 京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2
京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2
《中国塑料》编辑部 ©2008-2024 版权所有
地址:北京市海淀区阜成路11号 邮编:100048
编辑部:010-68985541 联系信箱:cp@plaschina.com.cn
广告部/发行部:010-68985253 本系统由北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司设计开发

中国塑料 ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (12): 142-154.DOI: 10.19491/j.issn.1001-9278.2022.12.020
曹宁1, 李凯1, 王志彦2, 李建华2( ), 王亚涛2, 陈曦2, 贾伟艺2, 刘洋1(
), 王亚涛2, 陈曦2, 贾伟艺2, 刘洋1( ), 汪晓东3, 连慧琴1, 崔秀国1
), 汪晓东3, 连慧琴1, 崔秀国1
收稿日期:2022-09-27
出版日期:2022-12-26
发布日期:2022-12-20
通讯作者:
李建华(1982—),男,正高级工程师,主要从事化工新材料研发与管理工作,ecljh@kailuan.com.cn基金资助:
CAO Ning1, LI Kai1, WANG Zhiyan2, LI Jianhua2( ), WANG Yatao2, CHEN Xi2, JIA Weiyi2, LIU Yang1(
), WANG Yatao2, CHEN Xi2, JIA Weiyi2, LIU Yang1( ), WANG Xiaodong3, LIAN Huiqin1, CUI Xiuguo1
), WANG Xiaodong3, LIAN Huiqin1, CUI Xiuguo1
Received:2022-09-27
Online:2022-12-26
Published:2022-12-20
Contact:
LI Jianhua, LIU Yang
E-mail:ecljh@kailuan.com.cn;yang.liu@bipt.edu.cn
摘要:
综述了质子交换膜纳米复合材料用于甲醇燃料电池的最新研究进展,全面阐述了纳米复合材料的形貌、结构对材料甲醇透过性、质子导电性等物理化学性能的影响,并展望了甲醇燃料电池质子交换膜复合材料的发展前景。
中图分类号:
曹宁, 李凯, 王志彦, 李建华, 王亚涛, 陈曦, 贾伟艺, 刘洋, 汪晓东, 连慧琴, 崔秀国. 阻醇燃料电池质子交换纳米复合膜研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(12): 142-154.
CAO Ning, LI Kai, WANG Zhiyan, LI Jianhua, WANG Yatao, CHEN Xi, JIA Weiyi, LIU Yang, WANG Xiaodong, LIAN Huiqin, CUI Xiuguo. Progress in proton⁃exchange nanocomposite films for alcohol⁃resistant fuel cells[J]. China Plastics, 2022, 36(12): 142-154.
| 质子交换膜 | 质子电导率/S·cm-1 | 甲醇渗透率/×10-7·cm2·s-1 | 吸水率/% | 离子交换容量/meq·g-1 | 拉伸强度/MPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPES/SiO2[ | 0.04(100 ℃) | 1.06 | 27.75 | - | - |
| SPEEK/SiO2⁃SiWA[ | 0.069 6 | 6.55 | - | - | - |
| SPSF/Nano⁃ZrO2[ | 0.077(30 ℃) | 11 | 72.0(30 ℃) | - | - |
| SPSF/Nano⁃TiO2[ | 0.072(30 ℃) | 11 | 71.6(30 ℃) | - | - |
| SPEEK/s⁃Fu[ | 0.0646(30 ℃) 0.0826(60 ℃) | 1.73(30 ℃) 2.23(60 ℃) | - | 1.68 | 14.2 |
| BSPAEKS/ s⁃Fu [ | 0.332(80 ℃) | 7.5 | 45.2(25 ℃) 52.7(80 ℃) | 1.81 | 14.4 |
| SPEEK/sul⁃MIL101(Cr)[ | 0.075(30 ℃) 0.22(75 ℃) | 7.38 | 30.8 | - | - |
| SPSF/AA⁃MOF[ | 0.212(80 ℃) | 5.8 | 16.7(20 ℃) 24.9(80 ℃) | - | - |
| SPEEK/sCNTs[ | 0.043 1 | 1.689 | 43.85 | 2.19 | 54.59 |
| SPEEK/SiO2⁃CNTs[ | 0.051 9 | 0.422 | - | - | - |
| Nafion/PVDF nanofibers[ | 0.073(20 ℃) | 14.8 | - | - | - |
| Nafion/PAN⁃ZrO2 nanofibers[ | 1.84 | 0.55 | 35(30 ℃) 40(60 ℃) 49(80 ℃) | 1.4 | - |
| SPEN/SGO/NGO[ | 0.064 | 1.43 | 50.5(80 ℃) | 1.67 | 62.02 |
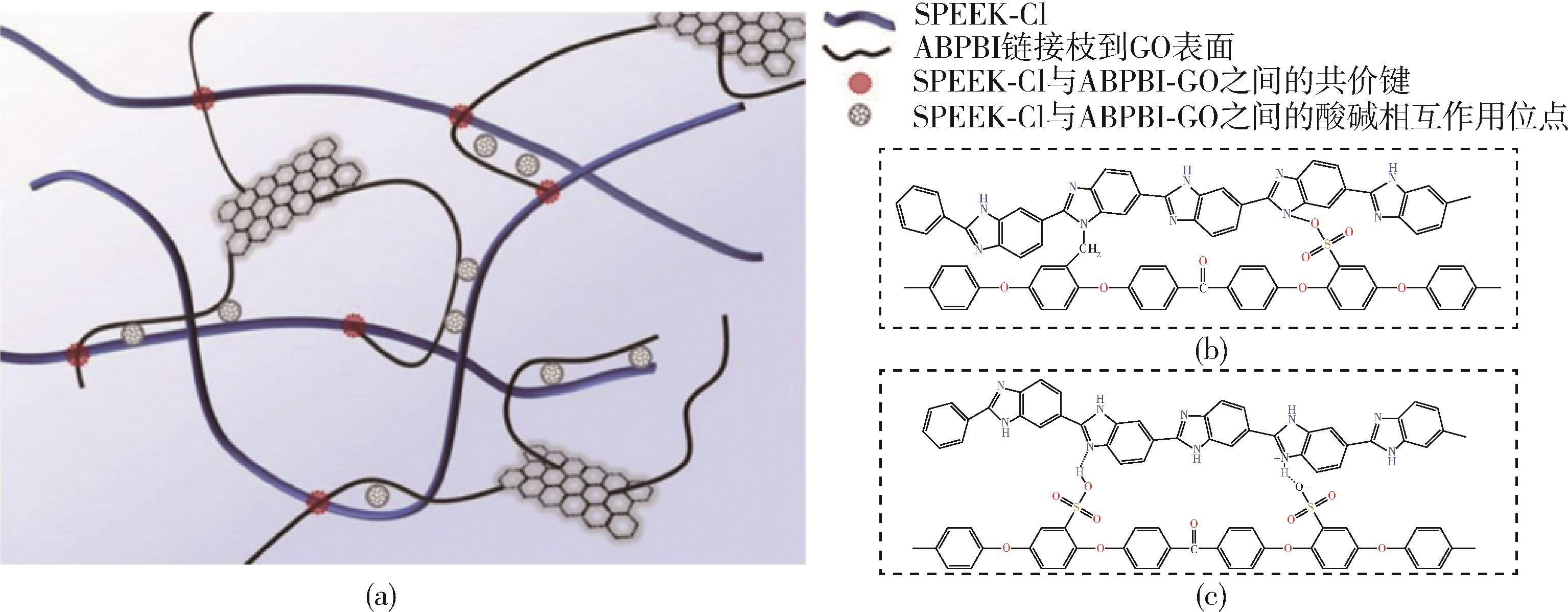
| C⁃SPEEK/ABPBI⁃GO[ | 0.185 3 | 12 | 40.3(60 ℃) | 1.96(25 ℃) | 133.6 |
| CS/E⁃MoS2[ | 0.003 6(80 ℃) | 0.328 | 25.7 | 0.51 | 74 |
| SPEEK/clay⁃SO3H[ | 0.059 5(25 ℃) 0.132(80 ℃) | 9.64 | 39.14(25 ℃) 52.78(80 ℃) | - | 43.3 |
| Nafion/CS⁃CNTs[ | 0.104 | 2.03(25 ℃) | 37.1 | 0.91 | - |
| PES/γ⁃Fe2O3[ | 0.145 | - | 28.1 | 1.59 | - |
| SPES/S⁃MoS2[ | 6.22(80 ℃) | 0.305 | 25.1(80 ℃) | 2.98 | 50.3 |
| 质子交换膜 | 质子电导率/S·cm-1 | 甲醇渗透率/×10-7·cm2·s-1 | 吸水率/% | 离子交换容量/meq·g-1 | 拉伸强度/MPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPES/SiO2[ | 0.04(100 ℃) | 1.06 | 27.75 | - | - |
| SPEEK/SiO2⁃SiWA[ | 0.069 6 | 6.55 | - | - | - |
| SPSF/Nano⁃ZrO2[ | 0.077(30 ℃) | 11 | 72.0(30 ℃) | - | - |
| SPSF/Nano⁃TiO2[ | 0.072(30 ℃) | 11 | 71.6(30 ℃) | - | - |
| SPEEK/s⁃Fu[ | 0.0646(30 ℃) 0.0826(60 ℃) | 1.73(30 ℃) 2.23(60 ℃) | - | 1.68 | 14.2 |
| BSPAEKS/ s⁃Fu [ | 0.332(80 ℃) | 7.5 | 45.2(25 ℃) 52.7(80 ℃) | 1.81 | 14.4 |
| SPEEK/sul⁃MIL101(Cr)[ | 0.075(30 ℃) 0.22(75 ℃) | 7.38 | 30.8 | - | - |
| SPSF/AA⁃MOF[ | 0.212(80 ℃) | 5.8 | 16.7(20 ℃) 24.9(80 ℃) | - | - |
| SPEEK/sCNTs[ | 0.043 1 | 1.689 | 43.85 | 2.19 | 54.59 |
| SPEEK/SiO2⁃CNTs[ | 0.051 9 | 0.422 | - | - | - |
| Nafion/PVDF nanofibers[ | 0.073(20 ℃) | 14.8 | - | - | - |
| Nafion/PAN⁃ZrO2 nanofibers[ | 1.84 | 0.55 | 35(30 ℃) 40(60 ℃) 49(80 ℃) | 1.4 | - |
| SPEN/SGO/NGO[ | 0.064 | 1.43 | 50.5(80 ℃) | 1.67 | 62.02 |
| C⁃SPEEK/ABPBI⁃GO[ | 0.185 3 | 12 | 40.3(60 ℃) | 1.96(25 ℃) | 133.6 |
| CS/E⁃MoS2[ | 0.003 6(80 ℃) | 0.328 | 25.7 | 0.51 | 74 |
| SPEEK/clay⁃SO3H[ | 0.059 5(25 ℃) 0.132(80 ℃) | 9.64 | 39.14(25 ℃) 52.78(80 ℃) | - | 43.3 |
| Nafion/CS⁃CNTs[ | 0.104 | 2.03(25 ℃) | 37.1 | 0.91 | - |
| PES/γ⁃Fe2O3[ | 0.145 | - | 28.1 | 1.59 | - |
| SPES/S⁃MoS2[ | 6.22(80 ℃) | 0.305 | 25.1(80 ℃) | 2.98 | 50.3 |
| 1 | Ilbeygi H, Ghasemi M, Emadzadeh D, et al. Power generation and wastewater treatment using a novel SPEEK nanocomposite membrane in a dual chamber microbial fuel cell[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40(1): 477⁃487. |
| 2 | Kamarudin S K, Achmad F, Daud W R W. Overview on the application of direct methanol fuel cell (DMFC) for portable electronic devices[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2009, 34(16): 6 902⁃6 916. |
| 3 | Roy A, Hickner M A, Einsla B R, et al. Synthesis and characterization of partially disulfonated hydroquinone⁃based poly(arylene ether sulfone)s random copolymers for application as proton exchange membranes[J]. Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry, 2009, 47(2): 384⁃391. |
| 4 | Felix C, Jao T⁃C, Pasupathi S, et al. Optimisation of electrophoretic deposition parameters for gas diffusion electrodes in high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2013, 243: 40⁃47. |
| 5 | Branco C M, Sharma S, De Camargo Forte M M, et al. New approaches towards novel composite and multilayer membranes for intermediate temperature⁃polymer electrolyte fuel cells and direct methanol fuel cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 316: 139⁃159. |
| 6 | Neelakandan S, Kanagaraj P, Sabarathinam R M, et al. Polypyrrole layered SPEES/TPA proton exchange membrane for direct methanol fuel cells[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2015, 359: 272⁃279. |
| 7 | Gittleman C S, Kongkanand A, Masten D, et al. Materials research and development focus areas for low cost automotive proton⁃exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry, 2019, 18: 81⁃89. |
| 8 | Goor M, Menkin S, Peled E. High power direct methanol fuel cell for mobility and portable applications[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(5): 3 138⁃3 143. |
| 9 | Lopez⁃Haro M, Guetaz L, Printemps T, et al. Three⁃dimensional analysis of Nafion layers in fuel cell electrodes[J]. Nat Commun, 2014, 5: 5 229. |
| 10 | Modestino M A, Kusoglu A, Hexemer A, et al. Controlling nafion structure and properties via wetting interactions[J]. Macromolecules, 2012, 45(11): 4 681⁃4 688. |
| 11 | Patel H A, Mansor N, Gadipelli S, et al. Superacidity in Nafion/MOF hybrid membranes retains water at low humidity to enhance proton conduction for fuel cells[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2016, 8(45): 30 687⁃30 691. |
| 12 | Junoh H, Jaafar J, Nordin N, et al. Performance of polymer electrolyte membrane for direct methanol fuel cell application: perspective on morphological structure[J]. Membranes (Basel), 2020, 10(3). |
| 13 | Hosseinpour M, Sahoo M, Perez⁃Page M, et al. Improving the performance of direct methanol fuel cells by implementing multilayer membranes blended with cellulose nanocrystals[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(57): 30 409⁃30 419. |
| 14 | Tsai J⁃C, Lin C⁃K, Kuo J⁃F, et al. Preparation and properties of crosslinked sulphonated poly(arylene ether sulphone) blend s for direct methanol fuel cell applications[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2010, 195(13): 4 072⁃4 079. |
| 15 | Sun X, Simonsen S C, Norby T, et al. Composite membranes for high temperature PEM fuel cells and electrolysers: a critical review[J]. Membranes (Basel), 2019, 9(7). |
| 16 | Sun P, Li Z, Wang S, et al. Performance enhancement of polybenzimidazole based high temperature proton exchange membranes with multifunctional crosslinker and highly sulfonated polyaniline[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018, 549: 660⁃669. |
| 17 | Tripathi B P, Shahi V K. Organic–inorganic nanocomposite polymer electrolyte membranes for fuel cell applications[J]. Progress in Polymer Science, 2011, 36(7): 945⁃979. |
| 18 | Ahmed M, Dincer I. A review on methanol crossover in direct methanol fuel cells: challenges and achievements[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2011, 35(14): 1 213⁃1 228. |
| 19 | Xu M, Xue H, Wang Q, et al. Sulfonated poly(arylene ether)s based proton exchange membranes for fuel cells[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(62): 31 727⁃31 753. |
| 20 | Kim D⁃J, Hwang H⁃Y, Jung S⁃B, et al. Sulfonated poly(arylene ether sulfone)/Laponite⁃SO3H composite membrane for direct methanol fuel cell[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2012, 18(1): 556⁃562. |
| 21 | Wang Z, Ni H, Zhao C, et al. Investigation of sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone sulfone)/heteropolyacid composite membranes for high temperature fuel cell applications[J]. Journal of Polymer Science Part B: Polymer Physics, 2006, 44(14): 1 967⁃1 978. |
| 22 | Liu K⁃L, Lee H⁃C, Wang B⁃Y, et al. Sulfonated poly(styrene⁃ block ⁃(ethylene⁃ ran ⁃butylene)⁃ block ⁃styrene (SSEBS)⁃zirconium phosphate (ZrP) composite membranes for direct methanol fuel cells[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2015, 495: 110⁃120. |
| 23 | Chen B, Li G, Wang L, et al. Proton conductivity and fuel cell performance of organic⁃inorganic hybrid membrane based on poly(methyl methacrylate)/silica[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2013, 38(19): 7 913⁃7 923. |
| 24 | Wen S, Gong C, Tsen W⁃C, et al. Sulfonated poly(ether sulfone)/silica composite membranes for direct methanol fuel cells[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2009. |
| 25 | Yan Chia M, San Thiam H, Kong Leong L, et al. Effect of coupling agents on the transport properties of sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone) based composite membrane[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2019, 268(1). |
| 26 | Neelakandan S, K N J, Kanagaraj P, et al. Effect of sulfonated graphene oxide on the performance enhancement of acid–base composite membranes for direct methanol fuel cells[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(57): 51 599⁃51 608. |
| 27 | Wu H, Cao Y, Shen X, et al. Preparation and performance of different amino acids functionalized titania⁃embedded sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone) hybrid membranes for direct methanol fuel cells[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2014, 463: 134⁃144. |
| 28 | Li J, Zhang Y, Wang L. Preparation and characterization of sulfonated polyimide/TiO2 composite membrane for vanadium redox flow battery[J]. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2013, 18(3): 729⁃737. |
| 29 | Lee W, Gil S C, Kim H, et al. Partially sulfonated poly(arylene ether sulfone)/organically modified metal oxide nanoparticle composite membranes for proton exchange membrane for direct methanol fuel cell[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2016, 129: 101⁃107. |
| 30 | Rambabu G, Bhat S D. Sulfonated fullerene in SPEEK matrix and its impact on the membrane electrolyte properties in direct methanol fuel cells[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2015, 176: 657⁃669. |
| 31 | Neelakandan S, Liu D, Wang L, et al. Highly branched poly(arylene ether)/surface functionalized fullerene‐based composite membrane electrolyte for DMFC applications[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2019, 43(8): 3 756⁃3 767. |
| 32 | Li Z, He G, Zhao Y, et al. Enhanced proton conductivity of proton exchange membranes by incorporating sulfonated metal⁃organic frameworks[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 262: 372⁃379. |
| 33 | Sun H, Tang B, Wu P. Two⁃dimensional zeolitic imidazolate framework/carbon nanotube hybrid networks modified proton exchange membranes for improving transport properties[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2017, 9(40): 35 075⁃35 085. |
| 34 | Wang S, Luo H, Li X, et al. Amino acid⁃functionalized metal organic framework with excellent proton conductivity for proton exchange membranes[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(1): 1 163⁃1 173. |
| 35 | Gahlot S, Kulshrestha V. Dramatic improvement in water retention and proton conductivity in electrically aligned functionalized CNT/SPEEK nanohybrid PEM[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2015, 7(1): 264⁃272. |
| 36 | Cui L, Geng Q, Gong C, et al. Novel sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone)/silica coated carbon nanotubes high⁃performance composite membranes for direct methanol fuel cell[J]. Polymers for Advanced Technologies, 2015, 26(5): 457⁃464. |
| 37 | Ranjani M, Yoo D J, Gnana Kumar G. Sulfonated Fe3O4@SiO2 nanorods incorporated sPVdF nanocomposite membranes for DMFC applications[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018, 555: 497⁃506. |
| 38 | Joo S H, Pak C, Kim E A, et al. Functionalized carbon nanotube⁃poly(arylene sulfone) composite membranes for direct methanol fuel cells with enhanced performance[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2008, 180(1): 63⁃70. |
| 39 | Li Y, Hui J, Kawchuk J, et al. Composite membranes of PVDF nanofibers impregnated with Nafion for increased fuel concentrations in direct methanol fuel cells[J]. Fuel Cells, 2019, 19(1): 43⁃50. |
| 40 | Sigwadi R, Mokrani T, Dhlamini S, et al. Nafion® reinforced with polyacrylonitrile/ZrO2 nanofibers for direct methanol fuel cell application[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2020, 138(10). |
| 41 | Huang Y, Cheng T, Zhang X, et al. Novel composite proton exchange membrane with long⁃range proton transfer channels constructed by synergistic effect between acid and base functionalized graphene oxide[J]. Polymer, 2018, 149: 305⁃315. |
| 42 | Han J, Kim K, Kim S, et al. Cross⁃linked sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) membranes formed by poly(2,5⁃benzimidazole)⁃grafted graphene oxide as a novel cross⁃linker for direct methanol fuel cell applications[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 448. |
| 43 | Feng K, Tang B, Wu P. Selective growth of MoS2 for proton exchange membranes with extremely high selectivity[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2013, 5(24): 13 042⁃13 049. |
| 44 | Divya K, Rana D, Alwarappan S, et al. Investigating the usefulness of chitosan based proton exchange membranes tailored with exfoliated molybdenum disulfide nanosheets for clean energy applications[J]. Carbohydr Polym, 2019, 208: 504⁃512. |
| 45 | Fu T, Cui Z, Zhong S, et al. Sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone)/clay⁃SO3H hybrid proton exchange membranes for direct methanol fuel cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2008, 185(1): 32⁃39. |
| 46 | Narayanaswamy Venkatesan P, Dharmalingam S. Characterization and performance study of phase inversed sulfonated poly ether ether ketone – silico tungstic composite membrane as an electrolyte for microbial fuel cell applications[J]. Renewable Energy, 2017, 102: 77⁃86. |
| 47 | Mohtar S S, Ismail A F, Matsuura T. Preparation and characterization of SPEEK/MMT⁃STA composite membrane for DMFC application[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2011, 371(1/2): 10⁃19. |
| 48 | Chen C⁃C, Tsi H⁃Y, Tsen W⁃C, et al. PWA/silica doped sulfonated poly(ether sulfone) composite membranes for direct methanol fuel cells[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2012, 123(2): 1 184⁃1 192. |
| 49 | Chia M Y, Thiam H S, Leong L K, et al. Effect of filler content on transport properties of sulfonated polyether ether ketone (SPEEK) composite proton exchange membranes[J]. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2018, 409. |
| 50 | Silva V S, Ruffmann B, Silva H, et al. Proton electrolyte membrane properties and direct methanol fuel cell performance[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2005, 140(1): 34⁃40. |
| 51 | Laberty⁃Robert C, Valle K, Pereira F, et al. Design and properties of functional hybrid organic⁃inorganic membranes for fuel cells[J]. Chem Soc Rev, 2011, 40(2): 961⁃1 005. |
| 52 | Lee D C, Yang H N, Park S H, et al. Self⁃humidifying Pt–graphene/SiO2 composite membrane for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2015, 474: 254⁃262. |
| 53 | Tasaki K, Gasa J, Wang H, et al. Fabrication and characterization of fullerene–Nafion composite membranes[J]. Polymer, 2007, 48(15): 4 438⁃4 448. |
| 54 | Chen H, Han S⁃Y, Liu R⁃H, et al. High conductive, long⁃term durable, anhydrous proton conductive solid⁃state electrolyte based on a metal⁃organic framework impregnated with binary ionic liquids: synthesis, characteristic and effect of anion[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 376: 168⁃176. |
| 55 | Yang F, Huang H, Wang X, et al. Proton conductivities in functionalized UiO-66: tuned properties, thermogravimetry mass, and molecular simulation analyses[J]. Crystal Growth & Design, 2015, 15(12): 5 827⁃5 833. |
| 56 | Ramaswamy P, Wong N E, Shimizu G K. MOFs as proton conductors⁃challenges and opportunities[J]. Chem Soc Rev, 2014, 43(16): 5 913⁃5 932. |
| 57 | Liang X, Zhang F, Feng W, et al. From metal–organic framework (MOF) to MOF–polymer composite membrane: enhancement of low⁃humidity proton conductivity[J]. Chem Sci, 2013, 4(3): 983⁃992. |
| 58 | Furukawa H, Cordova K E, O'keeffe M, et al. The chemistry and applications of metal⁃organic frameworks[J]. Science, 2013, 341(6149): 1230444. |
| 59 | Zhang X⁃H, Tang Q⁃Q, Yang D, et al. Preparation of poly(p⁃styrenesulfonic acid) grafted multi⁃walled carbon nanotubes and their application as a solid⁃acid catalyst[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2011, 126(1/2): 310⁃313. |
| 60 | Zhou W, Xiao J, Chen Y, et al. Sulfonated carbon nanotubes/sulfonated poly(ether sulfone ether ketone ketone) composites for polymer electrolyte membranes[J]. Polymers for Advanced Technologies, 2011, 22(12): 1 747⁃1 752. |
| 61 | Cele N P, Sinha Ray S, Pillai S K, et al. Carbon nanotubes based nafion composite membranes for fuel cell applications[J]. Fuel Cells, 2010. |
| 62 | Hasani⁃Sadrabadi M M, Dashtimoghadam E, Majedi F S, et al. Nafion/chitosan⁃wrapped CNT nanocomposite membrane for high⁃performance direct methanol fuel cells[J]. RSC Advances, 2013, 3(20). |
| 63 | Rambabu G, Bhat S D. Simultaneous tuning of methanol crossover and ionic conductivity of sPEEK membrane electrolyte by incorporation of PSSA functionalized MWCNTs: A comparative study in DMFCs[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 243: 517⁃525. |
| 64 | Hasanabadi N, Ghaffarian S R, Hasani⁃Sadrabadi M M. Magnetic field aligned nanocomposite proton exchange membranes based on sulfonated poly (ether sulfone) and Fe2O3 nanoparticles for direct methanol fuel cell application[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2011, 36(23): 15 323⁃15 332. |
| 65 | Ma C, Zhang W, Zhu Y, et al. Alignment and dispersion of functionalized carbon nanotubes in polymer composites induced by an electric field[J]. Carbon, 2008, 46(4): 706⁃710. |
| 66 | Xu X, Li L, Wang H, et al. Solution blown sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) nanofiber–Nafion composite membranes for proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(7): 4 934⁃4 940. |
| 67 | Wang H, Li X, Zhuang X, et al. Modification of Nafion membrane with biofunctional SiO2 nanofiber for proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 340: 201⁃209. |
| 68 | Wang H, Ma Y, Cheng B, et al. Solution blown biofunctionalized poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanofibers for application in proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2017, 258: 24⁃33. |
| 69 | Zizhou R E, Çay A, Akçakoca Kumbasar E P, et al. Production of poly(vinyl alcohol)/Nafion® nanofibers and their stability assessment for the use in direct methanol fuel cells[J]. Journal of Industrial Textiles, 2019, 50(6): 773⁃793. |
| 70 | Liu G, Tsen W⁃C, Jang S⁃C, et al. Mechanically robust and highly methanol⁃resistant sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone)/poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanofiber composite membranes for direct methanol fuel cells[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2019, 591. |
| 71 | Eda G, Chhowalla M. Chemically derived graphene oxide: towards large⁃area thin⁃film electronics and optoelectronics[J]. Adv Mater, 2010, 22(22): 2 392⁃2 415. |
| 72 | Ye Y⁃S, Tseng C⁃Y, Shen W⁃C, et al. A new graphene⁃modified protic ionic liquid⁃based composite membrane for solid polymer electrolytes[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2011, 21(28). |
| 73 | Feng K, Tang B, Wu P. "Evaporating" graphene oxide sheets (GOSs) for rolled up GOSs and its applications in proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2013, 5(4): 1 481⁃1 488. |
| 74 | Karim M R, Hatakeyama K, Matsui T, et al. Graphene oxide nanosheet with high proton conductivity[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2013, 135(22): 8 097⁃8 100. |
| 75 | Shafiei A, Oprea C, Alfantazi A, et al. In situ monitoring of the effects of hydrogen on Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 structure[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2011, 109(11). |
| 76 | Li J, Xu G, Cai W, et al. Non⁃destructive modification on Nafion membrane via in⁃situ inserting of sheared graphene oxide for direct methanol fuel cell applications[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2018, 282: 362⁃368. |
| 77 | Miao S, Zhang H, Li X, et al. A morphology and property study of composite membranes based on sulfonated polyarylene ether sulfone and adequately sulfonated graphene oxide[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41(1): 331⁃341. |
| 78 | Zhou K, Jiang S, Bao C, et al. Preparation of poly(vinyl alcohol) nanocomposites with molybdenum disulfide (MoS2): structural characteristics and markedly enhanced properties[J]. RSC Advances, 2012, 2(31). |
| 79 | Li J, Zhang Y, Zhang S, et al. Sulfonated polyimide/s⁃MoS2 composite membrane with high proton selectivity and good stability for vanadium redox flow battery[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2015, 490: 179⁃189. |
| 80 | Obianigwe N, Ngene B U. Soil Stabilization for road construction: comparative analysis of a three⁃prong approach[J]. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2018, 413. |
| 81 | Choi Y S, Kim T K, Kim E A, et al. Exfoliated sulfonated poly(arylene ether sulfone)⁃clay nanocomposites[J]. Advanced Materials, 2008, 20(12): 2 341⁃2 344. |
| 82 | Awang N, Jaafar J, Ismail A F, et al. Performance of void⁃free electrospun SPEEK/cloisite as a function of degree of dispersion state on nanocomposite proton exchange membrane for direct methanol fuel cell application[J]. Membranes (Basel), 2019, 9(1). |
| 83 | Charradi K, Ahmed Z, Aranda P, et al. Silica/montmorillonite nanoarchitectures and layered double hydroxide⁃SPEEK based composite membranes for fuel cells applications[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2019, 174: 77⁃85. |
| 84 | Divya K, Rana D, Saraswathi M, et al. Investigation of the versatility of SPES membranes customized with sulfonated molybdenum disulfide nanosheets for DMFC applications[J], 2020, 45(31). |
| 85 | 谢玉洁, 张博鑫, 徐 迪, et al. 燃料电池用新型复合质子交换膜研究进展[J]. 膜科学与技术[J], 2021, 41(04): 177⁃186. |
| XIE Y J, ZHANG B X, XU D, et al. Progress in novel composite proton exchange membrane for fuel cells[J]. Membrane Science and Technology, 2021, 41(04): 177⁃186. |
| [1] | 贾明印, 董贤文, 王佳明, 陈轲. 浸渍方式对纤维增强聚酰胺6复合材料真空袋压成型工艺及性能的影响[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(9): 1-6. |
| [2] | 张林, 夏章川, 何亚东, 信春玲, 王瑞雪, 任峰. 等离子体射流载气流量大小对玻璃纤维改性效果影响的研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(9): 7-15. |
| [3] | 焦志伟, 王克琛, 张杨, 杨卫民. 基于碳纳米涂层沉积滑石粉与炭黑协同填充PVC/ABS复合材料的性能研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(8): 10-15. |
| [4] | 汤小明, 曹宁, 蒋岳航, 王倩, 王志彦, 李建华, 王亚涛, 连慧琴, 汪晓东, 崔秀国. 聚砜类燃料电池质子交换膜研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(8): 146-158. |
| [5] | 喻九阳, 王众浩, 陈琦, 夏亚忠. 基于阀体制造的先进树脂基复合材料性能研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(8): 16-22. |
| [6] | 张陶忠, 陈晓龙, 郝晓宇, 于福家. 滑石、CaCO3、BaSO4填充PP复合材料力学性能及界面相互作用对比[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(8): 36-41. |
| [7] | 曲玉婷, 王立梅, 齐斌. 聚乙二醇对聚乳酸/淀粉纳米晶复合材料性能的影响[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(8): 56-61. |
| [8] | 王倩, 杨康宁, 翟绍雄, 尹立坤, 何少剑, 林俊. 高质子传导率及尺寸稳定性复合质子交换膜制备及性能研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(8): 62-68. |
| [9] | 冯冰涛, 王晓珂, 张信, 孙国华, 汪殿龙, 侯连龙, 马劲松. 连续碳纤维增强热塑性复合材料制备与应用研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(7): 165-173. |
| [10] | 宋银宝, 杨建军, 李传敏. PDMS/SiC功能梯度复合材料性能与制造精度研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(7): 30-36. |
| [11] | 杨小龙, 陈文静, 李永青, 闫晓堃, 王修磊, 谢鹏程, 马秀清. 导电型聚合物/石墨烯复合材料的研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(6): 165-173. |
| [12] | 王轲, 龙春光. PE⁃UHMW/海泡石纤维复合材料的力学性能与摩擦学性能研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(5): 19-23. |
| [13] | 陈胜, 梁颖超, 吴方娟, 方辉, 范新凤, 陈晖, 王永刚. 聚酰胺6/双向经编玻璃纤维复合材料的制备及其界面改性研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(5): 24-28. |
| [14] | 刘文, 师文钊, 刘瑾姝, 陆少锋, 周红娟. 电致形状记忆复合材料研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(4): 175-189. |
| [15] | 阮芳涛, 夏成龙, 张宝根, 曹叶, 刘志, 徐珍珍, 章劲草. 芳纶包覆碳纤维增强环氧树脂的轴向压缩性能研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(4): 19-23. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2
京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2