 京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2
京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2
《中国塑料》编辑部 ©2008-2024 版权所有
地址:北京市海淀区阜成路11号 邮编:100048
编辑部:010-68985541 联系信箱:cp@plaschina.com.cn
广告部/发行部:010-68985253 本系统由北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司设计开发

中国塑料 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (10): 54-59.DOI: 10.19491/j.issn.1001-9278.2025.10.010
收稿日期:2024-11-15
出版日期:2025-10-26
发布日期:2025-10-21
作者简介:刘中平(1982-),男,工程师,研究方向为机车车辆部件防火和材料失效分析,liuzp3@csrzic.com
LIU Zhongping( ), XIAO Yinhe, GE Huijun
), XIAO Yinhe, GE Huijun
Received:2024-11-15
Online:2025-10-26
Published:2025-10-21
摘要:
安装于某设备上的连接器组件,在运行过程中连接器母座螺纹管处出现脆性断裂。为了分析断裂的原因和机理,通过差示扫描量热分析、热失重分析、气相色谱⁃质谱分析和傅里叶变换红外光谱分析等方法对比分析断裂样品和运行正常的未断裂样品。结果表明,断裂样品存在可挥发的邻苯二甲酸二丁酯(DBP)成分,而未断裂样品则无此成分;进一步分析,该DBP成分来源于断裂样品通孔内安装的软质聚氯乙烯(PVC)套管。从Hansen溶度参数的角度分析,DBP与聚碳酸酯(PC)的相对能量差异(RED)值为0.72,说明DBP能够较好的溶解PC,即DBP能够侵蚀连接器母座。因此,连接器的断裂机理是环境应力开裂(ESC),连接器受到了PVC套管中的DBP污染,DBP渗透到螺纹处PC塑料内,消弱了PC分子间作用力,在锁紧螺母的拉伸应力作用下,导致由内向外的脆性开裂。
中图分类号:
刘中平, 肖银河, 葛会军. 软质PVC引发的PC塑料件开裂分析[J]. 中国塑料, 2025, 39(10): 54-59.
LIU Zhongping, XIAO Yinhe, GE Huijun. Cracking analysis of PC component initiated by plasticized PVC[J]. China Plastics, 2025, 39(10): 54-59.
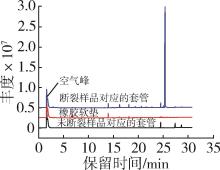
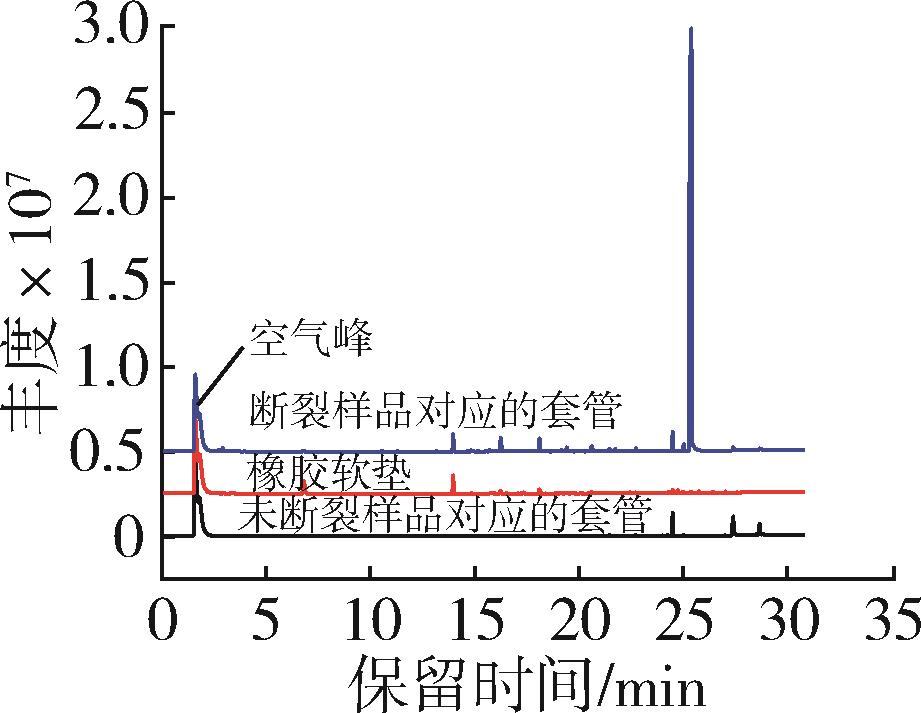
| 材料 | δD/MPa1/2 | δP/MPa1/2 | δH/MPa1/2 | Ro/MPa1/2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC | 18.1 | 5.9 | 6.9 | 5.5 |
| PA66 | 16 | 11 | 24 | 3 |
| DBP | 17.8 | 8.6 | 4.1 |
| 材料 | δD/MPa1/2 | δP/MPa1/2 | δH/MPa1/2 | Ro/MPa1/2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC | 18.1 | 5.9 | 6.9 | 5.5 |
| PA66 | 16 | 11 | 24 | 3 |
| DBP | 17.8 | 8.6 | 4.1 |
| 材料组合 | Ra/MPa1/2 | RED |
|---|---|---|
| PC⁃DBP | 3.94 | 0.72 |
| PA66⁃DBP | 20.36 | 6.79 |
| 材料组合 | Ra/MPa1/2 | RED |
|---|---|---|
| PC⁃DBP | 3.94 | 0.72 |
| PA66⁃DBP | 20.36 | 6.79 |
| [1] | Al⁃Saidi Lutfi F, Mortensen Kell, Almdal Kristoffer. Environment stress cracking resistance. Behaviour of polycarbonate in different chemicals by determination of the time⁃dependence of stress at constant strains [J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2003, 82(3): 451⁃461. |
| [2] | 何 洋,李洋洋,邵景昌,等. PC制件内应力表征及内应力开裂因素与改善措施分析[J]. 中国塑料,2019, 33(7): 63⁃68. |
| HE Y, LI Y Y, SHAO J C, et al. Characterization, analysis and improvement of internal stress cracks of PC[J]. China Plastics, 2019, 33(7):63⁃68. | |
| [3] | 江盛玲,华幼卿. 聚碳酸酯耐环境应力开裂性能的研究[J]. 塑料工业,2011, 39(5): 82⁃85+112. |
| JIANG S L, HUA Y Q. Study on environmental stress crack resistance property of polycarbonate[J]. China Plastics Industry, 2011, 39(5): 82⁃85+112. | |
| [4] | Mônica Martiniano Ferreira,Vanessa de Freitas Cunha Lins. Failure in automobile headlight lenses [J]. Engineering Failure analysis, 2019, 104: 844⁃855. |
| [5] | 周 啸,何向明. 聚合物性能与结构[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社,2015: 71⁃84. |
| [6] | Khalid Yasir, Achour Amine, Muhammad Aftab Akram,et al. Polycarbonate/titania composites incorporating TiO2 with different nanoscale morphologies for enhanced environmental stess cracking resistance in dioctyl phthalate [J]. Polymers, 2022, 14(17): 3 693. |
| [7] | Bok Nam Jang, Charles A, Wilkie A.TG/FTIR and mass spectral study on the thermal degradation of bisphenol a polycarbonate[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2004, 86(3), 419⁃430. |
| [8] | 高 欢,卫碧文,付 饶,等. 气相色谱⁃质谱法测定欧盟REACH法规相关的15种邻苯二甲酸酯的含量[J]. 化学研究与应用, 2021, 33(11): 2 262⁃2 268. |
| GAO H, WEI B W, FU R, et al. Determination of 15 phthalate esters restricted by EU REACH by GC⁃MS [J]. Chemical Research and Application, 2021, 33(11): 2 262⁃2 268. | |
| [9] | 樊小军,刘晓暄,崔艳艳. 气相色谱⁃质谱法测定玩具中邻苯二甲酸酯增塑剂[J]. 理化检验⁃化学检测, 2013, 49(4): 432⁃438. |
| FAN X J, LIU X X, CUI Y Y. GC⁃MS determination of phthalates added as plasticizers in toys [J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis(Part B: Chemical Analysis), 2013, 49(4): 432⁃438. | |
| [10] | Shen Hao⁃Yu, Jiang Hai⁃Liang, Mao Hong⁃Lei, et al. Simultaneous determination of seven phthalates and four parabens in cosmetic products using HPLC⁃DAD and GC⁃MS methods[J]. Journal of Separation Science, 2007, 30(1): 48⁃54. |
| [11] | Raman Arun, Farris Richard J, Lesser Alan J. Effect of stress state and polymer morphology on environmental stress cracking in polycarbonate[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2003, 88(2):550⁃564. |
| [12] | Jansen Jeffrey A. Environmental stress cracking⁃the plastic killer[J]. Advanced Materials & Processes, 2004, 162(6): 50⁃53. |
| [13] | Alperstein David, Knani Dafna, Borchmann Nikolai, et al. Prediction of environmental stress cracking in polycarbonate by molecular modeling[J]. Polymer for Advanced Technologies, 2014, 25(12): 1 433⁃1 438. |
| [14] | Hansen Charles M. On predicting environmental stress cracking in polymers[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2002, 77(1): 43⁃53. |
| [15] | Charles M, Hansen, Just Lisbeth. Prediction of environmental stress cracking in plastics with Hansen solubility parameters[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2001, 40(1):21⁃25. |
| [16] | Hildebrand Joel H, Scott Robert L. The solubility of nonelectrolytes[M]. 3rd ed. New York: Reinhold Publishing Corporation, 1950: Charpter VII. |
| [17] | Charles M. Hansen. Hansen solubility parameters⁃a user’s handbook[M]. 2nded. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2007. |
| [18] | 卢家荣,吴水珠,赵建青,等. PC/PA6共混体系的耐溶剂性及其结晶行为的研究[J]. 塑料工业, 2008, 36(10): 9⁃12+19. |
| LU J R, WU S Z, ZHAO J Q, et al. Study of solvent resistance and crystallization behavior of PC/PA6[J]. China Plastics Industry, 2008, 36(10): 9⁃12+19. | |
| [19] | 钱志国,尹继磊,李正梅,等. 耐化学高抗冲PC/PBT合金的制备[J]. 工程塑料应用, 2016, 44(1): 49⁃52. |
| QIAN Z G, YIN J L, LI Z M, et al. Preparation of chemical resistant and high impact PC/PBT alloys[J]. Engineering Plastics Application, 2016, 44(1): 49⁃52. |
| [1] | 李伟, 唐鹏飞, 潘栋, 石拓, 莫淑蓓. 多口径高性能聚氯乙烯管道爆管试验与压力计算[J]. 中国塑料, 2025, 39(9): 93-100. |
| [2] | 张宁, 李先铭, 李改花, 张红霞, 杨笑春, 于静. 不同种类偶联剂表面改性水滑石对PVC性能的影响[J]. 中国塑料, 2025, 39(8): 88-93. |
| [3] | 王政, 肖东, 黄锐, 孙孝谦. 废弃塑料颗粒含量对混凝土力学性能的影响[J]. 中国塑料, 2025, 39(7): 130-134. |
| [4] | 牛众, 吴遵红. 羽毛球场地用PVC地胶面层材料的改性研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2025, 39(6): 66-72. |
| [5] | 张辉, 唐站站, 鲍海霞, 程鑫远, 陈斌. 不同环境温度下UPVC管材的力学性能退化研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2025, 39(2): 26-31. |
| [6] | 杨笑春, 刘会媛, 张青, 于静. 钠⁃A型分子筛对PVC热稳定性能影响研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2025, 39(2): 77-81. |
| [7] | 李鑫宇, 陆书来, 王立伟, 许超, 牛经鹏, 马晓坤. PC/ABS合金专用改性ABS的研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2025, 39(10): 33-38. |
| [8] | 高挺, 彭强, 马秀清. 聚碳酸酯增韧改性研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2025, 39(1): 37-43. |
| [9] | 陈明光, 李梦迪, 郁辰, 曹鸿璋, 于晓丽, 柳召刚, 罗果萍. 富马酸季戊四醇酯基镧稀土化合物的制备及其在PVC中热稳定性能和抗菌性能的研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2025, 39(1): 6-12. |
| [10] | 施珣若. 聚氯乙烯塑料建材的现状和展望[J]. 中国塑料, 2024, 38(9): 145-153. |
| [11] | 孙芳芳, 宋运运. N⁃苯基马来酰亚胺共聚物的合成及对PVC树脂耐热改性效果研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2024, 38(7): 49-54. |
| [12] | 蒋琴瑶, 贾雨耀, 杨绍哲, 吴蓉, 白威, 孙腾. 改性聚碳酸酯耐高温性能研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2024, 38(6): 125-131. |
| [13] | 雷经发, 胡基波, 刘涛, 吴文奇, 沈朝阳. PVC/TPU共混材料静动态力学性能及本构模型研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2024, 38(5): 1-6. |
| [14] | 蓝擎, 侯欣怡, 李一凡, 潘凯, 周佳菊, 黄丹梦, 黄灏彬. 重质碳酸钙聚合改性及其在聚氯乙烯中的应用研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2024, 38(5): 61-65. |
| [15] | 张俊, 奚望, 钱立军, 周凤帅, 邱勇, 王靖宇, 张志鹏. 氮化硼/磷杂菲三嗪化合物阻燃导热聚碳酸酯复合材料的制备及其性能研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2024, 38(3): 31-37. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2
京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2