaros S, et al. Polylactide⁃based self⁃reinforced composites biodegradation: individual and combined influence of temperature, water and compost [J]. Polym Degradation Stab, 2018, 158: 40⁃51. |
| 57 | Wang Q, Li Y, Zhou X, et al. Toughened poly(lactic acid)/bep composites with good biodegradability and cytocompatibility [J]. Polymers, 2019, 11(9). |
| 58 | Karamanlioglu M, Houlden A, Robson G D. Isolation and characterisation of fungal communities associated with degradation and growth on the surface of poly(lactic) acid (PLA) in soil and compost [J]. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation, 2014, 95: 301⁃310. |
| [1] | 沈雪梅, 朱小龙, 胡燕超, 宋任远, 张现峰, 李席. 静电喷雾法制备聚乳酸/布洛芬微球及其性能研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(7): 61-67. |
| [2] | 周舒毅, 朱敏, 刘忆颖, 曹舒惠, 蔡启轩, 聂慧, 张玉霞, 周洪福. 高分子止血材料研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(7): 74-84. |
| [3] | 王镕琛, 张恒, 孙焕惟, 段书霞, 秦子轩, 李晗, 朱斐超, 张一风. 医疗卫生用聚乳酸非织造材料的制备及其亲水改性研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(5): 158-166. |
| [4] | 李梦琪, 陈雅君. 纳米材料阻燃聚乳酸的研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(4): 102-114. |
| [5] | 孙滔, 杨青, 胡健, 王洋样, 刘博, 云雪艳, 董同力嘎. 聚(乳酸⁃乙醇酸)薄膜制备及其性能研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(2): 33-40. |
| [6] | 毛晨, 刘番, 鄂毅, 邹姝燕, 龚兴厚. 纳米CoFe2O4的制备及其对PLA结晶性能的影响[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(1): 9-14. |
| [7] | 韦宗辰, 郗悦玮, 翁云宣. 聚乳酸基复合骨组织修复材料的研究现状及进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2021, 35(9): 136-146. |
| [8] | 唐于婧, 王亚桥, 倪敬越, 王从龙, 王向东. 立构复合晶对聚乳酸发泡行为的影响[J]. 中国塑料, 2021, 35(8): 117-124. |
| [9] | 李玉竹, 姚利辉, 叶世强, 吕国永, 刘盼盼, 徐龙飞, 仇丹. 生物降解材料在水环境中降解性能的研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2021, 35(7): 103-114. |
| [10] | 段续远, 郑红娟. 改性聚乳酸发泡技术研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2021, 35(7): 134-139. |
| [11] | 蔡小芳, 袁航, 刁晓倩, 李字义, 封棣. 食品接触聚乳酸杯盖中的滑石粉迁移分析[J]. 中国塑料, 2021, 35(7): 91-96. |
| [12] | 杨文杰, 何佳文, 朱寒宾, 王思思, 李熹平. 石墨烯增强聚乳酸力学性能及其发泡行为研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2021, 35(6): 26-32. |
| [13] | 孙东宝, 路琴, 陆鑫禹, 贾王一, 曹尚. PLA/稻壳粉复合材料界面改性方法及性能研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2021, 35(6): 80-84. |
| [14] | 张博, 王小峰, 郭萌, 白志媛, 任翠红, 韩文娟, 宇山浩, 李倩. 聚乳酸表面羧基化改性及细胞相容性研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2021, 35(5): 17-23. |
| [15] | 许佳怡. 羟丙甲纤维素增韧聚乳酸复合材料的制备及性能研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2021, 35(5): 59-64. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2
京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2