京ICP备13020181号-2
© 《China Plastics》
© 《China Plastics》

China Plastics ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (5): 66-72.DOI: 10.19491/j.issn.1001-9278.2024.05.012
• Materials and Properties • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Yi1,2,3,4, HUANG Yating1,2,3,4( ), WEI Yongbao1,2,3,4, TANG Wei2,3,4,5, QIAN Lijun2,3,4,5
), WEI Yongbao1,2,3,4, TANG Wei2,3,4,5, QIAN Lijun2,3,4,5
Received:2023-10-12
Online:2024-05-26
Published:2024-05-20
CLC Number:
ZHANG Yi, HUANG Yating, WEI Yongbao, TANG Wei, QIAN Lijun. Study on pyrolysis mechanism of intumescent flame⁃retardant system based on reaction force field[J]. China Plastics, 2024, 38(5): 66-72.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.plaschina.com.cn/EN/10.19491/j.issn.1001-9278.2024.05.012
| T/K | k1(PP)/fs-1 | k2(PP/PAPO⁃MP)/ fs-1 | k3(PP/PAPP/MPP)/ fs-1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 000 | 1.84×10-3 | 7.74×10-4 | 3.82×10-4 |
| 2 500 | 6.57×10-2 | 7.36×10-4 | 4.02×10-4 |
| 3 000 | 8.16×10-2 | 7.12×10-3 | 6.25×10-3 |
| 3 500 | 3.75×10-1 | 4.27×10-2 | 1.88×10-2 |
| T/K | k1(PP)/fs-1 | k2(PP/PAPO⁃MP)/ fs-1 | k3(PP/PAPP/MPP)/ fs-1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 000 | 1.84×10-3 | 7.74×10-4 | 3.82×10-4 |
| 2 500 | 6.57×10-2 | 7.36×10-4 | 4.02×10-4 |
| 3 000 | 8.16×10-2 | 7.12×10-3 | 6.25×10-3 |
| 3 500 | 3.75×10-1 | 4.27×10-2 | 1.88×10-2 |
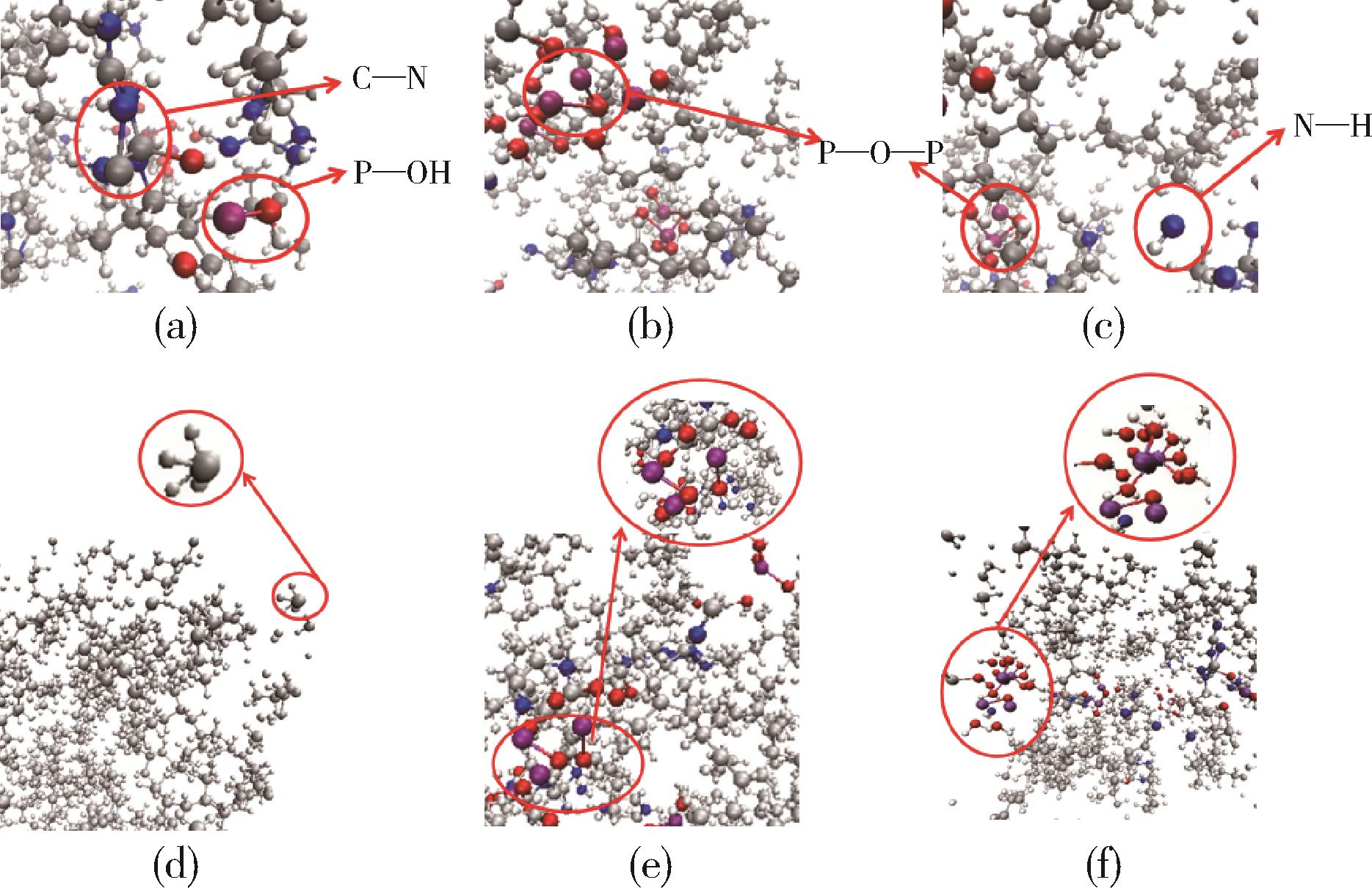
| 1 | Mengwei T, Lijun Q, Jingyu W,et al.From physical mixtures to block copolyme:Impose outstandingly toughening and flame retardant effect to polypropylene[J].Composites Part B,2023,253:110538. |
| 2 | Wu H Y, Li Y T, Zeng B R,et al.A high synergistic P/N/Si⁃containing additive with dandelion⁃shaped structure deriving from selfassembly for enhancing thermal and flame retardant property of epoxy resins[J].React Funct Polym,2018,131:89⁃99. |
| 3 | Liang W H, Yu B, Wang W,et al.A triazine⁃based hyperbranched charforming agent for efficient intumescent flame retardant poly (lactic acid) composites[J].Compos Commun,2022,33:101225. |
| 4 | Zhang W C, Camino G, Yang R J.Polymer/polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS) nanocomposites: an overview of fire retardance[J].Prog Polym Sci,2017,67:77⁃125. |
| 5 | Song P A, Shen Y, Du B X,et al.Effects of reactive compatibilization on the morphological, thermal, mechanical,and rheological properties of intumescent flame⁃retardant polypropylene[J].ACS Appl Mater Interfaces,2009,1:452⁃459. |
| 6 | 万永清.基于ReaxFF力场阻燃聚碳酸酯热解及阻燃机理研究[D].太原:中北大学,2022. |
| 7 | 孙浩,姚贵策,高慧,等.基于ReaxFF反应分子动力学模拟的正十二烷醇的热裂解特性研究[J].工程热物理学报,2023,44(02):444⁃450. |
| SUN H, YAO G C, GAO H,et al. ReaxFF molecular dynamics study on the pyrolysis process of N⁃dodecanol[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics,2023,44(02):444⁃450. | |
| 8 | 霍二光,刘朝,李期斌,等.基于ReaxFF模拟的正戊烷热分解机理研究[J].工程热物理报,2020,41(01):61⁃67. |
| HUO E G, LIU C, LI Q B,et al. Thermal decomposition mechanism of n⁃pentane by ReaxFF simulations[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics,2020,41(01):61⁃67. | |
| 9 | Xin Z Z, Na D, Liu Y X,et al.Study on the formation process of soot from 2,5⁃dimethylfuran pyrolysis by ReaxFF molecular dynamics[J].Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry,2023,148(17):9 145⁃3 166. |
| 10 | Min H Z, Bao F Z, Yi F C,et al.Kinetic mechanism for simulating the temperature and pressure effect on the explosive decomposition of acetylene by ReaxFF molecular dynamics[J].Chemistry Select,2023,8(10):202204563. |
| 11 | 刘连池. ReaxFF反应力场的开发及其在材料科学中的若干应用[D].上海交通大学,2012. |
| 12 | Brenner D W.Empirical potential for hydrocarbons for use in simulating the chemical vapor⁃deposition of diamond films[J].Physical Review B,1990,42(15):9 458⁃9 471. |
| 13 | Brenner D W, Shenderova O A, Harrison J A,et al.A second⁃generation reactive empirical bond order(REBO) potential energy expression for hydrocarbons[J].Journal of Physics_Condensed Matter,2002,14(4):783⁃802. |
| 14 | Root D M, Landis C R, Cleveland T.Valence bond concepts applied to the molecular mechanics description of molecular shapes.Application to nonhypervalent molecular of the P⁃block[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,1993,115(10):4 201⁃4 209. |
| 15 | Dasgupta Siddharth, Lorant Francois, C T van Duin Adri.ReaxFF:a reactive force field for hydrocarbons[J].J Phys Chem A,2001,105(41):9 396⁃9 409. |
| 16 | Russo M F, van Duin A C T.Atomistic⁃scale simulations of chemical reactions:Bridging from quantum chemistry to engineering[J].Nuclear Instruments & Methods in Physics Research Section B⁃Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms,2011,269(14):1 549⁃1 554. |
| 17 | Wu H Y, Li Y T, Zeng B R,et al.A high synergistic P/N/Si⁃containing additive with dandelion⁃shaped structure deriving from selfassembly for enhancing thermal and flame retardant property of epoxy resins[J].React Funct Polym, 2018,131:89⁃99. |
| 18 | Huo E, Liu C, Xu X,et al.A ReaxFF⁃based molecular dynamics study of the oxidation decomposition mechanism of HFO-1336mzz(Z)[J].International Journal of Refrigeration,2018,93(9):249⁃258. |
| 19 | Cao Y, Liu C, Xu X,et al.Infuence of water on HFO-1234yf oxidation pyrolysis via ReaxFF molecular dynamics simulation[J].Molecular Physics,2019,117(13):1 768⁃1 780. |
| 20 | Hong D, Guo X.A reactive molecular dynamics study of CH4 combustion in O2/CO2/H20 environments[J].Fuel Processing Technology,2017,167(13):416⁃424. |
| 21 | Hong D, Liu L, Huang Y,et al.Chemical effect of H2O on CH4 oxidation during combustion in O2/H2O environments[J].Energy & Fuels,2016,30(10):8 491⁃8 498. |
| 22 | Zheng M, Wang Z, Li X,et al.Initial reaction mechanisms of cellulose pyrolysis revealed by ReaxFF molecular dynamics[J].Fuel,2016,177(15):130⁃141. |
| 23 | Zhan J, Wu R, Liu X,et al.Preliminary understanding of initial reaction process for subbituminous coal pyrolysis with molecular dynamics simulation[J].Fuel,2014,134(16):283⁃292. |
| 24 | Foster D P, Pinettes C.Surface critical behaviour of the vertex⁃interacting self⁃avoiding walk on the square lattice[J].Journal of Physics A Mathematical and Theoretical,2012,45(50):505003. |
| 25 | Chenoweth K, Cheung S, Van D A,et al.Simulations on the thermal decomposition of a poly(dimethylsiloxane) polymer using the ReaxFF reactive force field[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,2005,127(19):7 192⁃7 202. |
| 26 | Hao H, Chow C L, Lau D.Carbon monoxide release mechanism in cellulose combustion using reactive forcefield[J].Fuel,2020,269:117422. |
| 27 | Zhao T, Li T, Xin Z,et al.A ReaxFF⁃based molecular dynamics simulation of the pyrolysis mechanism for polycarbonate[J].Energy & Fuels,2018,32(2):2 156⁃2 162. |
| 28 | Bo Zhang, van Duin A C T, Johnson J K.Development of a ReaxFF reactive force field for tetrabutylphosphonium glycinate/CO2 mixtures[J].J Phys Chem B,2014,118(41):12 008⁃12 016. |
| [1] | GUO Minghai. Studies on structure and properties of high⁃impact copolymerized polypropylene with high melt flow rate [J]. China Plastics, 2024, 38(5): 7-13. |
| [2] | GUO Jiang, XU Mengyi, LI Hui, HUANG Xiang, LIN Hao, JIANG Shengbao, CHEN Shang, CHEN Cheng. Preparation and dielectric properties of polypropylene/ZrO2 composite materials [J]. China Plastics, 2024, 38(3): 44-48. |
| [3] | WANG Peng, YAO Cheng, LIU Gang, CAI Xipeng, JIA Lei, WANG Kai, CHEN Long. Structural characteristics and electrical insulating properties of BOPP films based on different stretching modes [J]. China Plastics, 2024, 38(3): 54-58. |
| [4] | RUAN Fangtao, WU Hao, ZHU Jinwei, SU Yongsheng, CHEN Zhuolin, WANG Guofeng, WANG Hongjie. Effect of TEOS modification and long straw fiber orientation on properties of PP/SF composites [J]. China Plastics, 2024, 38(2): 14-19. |
| [5] | XU Yaohui, TANG Yiwen, GUO Peng, LYU Mingfu. Effect of ion modification on viscoelasticity of broad molecular weight distribution polypropylene [J]. China Plastics, 2024, 38(1): 7-13. |
| [6] | LI Dan, ZHAO Biao, CHEN Ke, WANG Fan, ZHANG Jingyu, ZHANG Fengbo, PAN Kai. Research progress in preparation and applications of hollow polypropylene fiber [J]. China Plastics, 2023, 37(9): 109-114. |
| [7] | DONG Dangfeng. Effect of content of recycled polyethylene/recycled polypropylene/recycled sulfur slag complex modifiers on properties of modified asphalt [J]. China Plastics, 2023, 37(8): 101-106. |
| [8] | WANG Wenhui, ZHU Huihao, LI Guo, WANG Yu, WU Fan, LIN Zhenbin, MA Yulu, XIE Linsheng. Preparation and optimization of PP/PC light diffusing materials for ultraviolet shielding effect [J]. China Plastics, 2023, 37(8): 8-12. |
| [9] | ZHANG Panpan, LIU Jing, JIANG Jianzhun, CAO Xuejun. Determination of nucleating agents in polypropylene through ultra high performance liquid chromatography [J]. China Plastics, 2023, 37(8): 93-100. |
| [10] | GUO Wenjiao, LI Juan, LI Ying. Research progress on electric property of polypropylene nanocomposites for HVDC cables insulation material [J]. China Plastics, 2023, 37(12): 135-142. |
| [11] | DAI Xiying, ZHANG Chong, WAN Caixia, YANG Wei, XING Zhaoliang. Microstructure of BOPP capacitor film affecting breakdown field strength and its relationship with preparation process [J]. China Plastics, 2023, 37(12): 29-34. |
| [12] | LI Zhenyin, ZHANG Xiaolin, WEI Cong, SHI Zhiyong, SHAO Chunguang. Effect of pressurization on crystallization behavior of iPP/MWCNTs melts [J]. China Plastics, 2023, 37(10): 117-124. |
| [13] | ZHANG Hengyuan, LIU Tao, ZHANG Shijun, LIU Jianye. Study on processing⁃structure⁃properties of selective laser sintered of polypropylene [J]. China Plastics, 2023, 37(10): 50-55. |
| [14] | LI Zhao, JIA Yuanshan. Error analysis of determination for grafting ratio of compatibilizer maleic anhydride⁃grafted polypropylene through acid⁃base back titration [J]. China Plastics, 2023, 37(10): 77-84. |
| [15] | ZHANG Hengyuan, LIU Jianye, WANG Shaojie, XU Yaohui, ZHANG Shijun. Isothermal crystallization behavior of polypropylene in solution [J]. China Plastics, 2023, 37(1): 13-17. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||