 京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2
京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2
《中国塑料》编辑部 ©2008-2024 版权所有
地址:北京市海淀区阜成路11号 邮编:100048
编辑部:010-68985541 联系信箱:cp@plaschina.com.cn
广告部/发行部:010-68985253 本系统由北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司设计开发

中国塑料 ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (8): 127-134.DOI: 10.19491/j.issn.1001-9278.2023.08.018
• 综述 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2023-05-22
出版日期:2023-08-26
发布日期:2023-08-21
通讯作者:
张彩丽(1989—),女,副教授,从事生物基与生物降解高分子材料研究,zhangcaili@btbu.edu.cn基金资助:
WANG Lei, ZHAO Min, WENG Yunxuan, ZHANG Caili( )
)
Received:2023-05-22
Online:2023-08-26
Published:2023-08-21
Contact:
ZHANG Caili
E-mail:zhangcaili@btbu.edu.cn
摘要:
综述了目前国内外关于机器学习(ML)在聚乳酸(PLA)加工及性能预测中的应用研究进展。首先,概述了目前ML在预测PLA结晶性能、疲劳寿命、拉伸强度、韧性、屈服应力、密度、降解程度等方面的应用。其次,介绍ML可监测PLA加工过程中可能出现的缺陷,进而降低PLA制品的生产成本、提高其使用寿命。最后,总结并展望了ML未来在PLA加工及应用中的作用及发展。
中图分类号:
王磊, 赵敏, 翁云宣, 张彩丽. 机器学习在聚乳酸加工及性能预测中的应用研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2023, 37(8): 127-134.
WANG Lei, ZHAO Min, WENG Yunxuan, ZHANG Caili. Research progress in applications and performance prediction of machine learning in PLA processing[J]. China Plastics, 2023, 37(8): 127-134.
| ML模型 | 应用以及性能预测 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| 线性回归、多项式回归、随机森林回归 | 研究PLA样条缺口形状、光栅方向和熔体内部空隙对疲劳寿命的影响 | [ |
| 支持向量机(SVM) | 监测PLA生产过程中的补全失效缺陷和几何缺陷 | [ |
| 人工神经网络(ANN)和人工神经网络⁃遗传算法(ANN⁃GN) | 预测PLA的韧性、零件 厚度和生产成本 | [ |
| 主成分分析与随机森林结合 | 预测PLA的拉伸性能,监测生产过程中的产品质量 | [ |
| 梯度提升、随机森林、核岭和支持向量回归模型 | 将PLA泡沫密度通过温度、时间、压力的函数表达 | [ |
| 使用回归树的统计分析 | 研究PLA复合材料的拉伸强度 | [ |
| 4个ANN、2个自适应神经模糊推理系统以及最小二乘支持向量回归 | 预测左旋聚乳酸/聚乙交酯(PLLA/PGA)复合材料的相对结晶度与结晶时间、温度和PGA含量的关系 | [ |
| 多分类逻辑回归和多分类神经网络 | 预测PLA的热降解程度 | [ |
| ML模型 | 应用以及性能预测 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| 线性回归、多项式回归、随机森林回归 | 研究PLA样条缺口形状、光栅方向和熔体内部空隙对疲劳寿命的影响 | [ |
| 支持向量机(SVM) | 监测PLA生产过程中的补全失效缺陷和几何缺陷 | [ |
| 人工神经网络(ANN)和人工神经网络⁃遗传算法(ANN⁃GN) | 预测PLA的韧性、零件 厚度和生产成本 | [ |
| 主成分分析与随机森林结合 | 预测PLA的拉伸性能,监测生产过程中的产品质量 | [ |
| 梯度提升、随机森林、核岭和支持向量回归模型 | 将PLA泡沫密度通过温度、时间、压力的函数表达 | [ |
| 使用回归树的统计分析 | 研究PLA复合材料的拉伸强度 | [ |
| 4个ANN、2个自适应神经模糊推理系统以及最小二乘支持向量回归 | 预测左旋聚乳酸/聚乙交酯(PLLA/PGA)复合材料的相对结晶度与结晶时间、温度和PGA含量的关系 | [ |
| 多分类逻辑回归和多分类神经网络 | 预测PLA的热降解程度 | [ |
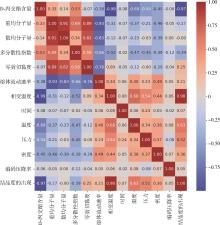

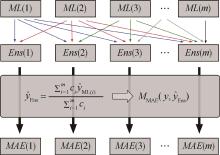
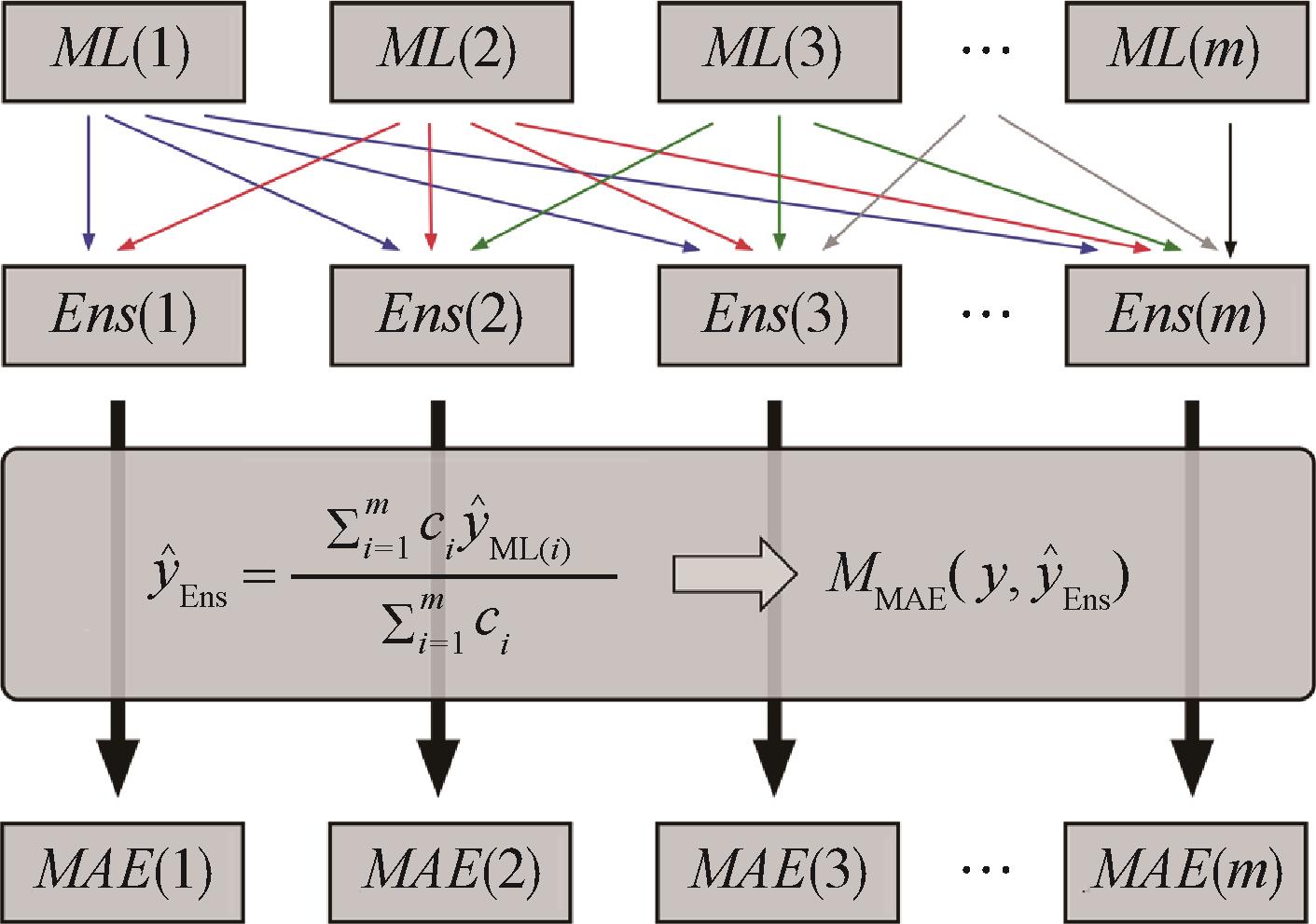
| 机器学习方法 | 结构特性 | 模型 数量/个 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 固定属性 | 可调属性 | ||
| 多层感知器神经网络 | 隐藏层的数量为2。第一个隐藏层的激活函数使用的是双曲正切函数。第二个隐藏层的激活函数使用的是逻辑函数。训练算法采用的是Levenberg⁃Marquardt算法。 | 隐藏层神经元数量 | 200 |
| 级联前馈神经网络 | 隐藏层的数量为2。第一个隐藏层的激活函数为双曲正切。第二个隐藏层的激活函数是逻辑函数。所使用的训练算法是Levenberg⁃Marquardt算法。 | 隐藏层神经元数量 | 200 |
| 循环神经网络 | 隐藏层的数量为2。第一个隐藏层的激活函数是双曲正切函数。第二个隐藏层的激活函数是逻辑函数。所使用的训练算法是缩放共轭梯度算法。 | 隐藏层神经元数量 | 160 |
| 最小二乘支持向量回归 | 训练算法,即最小平方法。 | 核函数 | 150 |
| 具有减法聚类的自适应神经模糊推理系统 | 隶属函数,即减法聚类。 | 聚类训练算法半径 | 400 |
| 具有C均值聚类的自适应神经模糊推理系统 | 隶属函数,即C均值聚类。 | 聚类训练算法数量 | 400 |
| 机器学习方法 | 结构特性 | 模型 数量/个 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 固定属性 | 可调属性 | ||
| 多层感知器神经网络 | 隐藏层的数量为2。第一个隐藏层的激活函数使用的是双曲正切函数。第二个隐藏层的激活函数使用的是逻辑函数。训练算法采用的是Levenberg⁃Marquardt算法。 | 隐藏层神经元数量 | 200 |
| 级联前馈神经网络 | 隐藏层的数量为2。第一个隐藏层的激活函数为双曲正切。第二个隐藏层的激活函数是逻辑函数。所使用的训练算法是Levenberg⁃Marquardt算法。 | 隐藏层神经元数量 | 200 |
| 循环神经网络 | 隐藏层的数量为2。第一个隐藏层的激活函数是双曲正切函数。第二个隐藏层的激活函数是逻辑函数。所使用的训练算法是缩放共轭梯度算法。 | 隐藏层神经元数量 | 160 |
| 最小二乘支持向量回归 | 训练算法,即最小平方法。 | 核函数 | 150 |
| 具有减法聚类的自适应神经模糊推理系统 | 隶属函数,即减法聚类。 | 聚类训练算法半径 | 400 |
| 具有C均值聚类的自适应神经模糊推理系统 | 隶属函数,即C均值聚类。 | 聚类训练算法数量 | 400 |
| 1 | 郑卫, 赵振新, 马名杰, 等. 可降解材料的市场现状及发展前景[J]. 河南化工,2023, 40 (1): 1⁃5. |
| ZHENG W, ZHAO Z X, MA M J,et al. Market status and development prospect of degradable materials[J]. Henan Chemical Industry, 2023, 40 (1): 1⁃5. | |
| 2 | 王艺涵, 贾丹, 詹胜鹏, 等. 机器学习在聚合物材料研究中的应用进展[J]. 高校化学工程学报,2023, 37(2):170⁃180. |
| WANG Y H, JIA D, ZHAN S P,et al. Review on application of machine learning in polymer material research[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Chinese Universities,2023,37(2):170⁃180 | |
| 3 | Xia K, Gao H, Liu C, et al. A novel superhard tungsten nitride predicted by machine⁃learning accelerated crystal structure search[J]. Science Bulletin, 2018, 63(13):817⁃824. |
| 4 | 刘海知, 徐辉, 包红军, 等. 机器学习分类算法在降雨型滑坡预报中的应用[J]. 应用气象学报,2022, 33(3): 282⁃292. |
| LIU H Z, XU H, BAO H J,et al.Application of machine learning classification algorithm to precipitation⁃induced landslides forecasting[J].Journal of Applied Meteorological Science,2022, 33(3): 282⁃292. | |
| 5 | Levin S, Toerper M, Hinson J, et al. Machine⁃learning⁃based electronic triage: a prospective evaluation[J]. Annals of Emergency Medicine, 2018, 72(4):116. |
| 6 | 钱琦淼, 张朵, 王映艨, 等. 机器学习在股价预测上的应用[J]. 中国市场, 2022, 21: 7⁃10. |
| 7 | Doan T H, Chiho K, Lihua C, et al. Machine⁃learning predictions of polymer properties with polymer genome[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2020, 128(17):171104. |
| 8 | Jha A, Chandrasekaran A, Kim C, et al. Impact of dataset uncertainties on machine learning model predictions: the example of polymer glass transition temperatures[J]. Modelling and Simulation in Materials Science and Engineering, 2019, 27(2): 024002. |
| 9 | 黄飞鸿, 李凤红, 笪伟, 等. 3D打印聚乳酸复合材料的改性研究进展[J]. 工程塑料应用, 2022, 50(11): 151⁃156. |
| HUANG F H, LI F H,DA W,et al.Research progress on modification of 3D printed polylactic acid composites[J]. Engineering Plastis Application, 2022, 50(11): 151⁃156. | |
| 10 | Hassanifard S, Behdinan K. Anisotropy and internal flaws effects on fatigue response of notched 3D⁃printed PLA parts[J]. Materials Today Communications, 2023, 35:105734. |
| 11 | Delli U, Chang S. Automated process monitoring in 3D printing using supervised machine learning[J]. Procedia Manufacturing 2018, 26: 865⁃870. |
| 12 | Meiabadi M S, Moradi M, Karamimoghadam M, et al. Modeling the producibility of 3D printing in polylactic acid using artificial neural networks and fused filament fabrication[J]. Polymers(Basel), 2021, 13(19) :13103219. |
| 13 | Wang C, Tan X P, Tor S B, et al. Machine learning in additive manufacturing: State⁃of⁃the⁃art and perspectives[J].Additive Manufacturing, 2020, 36:101538. |
| 14 | 李小强. 基于机器学习的零件加工在线监测研究[J]. 自动化与仪器仪表, 2022, 11:124⁃128,133. |
| LI X Q.Research on on⁃line monitoring of parts machining based on deep learning[J].Automation and Instruentation, 2022, 11:124⁃128,133. | |
| 15 | Mulrennan K, Donovan J, Creedon L, et al. A soft sensor for prediction of mechanical properties of extruded PLA sheet using an instrumented slit die and machine learning algorithms[J]. Polymer Testing, 2018, 69: 462⁃469. |
| 16 | Albuquerque R Q, Brütting C, Standau T, et al. A machine learning investigation of low⁃density polylactide batch foams[J]. E⁃Polymers, 2022, 22(1): 318⁃331. |
| 17 | 马喜峰. 聚乳酸复合材料在生物医学领域的应用研究[J]. 化学与粘合, 2022, 44(5): 436⁃440. |
| MA X F.Application of polylactic acid composites in biomedical field[J].Chemistry and Adhesion, 2022, 44(5): 436⁃440. | |
| 18 | Alakent B, Soyer⁃Uzun S. Implementation of statistical learning methods to develop guidelines for the design of PLA⁃based composites with high tensile strength values[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2019, 58(8):3 478⁃3 489. |
| 19 | 冯晓雯, 胡灵芝, 张文, 等. 左旋聚乳酸等温结晶动力学的超快扫描量热研究[J]. 伊犁师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 16(1): 39⁃43. |
| FENG X W, HU L Z, ZHANG W,et al.Study on isothermal crystallization and kinetics of polymer PLLA by fast scanning calorimetry[J].Journal of Yili Normal University(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 16(1): 39⁃43. | |
| 20 | Wang J, Ayari M A, Khandakar A, et al. Estimating the relative crystallinity of biodegradable polylactic acid and polyglycolide polymer composites by machine learning methodologies[J]. Polymers (Basel), 2022, 14(3):14030527. |
| 21 | 殷嘉骏, 琚艳云, 孙政权, 等. 连续化静电纺尼龙6/改性聚乳酸复合膜的制备及性能[J]. 塑料工业, 2022, 50(10):30⁃35. |
| YIN J J, JU Y Y, SUN Z Q,et al.Preparation and properties of continuous electrospinning nylon 6 /modified PLA composite film[J].China Plastis Industry, 2022, 50(10):30⁃35. | |
| 22 | Choi N Y, Shin B C, Zhang S U. A Comparative study of the linear⁃elastic and hyperelastic models for degradation of PLA prepared using fused filament fabrication[J]. Journal of the Korean Society of Manufacturing Process Engineers, 2020, 19(3):1⁃7. |
| 23 | Zhang S U. Classifying thermal degradation of polylactic acid by using machine learning algorithms trained on fourier transform infrared spectroscopy data[J]. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(21):10217470. |
| 24 | Å Rinnan, Berg F V D, Engelsen S B. Review of the most common pre⁃processing techniques for near⁃infrared spectra[J]. Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2009, 28(10): 1 201⁃1 222. |
| 25 | Andraju N, Curtzwiler G W, Ji Y, et al. Machine⁃learning⁃based predictions of polymer and postconsumer recycled polymer properties: a comprehensive review[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2022, 14(38): 42 771⁃42 790. |
| [1] | 汪杰, 张伟蒙, 胡晶. 聚乳酸⁃羟基乙酸共聚物涂层对聚乳酸3D打印支架的性能影响[J]. 中国塑料, 2023, 37(1): 1-7. |
| [2] | 孟鑫, 王小龙, 公维光, 金谊. “三源一体”壳核型阻燃剂的制备及其在聚乳酸中的应用[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(9): 96-104. |
| [3] | 宋丹阳, 郑红娟, 李一龙. 聚乳酸基油水分离材料研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(9): 187-192. |
| [4] | 曲玉婷, 王立梅, 齐斌. 聚乙二醇对聚乳酸/淀粉纳米晶复合材料性能的影响[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(8): 56-61. |
| [5] | 沈雪梅, 朱小龙, 胡燕超, 宋任远, 张现峰, 李席. 静电喷雾法制备聚乳酸/布洛芬微球及其性能研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(7): 61-67. |
| [6] | 周舒毅, 朱敏, 刘忆颖, 曹舒惠, 蔡启轩, 聂慧, 张玉霞, 周洪福. 高分子止血材料研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(7): 74-84. |
| [7] | 邵琳颖, 郗悦玮, 翁云宣. 可降解聚乳酸复合材料研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(6): 155-164. |
| [8] | 王镕琛, 张恒, 孙焕惟, 段书霞, 秦子轩, 李晗, 朱斐超, 张一风. 医疗卫生用聚乳酸非织造材料的制备及其亲水改性研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(5): 158-166. |
| [9] | 李梦琪, 陈雅君. 纳米材料阻燃聚乳酸的研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(4): 102-114. |
| [10] | 孙滔, 杨青, 胡健, 王洋样, 刘博, 云雪艳, 董同力嘎. 聚(乳酸⁃乙醇酸)薄膜制备及其性能研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(2): 33-40. |
| [11] | 杨尚山, 尚鹏鹏, 徐静, 解加卓, 张坤, 张丽丽. 可生物降解PBAT/PLA/生物质垃圾袋的制备和表征[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(11): 127-132. |
| [12] | 李桂丽, 余秋然, 郝明亮, 李海梅. 苎麻纤维表面改性对聚乳酸结晶及拉伸性能的影响[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(11): 51-58. |
| [13] | 毛晨, 刘番, 鄂毅, 邹姝燕, 龚兴厚. 纳米CoFe2O4的制备及其对PLA结晶性能的影响[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(1): 9-14. |
| [14] | 韦宗辰, 郗悦玮, 翁云宣. 聚乳酸基复合骨组织修复材料的研究现状及进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2021, 35(9): 136-146. |
| [15] | 唐于婧, 王亚桥, 倪敬越, 王从龙, 王向东. 立构复合晶对聚乳酸发泡行为的影响[J]. 中国塑料, 2021, 35(8): 117-124. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2
京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2