京ICP备13020181号-2
© 《China Plastics》
© 《China Plastics》

China Plastics ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (7): 102-111.DOI: 10.19491/j.issn.1001-9278.2025.07.016
• Plastic and Environment • Previous Articles Next Articles
FENG Shuo1, LIN Xiaoqi2, ZHU Yanli2, GAO Weichang3, WENG Yunxuan1, ZAHNG Caili1( )
)
Received:2024-08-09
Online:2025-07-26
Published:2025-07-22
CLC Number:
FENG Shuo, LIN Xiaoqi, ZHU Yanli, GAO Weichang, WENG Yunxuan, ZAHNG Caili. Chemical recovery and life cycle assessment of biodegradable plastic PBAT: current situation, challenges and prospects[J]. China Plastics, 2025, 39(7): 102-111.
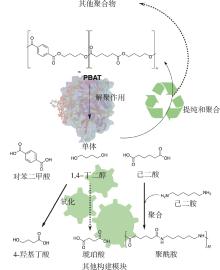
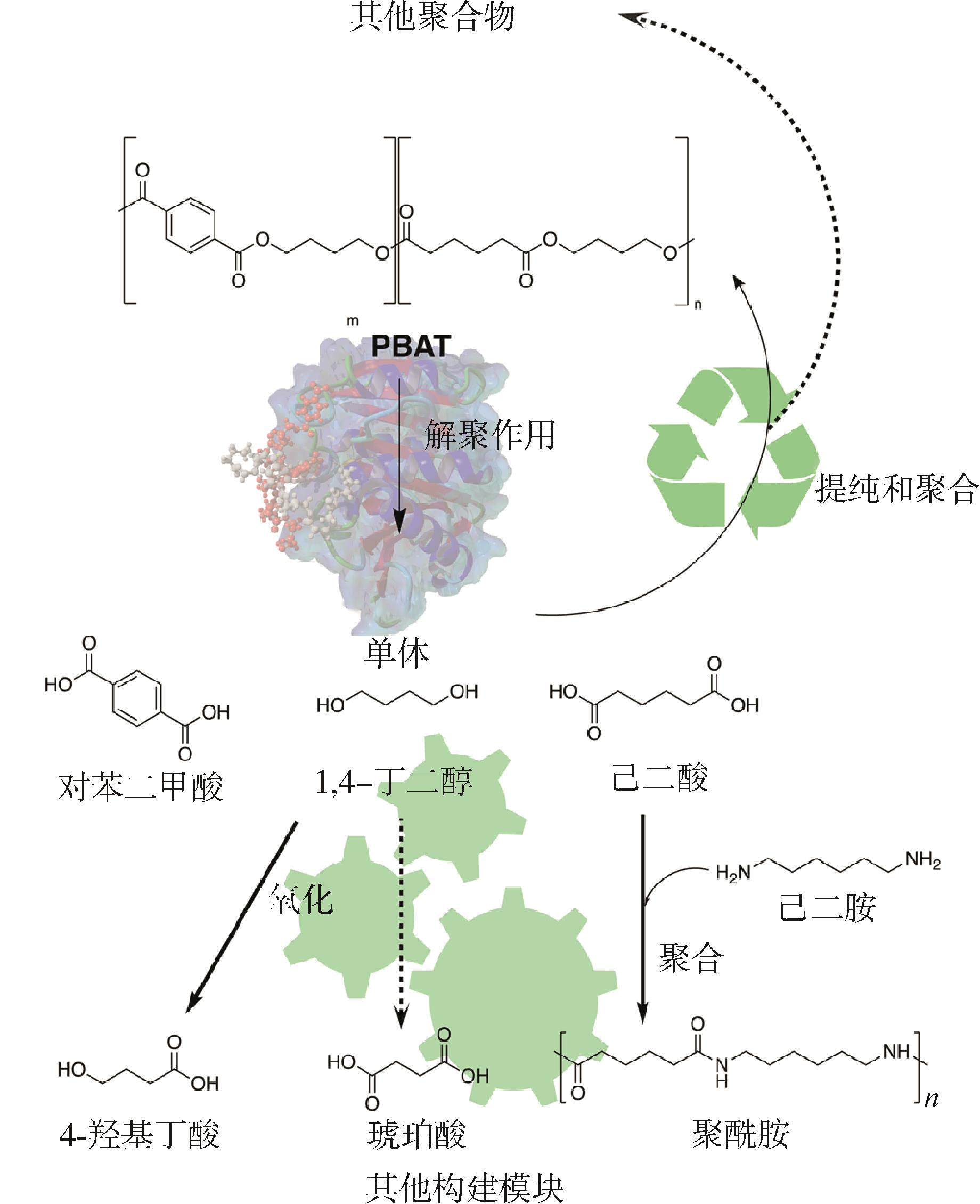
| 回收方式 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|
| ①水解 | (1)水解条件相对容易控制,产物较为纯净; (2)水解产生的单体可以用于重新合成PBAT或其他材料,保持一定的经济价值。 | (1)对设备可能有一定的腐蚀性; (2)存在回收效率不高的情况,导致整体回收效果受到一定影响。 |
| ②醇解 | (1)相对较为成熟,能够有效回收单体或低聚物,可用于再生产; (2)反应条件相对温和。 | (1)可能会产生一些副产物,需要进一步处理; (2)回收过程中可能会有一定的溶剂消耗和排放。 |
| ③热化学 | (1)可实现对 PBAT 的大规模处理,能回收得到有价值的化学品; (2)在回收过程中可回收一部分能量。 | (1)需要较高的温度,能耗较大; (2)可能会产生一些复杂的混合物,后续分离提纯有一定难度。 |
| ④生物催化 | (1)环境友好,减少了化学试剂的使用和潜在污染; (2)具有针对性,提高回收PBAT效率和纯度; (3)常温、常压等,降低能源消耗。 | (1)生物催化剂的开发和应用成本较高; (2)在回收速度和规模上存在一定局限性; (3)生物催化剂可能对环境条件较为敏感,如温度、酸碱度等,稳定性方面有待进一步加强。 |
| 回收方式 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|
| ①水解 | (1)水解条件相对容易控制,产物较为纯净; (2)水解产生的单体可以用于重新合成PBAT或其他材料,保持一定的经济价值。 | (1)对设备可能有一定的腐蚀性; (2)存在回收效率不高的情况,导致整体回收效果受到一定影响。 |
| ②醇解 | (1)相对较为成熟,能够有效回收单体或低聚物,可用于再生产; (2)反应条件相对温和。 | (1)可能会产生一些副产物,需要进一步处理; (2)回收过程中可能会有一定的溶剂消耗和排放。 |
| ③热化学 | (1)可实现对 PBAT 的大规模处理,能回收得到有价值的化学品; (2)在回收过程中可回收一部分能量。 | (1)需要较高的温度,能耗较大; (2)可能会产生一些复杂的混合物,后续分离提纯有一定难度。 |
| ④生物催化 | (1)环境友好,减少了化学试剂的使用和潜在污染; (2)具有针对性,提高回收PBAT效率和纯度; (3)常温、常压等,降低能源消耗。 | (1)生物催化剂的开发和应用成本较高; (2)在回收速度和规模上存在一定局限性; (3)生物催化剂可能对环境条件较为敏感,如温度、酸碱度等,稳定性方面有待进一步加强。 |
| [1] | Omelan M C V, Lachmann K, Meyer H, et al. RETRACTED: bio⁃based thin film coatings using sustainable materials[J]. 2022: 20⁃25. |
| [2] | De Lima L F, Lopes Ferreira A, Martinez de Freitas A S, et al. Biodegradable and flexible thermoplastic composite graphite electrodes: a promising platform for inexpensive and sensitive electrochemical detection of creatine kinase at the point⁃of⁃care[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2023, 15(15): 18 694⁃18 706. |
| [3] | Kim H, Jeon H, Lee M, et al. Enhanced mechanical properties of poly (butylene adipate⁃co⁃terephthalate)/cellulose nanocrystal nanocomposites obtained by in situ polymerization[J]. ACS Applied Polymer Materials, 2022, 5(1): 635⁃643. |
| [4] | Sim J Y, Raj C J, Yu K H. Poly (butylene adipate⁃co⁃terephthalate)(PBAT)/antimony⁃doped tin oxide polymer composite for near infrared absorption coating applications[J]. Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society, 2019, 40(7): 674⁃679. |
| [5] | Ki H C, Park O O. Synthesis, characterization and biodegradability of the biodegradable aliphatic–aromatic random copolyesters[J]. Polymer, 2001, 42(5): 1 849⁃1 861. |
| [6] | Cranston E, Kawada J, Raymond S, et al. Cocrystallization model for synthetic biodegradable poly (butylene adipate⁃co⁃butylene terephthalate)[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2003, 4(4): 995⁃999. |
| [7] | Da Silva J S P, Da Silva J M F, Soares B G, et al. Fully biodegradable composites based on poly (butylene adipate⁃co⁃terephthalate)/peach palm trees fiber[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2017, 129: 117⁃123. |
| [8] | Dedieu I, Peyron S, Gontard N, et al. The thermo⁃mechanical recyclability potential of biodegradable biopolyesters: perspectives and limits for food packaging application[J]. Polymer Testing, 2022, 111: 107620. |
| [9] | Merchan A L, Fischöder T, Hee J, et al. Chemical recycling of bioplastics: technical opportunities to preserve chemical functionality as path towards a circular economy[J]. Green Chemistry, 2022, 24(24): 9 428⁃9 449. |
| [10] | Marinho V A D, Pereira C A B, Vitorino M B C, et al. Degradation and recovery in poly (butylene adipate⁃co⁃terephthalate)/thermoplastic starch blends[J]. Polymer Testing, 2017, 58: 166⁃172. |
| [11] | Šerá J, Kadlečková M, Fayyazbakhsh A, et al. Occurrence and analysis of thermophilic poly (Butylene adipate⁃co⁃terephthalate)⁃degrading microorganisms in temperate zone soils[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2020, 21(21): 7 857. |
| [12] | Álvarez⁃Méndez S J, Ramos⁃Suárez J L, Ritter A, et al. Anaerobic digestion of commercial PLA and PBAT biodegradable plastic bags: potential biogas production and 1H⁃NMR and ATR⁃FTIR assessed biodegradation[J]. Heliyon, 2023, 9(6):e16691. |
| [13] | Wu P, Li Z, Gao J, et al. Characterization of a PBAT degradation carboxylesterase from Thermobacillus composti KWC4[J]. Catalysts, 2023, 13(2): 340. |
| [14] | Gioia C, Giacobazzi G, Vannini M, et al. End of life of biodegradable plastics: composting versus Re/upcycling[J]. ChemSusChem, 2021, 14(19): 4 167⁃4 175. |
| [15] | Wong P C, Kurniawan D, Wu J L, et al. Plasma⁃enabled graphene quantum dot hydrogel–magnesium composites as bioactive scaffolds for in vivo bone defect repair[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2023, 15(38): 44 607⁃44 620. |
| [16] | Lee S, Lee J, Park Y K. Simultaneous upcycling of biodegradable plastic and sea shell wastes through thermocatalytic monomer recovery[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2022, 10(42): 13 972⁃13 979. |
| [17] | Kim S, Lee H S, Yang W, et al. Recovery of lactic acid from biodegradable straw waste through a CO2⁃assisted thermochemical process[J]. Journal of CO2 Utilization, 2022, 64: 102164. |
| [18] | Kim S, Yang W, Lee H S, et al. Effectiveness of CO2⁃mediated pyrolysis for the treatment of biodegradable plastics: A case study of polybutylene adipate terephthalate/polylactic acid mulch film[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 372: 133763. |
| [19] | Arias J J R, Thielemans W. Instantaneous hydrolysis of PET bottles: an efficient pathway for the chemical recycling of condensation polymers[J]. Green Chemistry, 2021, 23(24): 9 945⁃9 956. |
| [20] | Pham D D, Cho J. Low⁃energy catalytic methanolysis of poly (ethyleneterephthalate) Green Chem[J]. 2021,23: 511⁃525. |
| [21] | Wang Q, Geng Y, Lu X, et al. First⁃row transition metal⁃containing ionic liquids as highly active catalysts for the glycolysis of poly (ethylene terephthalate)(PET)[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2015, 3(2): 340⁃348. |
| [22] | Raheem A B, Noor Z Z, Hassan A, et al. Current developments in chemical recycling of post⁃consumer polyethylene terephthalate wastes for new materials production: a review[J]. Journal of cleaner production, 2019, 225: 1 052⁃1 064. |
| [23] | Pang W, Li B, Wu Y, et al. Upgraded recycling of biodegradable PBAT plastic: efficient hydrolysis and electrocatalytic conversion[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 486: 150342. |
| [24] | Ratshoshi B K, Farzad S, Görgens J F. A techno⁃economic study of polybutylene adipate terephthalate (PBAT) production from molasses in an integrated sugarcane biorefinery[J]. Food and Bioproducts Processing, 2024, 145: 11⁃20. |
| [25] | Ma J, Cao Y, Fan L, et al. Degradation characteristics of polybutylene adipate terephthalic acid (PBAT) and its effect on soil physicochemical properties: a comparative study with several polyethylene (PE) mulch films[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2023, 456: 131661. |
| [26] | Shi X Q, Aimi K, Ito H, et al. Characterization on mixed⁃crystal structure of poly (butylene terephthalate/succinate/adipate) biodegradable copolymer fibers[J]. Polymer, 2005, 46(3): 751⁃760. |
| [27] | Shi X Q, Ito H, Kikutani T. Characterization on mixed⁃crystal structure and properties of poly (butylene adipate⁃co⁃terephthalate) biodegradable fibers[J]. Polymer, 2005, 46(25): 11 442⁃11 450. |
| [28] | Niu H, Lyu M, Guo P, et al. Effect of antihydrolysis agents on the structure and properties of PBAT/PGA blend films under artificial accelerated weathering[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2024, 63(8): 3 504⁃3 513. |
| [29] | Wang J H, Tian Y, Zhou B. Degradation and stabilization of poly (butylene adipate⁃co⁃terephthalate)/polyhydroxyalkanoate biodegradable mulch films under different aging tests[J]. Journal of Polymers and the Environment, 2022: 1⁃14. |
| [30] | Xu P Y, Liu T Y, Huang D, et al. Enhanced degradability of novel PBATCL copolyester: study on the performance in different environment and exploration of mechanism[J]. European Polymer Journal, 2023, 186: 111834. |
| [31] | Tseng W S, Lee M J, Wu J A, et al. Poly (butylene adipate⁃co⁃terephthalate) biodegradation by Purpureocillium lilacinum strain BA1S[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2023, 107(19): 6 057⁃6 070. |
| [32] | Kijchavengkul T, Auras R, Rubino M, et al. Biodegradation and hydrolysis rate of aliphatic aromatic polyester[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2010, 95(12): 2 641⁃2 647. |
| [33] | Yang Y, Min J, Xue T, et al. Complete bio⁃degradation of poly (butylene adipate⁃co⁃terephthalate) via engineered cutinases[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 1 645. |
| [34] | Lin W, Zhao Y, Su T, et al. Enzymatic hydrolysis of poly (butylene adipate⁃co⁃terephthalate) by Fusarium solani cutinase[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2023, 211: 110335. |
| [35] | Jiang Z, Hou F, Chen J, et al. Synthesis and properties of biodegradable PBAT prepared from PBT chemically recycled resources[J]. Polymer, 2024, 307: 127326. |
| [36] | Sun C, Wei S, Tan H, et al. Progress in upcycling polylactic acid waste as an alternative carbon source: a review[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 446: 136881. |
| [37] | Czajczyńska D, Anguilano L, Ghazal H, et al. Potential of pyrolysis processes in the waste management sector[J]. Thermal science and engineering progress, 2017, 3: 171⁃197. |
| [38] | Nandakumar A, Chuah J A, Sudesh K. Bioplastics: a boon or bane?[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2021, 147: 111237. |
| [39] | Coralli I, Rombolà A G, Fabbri D. Analytical pyrolysis of the bioplastic PBAT poly (butylene adipate⁃co⁃terephthalate)[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2024, 181: 106577. |
| [40] | Ismail M, Abouhmad A, Warlin N, et al. Closing the loop for poly (butylene⁃adipate⁃co⁃terephthalate) recycling: depolymerization, monomers separation, and upcycling[J]. Green Chemistry, 2024, 26(7): 3 863⁃3 873. |
| [41] | Santos⁃Beneit F, Chen L M, Bordel S, et al. Screening enzymes that can depolymerize commercial biodegradable polymers: heterologous expression of fusarium solani cutinase in Escherichia coli[J]. Microorganisms, 2023, 11 (2):328. |
| [42] | Sharp B E, Miller S A. Potential for integrating diffusion of innovation principles into life cycle assessment of emerging technologies[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(6): 2 771⁃2 781. |
| [43] | Earles J M, Halog A. Consequential life cycle assessment: a review[J]. The International Journal of Life Cycle Assessment, 2011, 16: 445⁃453. |
| [44] | Pauliuk S. Critical appraisal of the circular economy standard BS 8001: 2017 and a dashboard of quantitative system indicators for its implementation in organizations[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2018, 129: 81⁃92. |
| [45] | Lam K L, Zlatanović L, van Der Hoek J P. Life cycle assessment of nutrient recycling from wastewater: a critical review[J]. Water research, 2020, 173: 115519. |
| [46] | He Y, Kiehbadroudinezhad M, Hosseinzadeh⁃Bandbafha H, et al. Driving sustainable circular economy in electronics: a comprehensive review on environmental life cycle assessment of e⁃waste recycling[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2024, 342: 123081. |
| [47] | Sheik A G, Krishna S B N, Patnaik R, et al. Digitalization of phosphorous removal process in biological wastewater treatment systems: challenges, and way forward[J]. Environmental Research, 2024: 119133. |
| [48] | Mohan S V, Hemalatha M, Chakraborty D, et al. Algal biorefinery models with self⁃sustainable closed loop approach: trends and prospective for blue⁃bioeconomy[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 295: 122128. |
| [49] | Mohan S V, Nikhil G N, Chiranjeevi P, et al. Waste biorefinery models towards sustainable circular bioeconomy: critical review and future perspectives[J]. Bioresource technology, 2016, 215: 2⁃12. |
| [50] | Al⁃Sakkari E G, Ragab A, Dagdougui H, et al. Carbon capture, utilization and sequestration systems design and operation optimization: assessment and perspectives of artificial intelligence opportunities[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2024, 917: 170085. |
| [51] | Fonseca A, Ramalho E, Gouveia A, et al. Systematic Insights into a textile industry: reviewing life cycle assessment and eco⁃design[J]. Sustainability, 2023, 15(21): 15267. |
| [52] | Cristofoli N L, Lima A R, Tchonkouang R D N, et al. Advances in the food packaging production from agri⁃food waste and by⁃products: market trends for a sustainable development[J]. Sustainability, 2023, 15(7): 6 153. |
| [53] | Rastogi P, Kandasubramanian B. Breakthrough in the printing tactics for stimuli⁃responsive materials: 4D printing[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 366: 264⁃304. |
| [54] | Abdallah M, Rahmat⁃Ullah Z, Hosny M, et al. Minimizing the environmental impacts of waste valorization systems using multi⁃criteria life cycle optimization[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2024, 449: 141619. |
| [55] | Veksha A, Ahamed A, Wu X Y, et al. Technical and environmental assessment of laboratory scale approach for sustainable management of marine plastic litter[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 421: 126717. |
| [56] | Dong J, Chi Y, Zou D, et al. Energy–environment–economy assessment of waste management systems from a life cycle perspective: Model development and case study[J]. Applied Energy, 2014, 114: 400⁃408. |
| [57] | Parascanu M M, Gamero M P, Sánchez P, et al. Life cycle assessment of olive pomace valorisation through pyrolysis[J]. Renewable Energy, 2018, 122: 589⁃601. |
| [58] | Davidson M G, Furlong R A, McManus M C. Developments in the life cycle assessment of chemical recycling of plastic waste⁃a review[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 293: 126163. |
| [59] | Schrijvers D L, Leroux F, Verney V, et al. Ex⁃ante life cycle assessment of polymer nanocomposites using organo⁃modified layered double hydroxides for potential application in agricultural films[J]. Green Chemistry, 2014, 16(12): 4 969⁃4 984. |
| [60] | Brookes C K. Advancement of biobased products through design, synthesis and engineering of biopolyesters[M]. Michigan State University. Department of Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, 2007. |
| [61] | Saibuatrong W, Cheroennet N, Suwanmanee U. Life cycle assessment focusing on the waste management of conventional and bio⁃based garbage bags[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 158: 319⁃334. |
| [62] | Dunn J B, Adom F, Sather N, et al. Life⁃cycle analysis of bioproducts and their conventional counterparts in GREET[R]. Argonne National Lab.(ANL), Argonne, IL (United States), 2015. |
| [63] | Moutousidi E S, Kookos I K. Life cycle assessment of biobased chemicals from different agricultural feedstocks[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 323: 129201. |
| [64] | Wang B X, Cortes⁃Peña Y, Grady B P, et al. Techno⁃economic analysis and life cycle assessment of the production of biodegradable polyaliphatic–polyaromatic polyesters[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2024, 12(24): 9 156⁃9 167. |
| [65] | Carmona E, Rojo⁃Nieto E, Rummel C D, et al. A dataset of organic pollutants identified and quantified in recycled polyethylene pellets[J]. Data in Brief, 2023, 51: 109740. |
| [1] | SHANG Yunlong, WANG Donghao, REN Zhibin. Storage stability of wet asphalt rubber: A comprehensive review [J]. China Plastics, 2025, 39(8): 75-82. |
| [2] | LIANG Yonghuang, LIU Jing, GE Dongqi. Overview of China’s plastic chemical recycling: status, problems, trends [J]. China Plastics, 2025, 39(7): 112-120. |
| [3] | ZHANG Liping, XIE Tong, GAO Yongping. Development situation, problems and suggestions of biodegradable plastic industry [J]. China Plastics, 2025, 39(4): 75-83. |
| [4] | CHEN Zhuo, HU Jie, MA Chao, LI Xiaohui, BAN Tiantian, LIU Xiaocui. Effects of biodegradable mulching films on yield, soil environment and economic benefit of Chinese cabbage under terrain and climate conditions in Guizhou province [J]. China Plastics, 2025, 39(1): 97-103. |
| [5] | WEN Qilin, JIA Xuehua, SUN Yanjun, NIU Siji, CHEN Yinghong, CHEN Ning. Research progress in preparation and applications of biodegradable plastic packaging films [J]. China Plastics, 2024, 38(9): 112-122. |
| [6] | YIN Maofeng, WANG Xiaoke, SUN Guohua, ZHANG Xin, LI Pengpeng, MA Jinsong, XIAO Jun, HOU Lianlong. Research on rapid detection of biodegradable polyester by infrared spectroscopy [J]. China Plastics, 2024, 38(9): 94-100. |
| [7] | JIAO Xiaolong, DANG Kaifang, ZHOU Yang, MA Yitao, WANG Jinling, XIE Pengcheng. New trends in injection molding industry from “K⁃show 2022” in Germany [J]. China Plastics, 2024, 38(1): 49-54. |
| [8] | MA Teng, LIU Qianqian, WEI Xiaoli, SONG Haitao, LI Mingfeng. Influence and countermeasures of silicon and chlorine impurities on waste plastic pyrolysis oil [J]. China Plastics, 2022, 36(8): 127-134. |
| [9] | DONG Shaoce, LI Chenggao, ZHANG Xufeng, XIAN Guijun. Environmental impact assessment for manufacture of plant fiber honeycomb core [J]. China Plastics, 2022, 36(6): 108-115. |
| [10] | ZHANG Zongyin, LYU Mingfu, GUO Peng, XU Yaohui, ZHANG Shijun. Influence of ultraviolet absorbers on weather resistance of PBST film [J]. China Plastics, 2022, 36(5): 110-115. |
| [11] | WU Xiongjie, TAO Qiang, ZHU Dongbo, CHENG Jinsong, CHU Yu, XU Lei. Study on material identification and total migration of biodegradable plastic shopping bags used for food contact [J]. China Plastics, 2022, 36(5): 127-132. |
| [12] | YAO Yi, ZHANG Erjie, LU Changli, WANG Chaojun, JIAO Jian, ZENG Xiangbin. Influence of food contact regulations on the development of PBS [J]. China Plastics, 2022, 36(10): 125-130. |
| [13] | LI Xiangyang, YANG Linzhu, ZHAI Guoqiang, GAO Wanqin, WANG Kezhi, LI Xungang. Effect of Nucleating Agent on Crystallization and Properties of Poly(butylene succinate) [J]. China Plastics, 2021, 35(8): 146-151. |
| [14] | DIAO Xiaoqian, WENG Yunxuan, FU Ye, ZHOU Yingxin. Review of Applications and Performance Evaluation Methods of Biodegradable Plastics [J]. China Plastics, 2021, 35(8): 152-161. |
| [15] | ZHOU Yingxin, WENG Yunxuan, ZHANG Caili, DIAO Xiaoqian, SONG Xinyu. Review of Recovery Technology and Standard Status of Poly(ethylene terephthalate) [J]. China Plastics, 2021, 35(8): 162-171. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||