 京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2
京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2
《中国塑料》编辑部 ©2008-2024 版权所有
地址:北京市海淀区阜成路11号 邮编:100048
编辑部:010-68985541 联系信箱:cp@plaschina.com.cn
广告部/发行部:010-68985253 本系统由北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司设计开发

中国塑料 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (10): 18-24.DOI: 10.19491/j.issn.1001-9278.2025.10.004
侯钦正1( ), 刘文龙1, 李长金2, 秦柳3, 丁玉梅1, 李好义1, 杨卫民1(
), 刘文龙1, 李长金2, 秦柳3, 丁玉梅1, 李好义1, 杨卫民1( ), 霍正元4
), 霍正元4
收稿日期:2024-09-12
出版日期:2025-10-26
发布日期:2025-10-21
通讯作者:
杨卫民,教授,主要研究方向为高分子材料先进制造,yangwm@mail.buct.edu.cn作者简介:侯钦正,博士研究生,主要研究方向为高分子材料先进制造,17864215873@163.com
基金资助:
HOU Qinzheng1( ), LIU Wenlong1, LI Changjin2, QIN Liu3, DING Yumei1, LI Haoyi1, YANG Weimin1(
), LIU Wenlong1, LI Changjin2, QIN Liu3, DING Yumei1, LI Haoyi1, YANG Weimin1( ), HOU Zhengyuan4
), HOU Zhengyuan4
Received:2024-09-12
Online:2025-10-26
Published:2025-10-21
Contact:
YANG Weimin
E-mail:17864215873@163.com;yangwm@mail.buct.edu.cn
摘要:
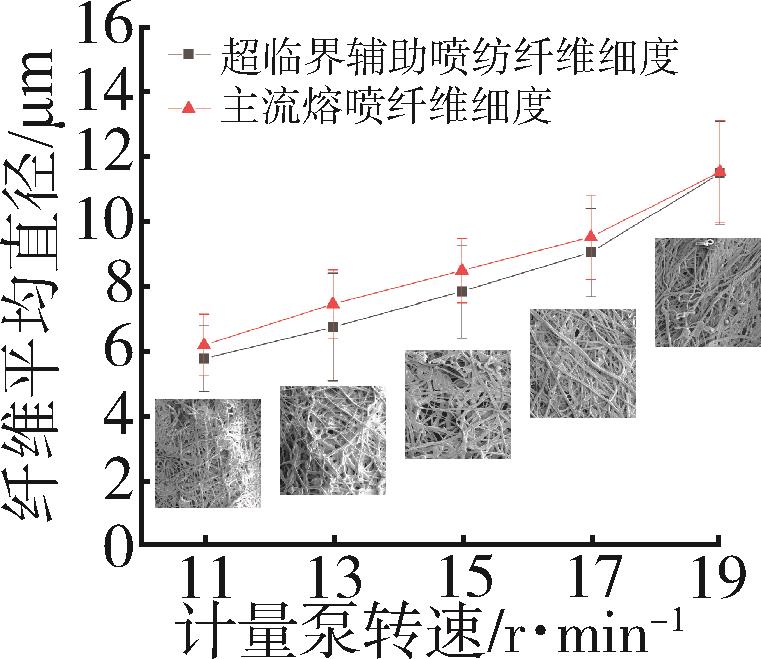
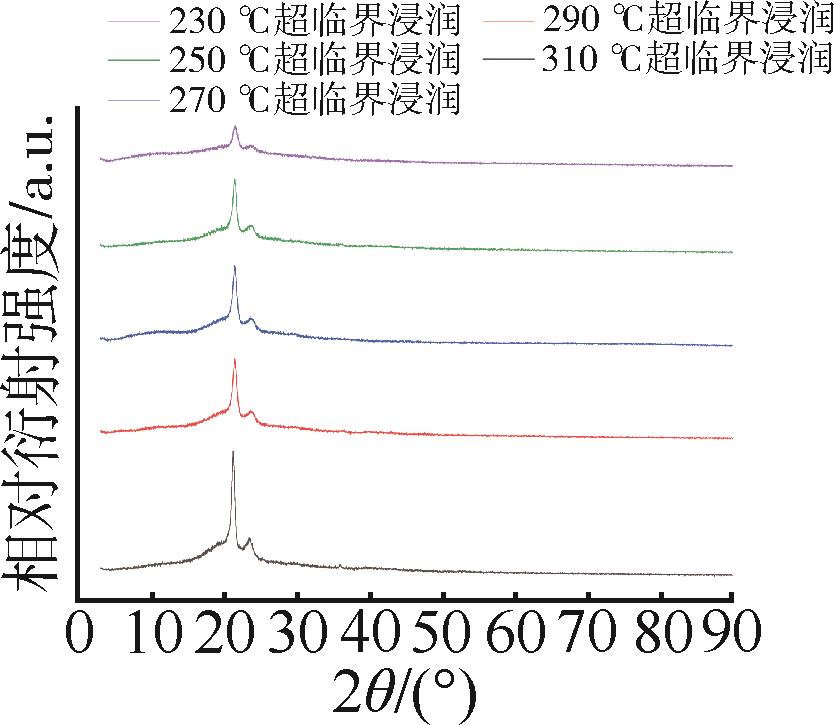
低密度聚乙烯(PE⁃LD)超细纤维膜制品具有耐腐蚀、疏水、柔韧抗冲击等特点,在医疗、防护、建材等领域有着广泛的应用前景。本文通过自制的超临界二氧化碳(SC⁃CO2)浸润装置,研究了SC⁃CO2增塑熔喷的主要工艺参数热风温度、热风流量、计量泵转速对PE⁃LD纤维膜纤维形貌、结晶性能的影响,对影响机理进行了分析,并考察了其过滤与拉伸性能。结果表明,SC⁃CO2浸渍,提高热风温度、热风流量,降低计量泵转速都有利于降低PE⁃LD纤维直径,其平均直径最小可达3.88 μm;SC⁃CO2处理、热风温度增加均有利于结晶度的提高;制备的样品热压后滤效达72.9 %,滤阻仅51.4 Pa;最大拉伸强度为4.5 MPa,断裂伸长率最大可达30 %。本研究提出了PE⁃LD纤维膜的制备新工艺,相关研究成果有望为聚乙烯纤维膜制备工艺的发展提供参考。
中图分类号:
侯钦正, 刘文龙, 李长金, 秦柳, 丁玉梅, 李好义, 杨卫民, 霍正元. SC⁃CO2增塑熔喷聚乙烯纤维膜制备工艺及性能研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2025, 39(10): 18-24.
HOU Qinzheng, LIU Wenlong, LI Changjin, QIN Liu, DING Yumei, LI Haoyi, YANG Weimin, HOU Zhengyuan. Preparation and properties of supercritical carbon dioxide⁃plasticized melt⁃blown polyethylene fiber film[J]. China Plastics, 2025, 39(10): 18-24.
| 组号 | 实验变量 | 实验变量组设置 | 材料处理方式 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 热风温度 | 230、250、270、290、310 ℃ | 未浸润/SC⁃CO2浸润 |
| 2 | 热风流量 | 520、600、680、760、840 L/min | 未浸润/SC⁃CO2浸润 |
| 3 | 计量泵转速 | 11、13、15、17、19 r/min | 未浸润/SC⁃CO2浸润 |
| 组号 | 实验变量 | 实验变量组设置 | 材料处理方式 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 热风温度 | 230、250、270、290、310 ℃ | 未浸润/SC⁃CO2浸润 |
| 2 | 热风流量 | 520、600、680、760、840 L/min | 未浸润/SC⁃CO2浸润 |
| 3 | 计量泵转速 | 11、13、15、17、19 r/min | 未浸润/SC⁃CO2浸润 |
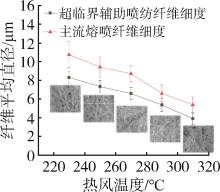
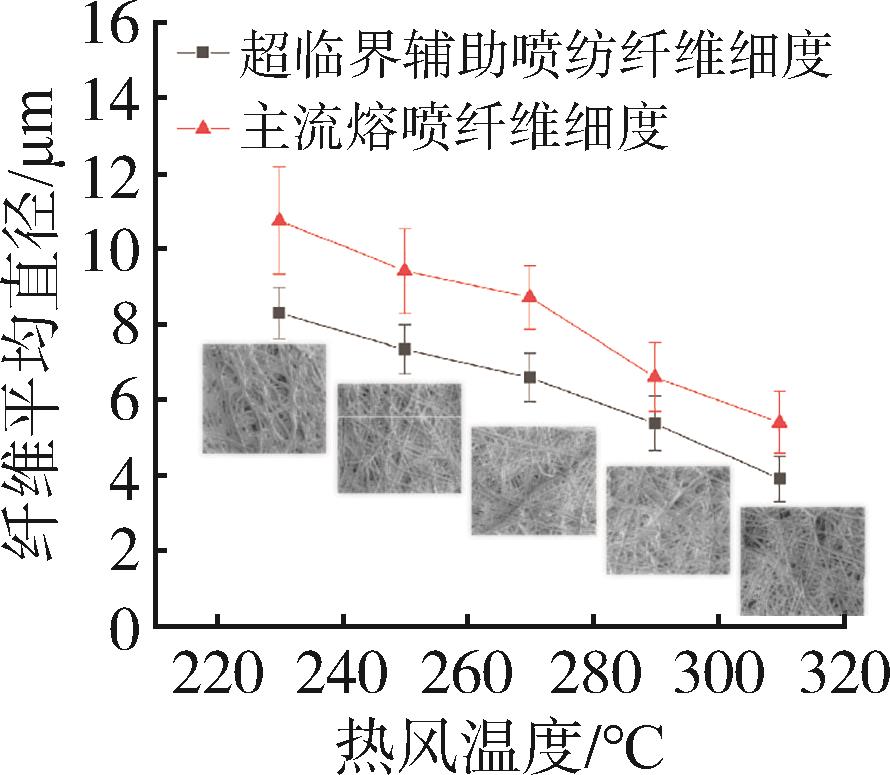
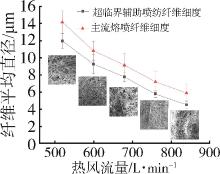
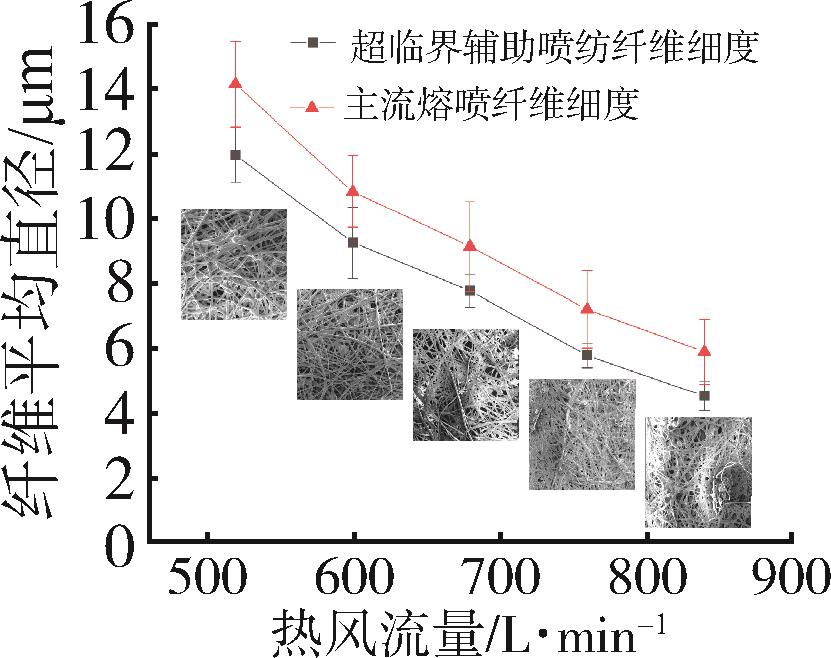
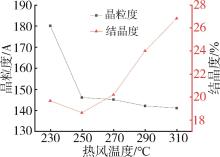
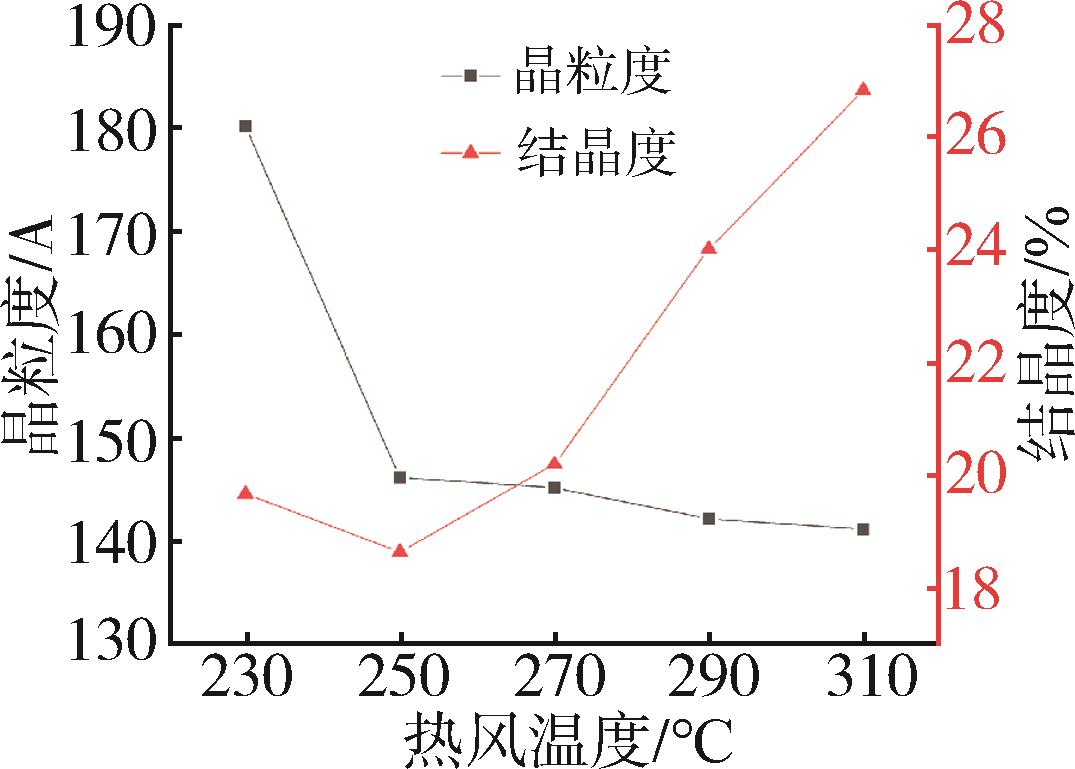
| 实验条件 | 晶粒度/A | 结晶度/% |
|---|---|---|
| 310 ℃超临界浸润 | 141 | 26.80 |
| 310 ℃未超临界浸润 | 187 | 20.54 |
| MG6000原料 | 127 | 16.82 |
| 实验条件 | 晶粒度/A | 结晶度/% |
|---|---|---|
| 310 ℃超临界浸润 | 141 | 26.80 |
| 310 ℃未超临界浸润 | 187 | 20.54 |
| MG6000原料 | 127 | 16.82 |
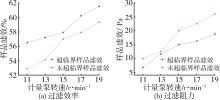
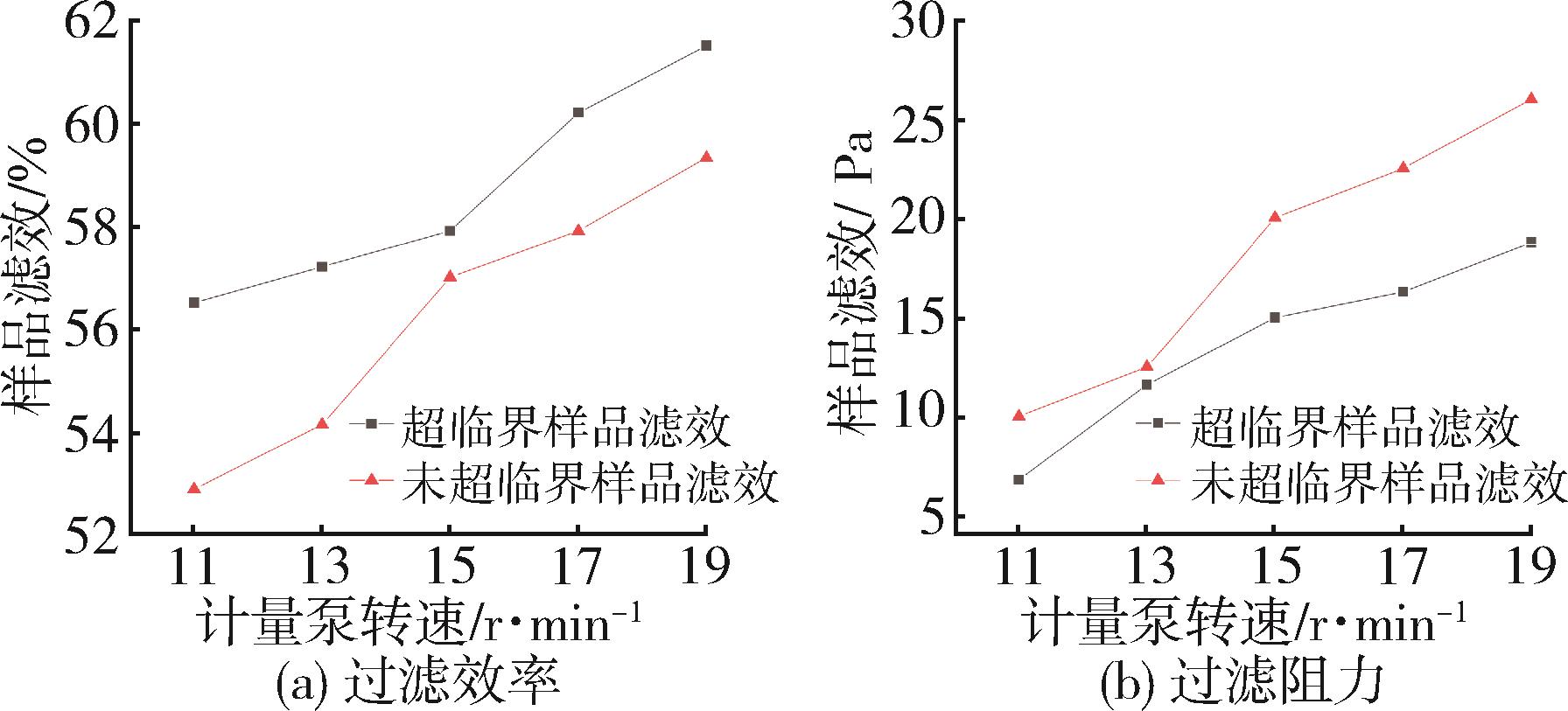
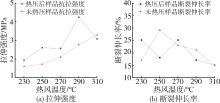
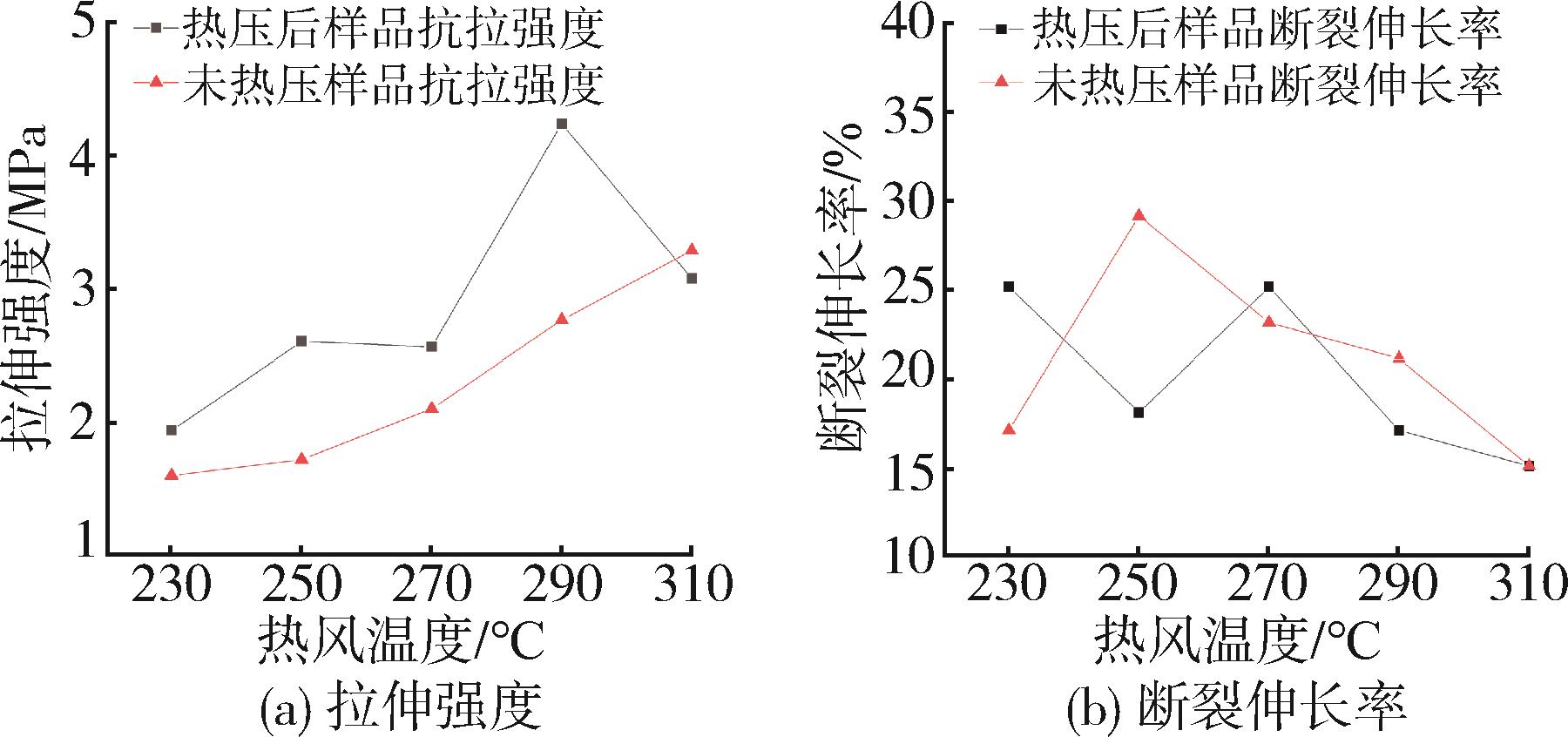
| [1] | 邱 芳,卫志美,彭民乐,等.静电纺丝法制备多孔超细聚醚砜纤维及其对双酚A的吸附性能[J].中国塑料, 2015(6):6. |
| QIU F, WEI Z M, PENG M L, et al. Preparation of porous ultrafine polyethersulfone fibers by electrospinning and their adsorption performance for bisphenol A[J]. China Plastics, 2015(6): 6. | |
| [2] | 孙子佳,雒翠梅,王启航,等.ODATA@LCNC的制备及对多功能PLA复合膜的影响[J].中国塑料,2023, 37(12):14⁃22. |
| SUN Z J, LUO C M, WANG Q H, et al. Preparation of ODATA@LCNC and its effects on multifunctional PLA composite Films[J]. China Plastics, 2023, 37(12): 14⁃22. | |
| [3] | 王 迎,杨 云,魏春艳,等.沉积静电纺聚丙烯腈纳米纤维膜窗纱的制备及其性能[J].纺织学报,2018,39(4):14⁃18. |
| WANG Y, YANG Y, WEI C Y, et al. Preparation and properties of sedimentation electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofiber membrane window screen[J]. Journal of Textile Research, 2018, 39(4): 14⁃18. | |
| [4] | 周舒毅,朱 敏,刘忆颖,等.高分子止血材料研究进展[J].中国塑料,2022,36(7):74. |
| ZHOU S Y, ZHU M, LIU Y Y, et al. Research progress of polymer hemostatic materials[J]. China Plastics, 2022, 36(7): 74. | |
| [5] | Hufenus R, Yan Y, Dauner M, et al. Melt⁃spun fibers for textile applications[J]. Materials, 2020, 13(19): 4 298. |
| [6] | Han M C, He H W, Kong W K, et al. High⁃performance electret and antibacterial polypropylene meltblown nonwoven materials doped with boehmite and ZnO nanoparticles for air filtration[J]. Fibers and Polymers, 2022, 23(7): 1 947⁃1 955. |
| [7] | Bhat G. Melt blown polymeric nanofibers for medical applications⁃an overview[J]. Nanoscience & Technology: Open Access, 2015, 2(1):1⁃9. |
| [8] | 王晓梅,陈才深.聚乳酸/聚丙烯共混纺粘纤维的制备及其性能[J].纺织学报,2017,38(1):13⁃16. |
| WANG X M, CHEN C S. Preparation and properties of poly(lactic acid)/polypropylene blended spunbond fiber[J]. Journal of Textile Research, 2017, 38(1): 13⁃16. | |
| [9] | Zhang L, Hou Q, Li H, et al. Investigation on the sound absorption performance of polypropylene/polyethylene glycol ultrafine fibers by melt differential electrospinning process[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2022, 200: 109056. |
| [10] | Wu W, Sota H, Hirogaki T, et al. Investigation of air filter properties of nanofiber non⁃woven fabric manufactured by a modified melt⁃blowing method along with flash spinning method[J]. Precision Engineering, 2021, 68: 187⁃196. |
| [11] | 王月勤,周世蛟,胡玉涛,等.铸片工艺对锂电池隔膜成孔性能的影响[J].信息记录材料,2020,21(8):1⁃4. |
| WANG Y Q, ZHOU S J, HU Y T, et al. The influence of casting process on the pore⁃forming performance of lithium battery separators[J]. Information Recording Materials, 2020, 21(8): 1⁃4. | |
| [12] | Yu B, Han J, Sun H, et al. The preparation and property of poly (lactic acid)/tourmaline blends and melt‐blown nonwoven[J]. Polymer Composites, 2015, 36(2): 264⁃271. |
| [13] | 戴 行,高瑞雪,李奕国,等.高玻璃化转变温度抗冲击透明聚酯的研究进展[J].化工进展, 2023, 42(5):2 555⁃2 565. |
| DAI X, GAO R X, LI Y G, et al. Research progress on impact⁃resistant transparent polyester with high glass transition temperature[J]. Chemical Industry & Engineering Progress, 2023, 42(5): 2 555⁃2 565. | |
| [14] | 王富玉,高振勇,马祥艳,等.全生物降解聚乳酸/聚碳酸亚丙酯共混物研究进展[J].中国塑料, 2015(2):7. |
| WANG F Y, GAO Z Y, MA X Y, et al. Research progress on fully biodegradable poly(lactic acid)/poly(ethyl carbonate) blends[J]. China Plastics, 2015(2): 7. | |
| [15] | 朱斐超, 张宇静, 张 强, 等. 聚乳酸基生物可降解熔喷非织造材料的研究进展与展望[J]. 纺织学报, 2022, 43(1): 49⁃57. |
| ZHU F C, ZHANG Y J, ZHANG Q, et al. Research progress and prospects of biodegradable poly(lactic acid)⁃based nonwoven materials for meltblown applications[J]. Journal of Textile Research, 2022, 43(1): 49⁃57. | |
| [16] | 王镕琛,张 恒,孙焕惟,等.医疗卫生用聚乳酸非织造材料的制备及其亲水改性研究进展[J].中国塑料, 2022, 36(5):158⁃166. |
| WANG R C, ZHANG H, SUN H Y, et al. Research progress on preparation and hydrophilic modification of poly(lactic acid) nonwoven materials for medical and healthcare applications[J]. China Plastics, 2022, 36(5): 158⁃166. | |
| [17] | 张莉彦,侯钦正,徐锦龙,等.熔体微分静电纺热塑性聚氨酯防水透湿透气超细纤维膜的制备及其性能研究[J].毛纺科技, 2022, 50(12):1⁃10. |
| ZHANG L Y, HOU Q Z, XU J L, et al. Preparation and performance study of thermoplastic polyurethane waterproof, breathable and moisture⁃permeable ultrafine fiber membrane by melt differential electrospinning[J]. Textile Science and Technology, 2022, 50(12): 1⁃10. | |
| [18] | Wu Y, Xia C, Cai L, et al. Water⁃resistant hemp fiber⁃reinforced composites: In⁃situ surface protection by polyethylene film[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2018, 112: 210⁃216. |
| [19] | 赵 博.PP/PE医用淋膜非织造布的制备及性能研究[J].合成纤维工业, 2022, 45(6):29⁃32. |
| ZHAO B. Preparation and performance study of PP/PE medical laminated nonwoven fabric[J]. Synthetic Fibre Industry, 2022, 45(6): 29⁃32. | |
| [20] | 盖景刚, 李惠林, 胡国华. 超高分子量聚乙烯二元共混物降粘机理研究[J]. 2009 年全国高分子学术论文报告会论文摘要集 (上册), 2009. |
| GAI J G, LI H L, HU G H. Research on the viscosity reduction mechanism of ultra⁃high molecular weight polyethylene binary blend[J]. Abstracts of Papers from the 2009 National Polymer Academic Conference (Volume 1), 2009. | |
| [21] | Nayak R, Kyratzis I L, Truong Y B, et al. Melt⁃electrospinning of polypropylene with conductive additives[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2012, 47: 6 387⁃6 396. |
| [22] | Li Y, He H, Ma Y, et al. Rheological and mechanical properties of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene/high density polyethy⁃lene/polyethylene glycol blends[J]. Advanced Industrial and Engineering Polymer Research, 2019, 2(1): 51⁃60. |
| [23] | 徐兴家,甄卫军,赵 玲.超临界CO2发泡制备聚氯乙烯微孔材料研究进展[J].中国塑料, 2019, 33(7):117⁃129. |
| XU X J, ZHEN W J, ZHAO L. Research progress on preparation of polyvinyl chloride micro⁃porous materials by supercritical CO2 foaming[J]. China Plastics, 2019, 33(7): 117⁃129. | |
| [24] | 万 辰. 超临界CO2环境下聚乙烯的流变特性及其影响发泡行为的作用机制[D]. 上海, 2017. |
| [25] | Areerat S, Nagata T, Ohshima M. Measurement and prediction of PE⁃LD/CO2 solution viscosity[J]. Polymer Engineering & Science, 2002, 42(11): 2 234⁃2 245. |
| [26] | Ibarra⁃Garza C M, Treviño⁃Quintanilla C D, Bonilla⁃Ríos J. Estimation of the effects of CO2 and temperature on the swelling of PS⁃CO2 mixtures at supercritical conditions on rheological testing[J]. Polymers, 2022, 14(17): 3 490. |
| [27] | 崔文豪,顾瑞星,米皓阳.超临界二氧化碳流场作用下线型聚乙烯剪切塑化行为的分子动力学模拟研究[J].高分子学报, 2024, 55(10): 1 414⁃1 429. |
| CUI W H, GU R X, MI H Y. Molecular dynamics simulation study on shear plasticization behavior of linear polyethylene under supercritical carbon dioxide flow field[J]. Acta Polymerologica Sinica, 2024, 55(10): 1 414⁃1 429. | |
| [28] | 陈明钟, 杨卫民, 李好义, 等. 基于超临界 CO2 制备熔体微分静电纺聚丙烯纤维[J]. 中国塑料, 2016, 30(6): 70⁃73. |
| CHEN M Z, YANG W M, LI H Y, et al. Preparation of melt differential electrospun polypropylene fibers based on supercritical CO2 [J]. China Plastics, 2016, 30(6): 70⁃73. | |
| [29] | 张淑苹, 康卫民, 程博闻, 等. 熔喷非织造过滤材料驻极技术研究进展[J]. 毛纺科技, 2022, 50(5): 117⁃125. |
| ZHANG S P, KANG W M, CHENG B W, et al. Research progress on electrification technology for meltblown nonwoven filter materials[J]. Textile Science and Technology, 2022, 50(5): 117⁃125. |
| [1] | 王硕, 袁文博, 陈弋翀, 臧云涛, 冷栋梁, 李海艳, 赵玲, 胡冬冬. 支化结构聚丙烯的超临界CO2模压发泡及其力学性能[J]. 中国塑料, 2025, 39(9): 1-6. |
| [2] | 林明华, 王华, 郭建兵, 郑斌, 王瑶. 环氧大豆油/桐油酸酐协同增韧聚乳酸⁃木质素复合材料[J]. 中国塑料, 2025, 39(9): 38-43. |
| [3] | 郑世伦, 周启伟, 刘斌, 梁旭之, 袁明园. 超支化聚酯改性碳纳米管/水性不饱和聚酯复合材料的结构与性能研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2025, 39(9): 63-67. |
| [4] | 闵家璇, 江学良, 游峰, 陆刚. PPC/PHBV共混材料的力学及热学性能研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2025, 39(8): 6-11. |
| [5] | 刘霖, 寿韬, 廖飞扬, 郑梓康, 冯馨禾, 赵秀英. 高韧性生物基聚乳酸/聚氨酯共混物的制备及性能研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2025, 39(7): 1-5. |
| [6] | 王政, 肖东, 黄锐, 孙孝谦. 废弃塑料颗粒含量对混凝土力学性能的影响[J]. 中国塑料, 2025, 39(7): 130-134. |
| [7] | 王文昊, 仇思源, 李亚娇, 孙靖尧, 吴大鸣, 王树远, 许红, 盖云卿. 基于渐进失效模型的RTP管力学性能分析[J]. 中国塑料, 2025, 39(7): 44-48. |
| [8] | 宁丁怡, 赵恬娇, 董亚鹏, 王美珍, 郝新宇, 王波. 共混改性调控聚乳酸结晶及力学性能的研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2025, 39(6): 126-132. |
| [9] | 朱奎霖, 吕冲, 郭雷, 陈艺琳, 黄易峰, 赵培琦, 江学良, 游峰. 氧化铈改性聚丙烯复合材料的介电及力学性能研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2025, 39(6): 19-23. |
| [10] | 甄琪, 秦子轩, 张恒, 崔景强, 王国锋, 程文胜, 李晗. 医疗包装用聚乳酸熔喷超细纤维材料的退火工艺研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2025, 39(6): 24-30. |
| [11] | 周琦, 李全, 李雅静, 刘新安, 谷新春, 黄守莹. PPC与PLA共混物的流变学及力学性能研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2025, 39(6): 31-35. |
| [12] | 金裕程, 王璟璠, 赵世成. PE⁃LD的添加对双峰聚乙烯抗熔垂性能的影响[J]. 中国塑料, 2025, 39(6): 6-9. |
| [13] | 马海龙, 代明欣. 废旧塑料骨料在水泥混凝土中的应用研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2025, 39(6): 89-99. |
| [14] | 刘文龙, 周翔, 楼爽, 马秀清, 李好义, 李长金, 杨卫民. 熔喷纤维细化机理及影响因素研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2025, 39(5): 118-122. |
| [15] | 李长金, 刘文龙, 杨卫民, 郭子芳, 李好义. 静电喷纺低密度聚乙烯超细纤维及其性能[J]. 中国塑料, 2025, 39(5): 25-29. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2
京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2