 京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2
京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2
《中国塑料》编辑部 ©2008-2024 版权所有
地址:北京市海淀区阜成路11号 邮编:100048
编辑部:010-68985541 联系信箱:cp@plaschina.com.cn
广告部/发行部:010-68985253 本系统由北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司设计开发

中国塑料 ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (7): 1-8.DOI: 10.19491/j.issn.1001-9278.2024.07.001
• 材料与性能 • 下一篇
收稿日期:2023-11-22
出版日期:2024-07-26
发布日期:2024-07-24
作者简介:何和智(1963-),博士,教授,从事高分子材料成型加工理论及设备的研究,pmhzhe@scut.edu.cn
基金资助:
HE Hezhi( ), HUANG Zonghai, LAI Wen, XIONG Huawei
), HUANG Zonghai, LAI Wen, XIONG Huawei
Received:2023-11-22
Online:2024-07-26
Published:2024-07-24
摘要:
通过熔融共混法制备了聚乳酸(PLA)和聚己二酸/对苯二甲酸丁二酯(PBAT)的共混物,并添加了不同含量的炭黑(CB)。研究了CB对PLA/PBAT复合材料的微观形貌、流变性能、结晶性能、热稳定性、导电性能和力学性能的影响。结果表明,CB选择性地分布在PBAT相中,且当CB含量高于2 %(质量分数,下同)时,相形态发生了明显的变化。复合材料的黏度随着CB含量的增加而增加。随着CB含量的不断增加,PLA的结晶度先下降再上升。CB能小幅度改善复合材料的热稳定性。适量的CB可以提高复合材料的电导率,并保持良好的力学性能,但过量的CB会大幅度地降低韧性。当CB含量为2 %时,复合材料的拉伸强度、弹性模量和断裂伸长率分别为40.7 MPa、830 MPa和365 %,电导率为8.69×10-7 S/m,比PLA/PBAT的电导率提升了约8个数量级,该复合材料既具有合适的导电性能,又具有优良的力学性能。提供了一种制备具有导电性能的生物基聚合物复合材料的方法,这将有助于可降解材料在防静电包装领域的实际应用。
中图分类号:
何和智, 黄宗海, 赖文, 熊华威. PLA/PBAT/CB防静电包装材料的制备及其性能研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2024, 38(7): 1-8.
HE Hezhi, HUANG Zonghai, LAI Wen, XIONG Huawei. Preparation and properties of PLA/PBAT/CB antistatic packaging materials[J]. China Plastics, 2024, 38(7): 1-8.
| 样品编号 | PLA含量 | PBAT含量 | CB含量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLA/PBAT/0 | 80 | 20 | 0 |
| PLA/PBAT/1 | 79.2 | 19.8 | 1 |
| PLA/PBAT/2 | 78.4 | 19.6 | 2 |
| PLA/PBAT/3 | 77.6 | 19.4 | 3 |
| PLA/PBAT/4 | 76.8 | 19.2 | 4 |
| 样品编号 | PLA含量 | PBAT含量 | CB含量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLA/PBAT/0 | 80 | 20 | 0 |
| PLA/PBAT/1 | 79.2 | 19.8 | 1 |
| PLA/PBAT/2 | 78.4 | 19.6 | 2 |
| PLA/PBAT/3 | 77.6 | 19.4 | 3 |
| PLA/PBAT/4 | 76.8 | 19.2 | 4 |
| 材料 | 表面张力/mN·m-1 | 材料 | 界面张力/mN·m-1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CB⁃PLA | 37.98 | ||||
| PLA | 39.4 | 33.6 | 5.8 | CB⁃PBAT | 35.73 |
| PBAT | 38.4 | 32.1 | 6.3 | PLA⁃PBAT | 0.055 |
| CB | 42.46 | 7.29 | 35.17 | ω | 40.91 |
| 材料 | 表面张力/mN·m-1 | 材料 | 界面张力/mN·m-1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CB⁃PLA | 37.98 | ||||
| PLA | 39.4 | 33.6 | 5.8 | CB⁃PBAT | 35.73 |
| PBAT | 38.4 | 32.1 | 6.3 | PLA⁃PBAT | 0.055 |
| CB | 42.46 | 7.29 | 35.17 | ω | 40.91 |
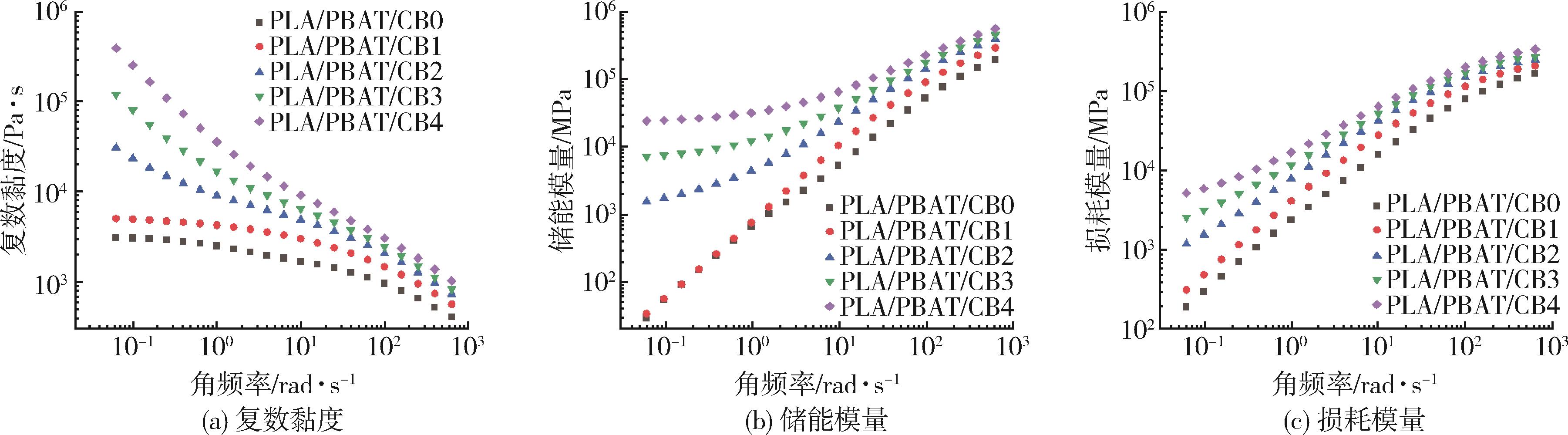
| 样品 | Tc/℃ | ΔHc/J·g-1 | ΔHm/J·g-1 | χc/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA/PBAT/0 | 103.7 | 21.63 | 27.81 | 8.25 |
| PLA/PBAT/1 | 105.7 | 20.31 | 22.94 | 3.55 |
| PLA/PBAT/2 | 106.6 | 20.46 | 23.24 | 3.79 |
| PLA/PBAT/3 | 105.3 | 18.34 | 22.95 | 6.35 |
| PLA/PBAT/4 | 103.6 | 18.72 | 25.55 | 9.50 |
| 样品 | Tc/℃ | ΔHc/J·g-1 | ΔHm/J·g-1 | χc/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA/PBAT/0 | 103.7 | 21.63 | 27.81 | 8.25 |
| PLA/PBAT/1 | 105.7 | 20.31 | 22.94 | 3.55 |
| PLA/PBAT/2 | 106.6 | 20.46 | 23.24 | 3.79 |
| PLA/PBAT/3 | 105.3 | 18.34 | 22.95 | 6.35 |
| PLA/PBAT/4 | 103.6 | 18.72 | 25.55 | 9.50 |
| 样品 | T5 % /℃ | Tmax /℃ | R595 /% |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLA/PBAT/0 | 322.7 | 358.1 | 2.51 |
| PLA/PBAT/1 | 324.5 | 356.9 | 3.83 |
| PLA/PBAT/2 | 326.7 | 358.4 | 4.72 |
| PLA/PBAT/3 | 329 | 359.3 | 5.92 |
| PLA/PBAT/4 | 328.3 | 359.3 | 6.78 |
| 样品 | T5 % /℃ | Tmax /℃ | R595 /% |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLA/PBAT/0 | 322.7 | 358.1 | 2.51 |
| PLA/PBAT/1 | 324.5 | 356.9 | 3.83 |
| PLA/PBAT/2 | 326.7 | 358.4 | 4.72 |
| PLA/PBAT/3 | 329 | 359.3 | 5.92 |
| PLA/PBAT/4 | 328.3 | 359.3 | 6.78 |
| 样品 | 拉伸强度/MPa | 弹性模量/MPa | 断裂伸长率/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLA/PBAT/0 | 45.7±1.5 | 904±38 | 344±15 |
| PLA/PBAT/1 | 44.5±0.8 | 877±33 | 408±10 |
| PLA/PBAT/2 | 40.7±1.0 | 830±37 | 365±23 |
| PLA/PBAT/3 | 40.5±1.7 | 834±32 | 292±35 |
| PLA/PBAT/4 | 43.0±1.2 | 855±35 | 106±24 |
| 样品 | 拉伸强度/MPa | 弹性模量/MPa | 断裂伸长率/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLA/PBAT/0 | 45.7±1.5 | 904±38 | 344±15 |
| PLA/PBAT/1 | 44.5±0.8 | 877±33 | 408±10 |
| PLA/PBAT/2 | 40.7±1.0 | 830±37 | 365±23 |
| PLA/PBAT/3 | 40.5±1.7 | 834±32 | 292±35 |
| PLA/PBAT/4 | 43.0±1.2 | 855±35 | 106±24 |
| 1 | Liu Y, Lu S, Luo J, et al. Research progress of antistatic‐reinforced polymer materials: a review[J]. Polymers for Advanced Technologies, 2023,34(4):1 393⁃1 404. |
| 2 | 石 磊, 尹 波, 田春蓉, 等. 抗静电泡沫塑料[J]. 中国塑料, 2004,18(5):6⁃11. |
| SHI L, YIN B, TIAN C R, et al. Antistatic foam plastics[J]. China Plastics, 2004,18(5):6⁃11. | |
| 3 | Sd Santos M, Montagna L S, Rezende M C, et al. A new use for glassy carbon: development of LDPE/glassy carbon composites for antistatic packaging applications[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2019,136(11):47204. |
| 4 | 杨小龙, 陈文静, 李永青, 等. 导电型聚合物/石墨烯复合材料的研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2022,36(6):165⁃173. |
| YANG X L, CHEN W J, LI Y Q, et al. Research progress in polymer/graphene conductive composites[J]. China Plastics, 2022,36(6):165⁃173. | |
| 5 | Liu Y F, Feng L M, Chen Y F, et al. Segregated polypropylene/cross⁃linked poly(ethylene⁃co-1⁃octene)/multi⁃walled carbon nanotube nanocomposites with low percolation threshold and dominated negative temperature coefficient effect: towards electromagnetic interference shielding and thermistors[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2018,159:152⁃161. |
| 6 | 金燚翥, 孙晓玮, 张晓亮, 等. 导电炭黑的发展现状和行业研究[J]. 炭素, 2023(2): 43⁃46. |
| JIN Y Z, SUN X W, ZHANG X L, et al. Development status and industry research of conductive carbon black[J]. Carbon, 2023(2): 43⁃46. | |
| 7 | Marischal L, Cayla A, Lemort G, et al. Selection of immiscible polymer blends filled with carbon nanotubes for heating applications[J]. Polymers, 2019,11(11):1 827. |
| 8 | 邵琳颖, 郗悦玮, 翁云宣. 可降解聚乳酸复合材料研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2022,36(6):155⁃164. |
| SHAO L Y, XI Y W, WENG Y X. Research progress in degradation characteristics of poly(lactic acid)composites[J]. China Plastics, 2022,36(6):155⁃164. | |
| 9 | 张 禹, 何继敏, 周 麒, 等. PLA与PBAT共混改性研究进展[J]. 工程塑料应用, 2023,51(10): 173⁃178. |
| ZHANG Y, HE J M, ZHOU L, et al. Research progress in PLA and PBAT blending modification[J]. Engineering Plastics Application, 2023,51(10):173⁃178. | |
| 10 | Guo J, Tsou C H, Yu Y, et al. Conductivity and mechanical properties of carbon black⁃reinforced poly(lactic acid) (PLA/CB) composites[J]. Iranian Polymer Journal. 2021,30(12):1 251⁃1 262. |
| 11 | Fd Silva T, Menezes F, Montagna L S, et al. Preparation and characterization of antistatic packaging for electronic components based on poly(lactic acid)/carbon black composites[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2019,136(13):47273. |
| 12 | Xiao Z, Li G, Liu C, et al. The carbon nanotubes effects on the morphology and properties of poly(lactic) acid/poly(butylene adipate‐co‐terephthalate) blends[J]. Polymer Composites, 2022,43(12):8 725⁃8 736. |
| 13 | Harada J M J, Machado G A F, Valenzuela⁃Diaz F, et al. Effects of carbon black incorporation on morphological, mechanical and thermal properties of biodegradable films[R]. Characterization of Minerals, Metals, and Materials, 2016. |
| 14 | Shi Y D, Cheng Y H, Chen Y F, et al. Morphology, rheological and crystallization behavior in thermoplastic polyurethane toughed poly(l⁃lactide) with stereocomplex crystallites[J]. Polymer Testing, 2017,62:1⁃12. |
| 15 | Garlotta D. A literature review of poly(lactic acid) [J]. Journal of Polymers and the Environment, 2001,9(2):22. |
| 16 | Wang Q, Zhang J, Wang X, et al. Significant enhancement of notched Izod impact strength of PLA⁃based blends through encapsulating PA11 particles of low amounts by EGMA elastomer[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2020,526:146657. |
| 17 | Chen Y, Wu Z, Fan Q, et al. Great toughness reinforcement of isotactic polypropylene/elastomer blends with quasi⁃cocontinuous phase morphology by traces of β⁃nucleating agents and carbon nanotubes[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2018,167:277⁃284. |
| 18 | Decol M, Pachekoski W M, Segundo E H, et al. Effects of processing conditions on hybrid filler selective localization, rheological, and thermal properties of poly(ε‐caprolactone)/poly(lactic acid) blends[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2020,137(20):48711. |
| 19 | Zolali A M, Favis B D. Partial to complete wetting transitions in immiscible ternary blends with PLA: the influence of interfacial confinement[J]. Soft Matter, 2017,13(15):2 844⁃2 856. |
| 20 | Stammitti⁃Scarpone A, Acosta E J. Solid⁃liquid⁃liquid wettability and its prediction with surface free energy models[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2019,264:28⁃46. |
| 21 | Jalali Dil E, Favis B D. Localization of micro⁃ and nano⁃silica particles in heterophase poly(lactic acid)/poly(butylene adipate⁃co⁃terephthalate) blends[J]. Polymer, 2015,76:295⁃306. |
| 22 | Mezgebe M, Shen Q, Zhang J Y, et al. Liquid adsorption behavior and surface properties of carbon blacks[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2012,403:25⁃28. |
| 23 | Zhan Z, He H, Zhu Z, et al. Blends of rABS and SEBS: influence of in⁃situ compatibilization on the mechanical properties[J]. Materials, 2019,12:2352. |
| 24 | Ren D, Zheng S, Wu F, et al. Formation and evolution of the carbon black network in polyethylene/carbon black composites: rheology and conductivity properties[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2014,131(7):39953. |
| 25 | Chenal J M, Chazeau L, Bomal Y, et al. New insights into the cold crystallization of filled natural rubber[J]. Journal of Polymer Science Part B: Polymer Physics, 2007,45(8):955⁃962. |
| 26 | Ahmad I A, Kim H K, Deveci S, et al. Non⁃isothermal crystallisation kinetics of carbon black⁃ graphene⁃based multimodal⁃polyethylene nanocomposites[J]. Nanomaterials, 2019,9(1):110. |
| 27 | Knyazheva O A, Kokhanovskaya O A, Vasilevich A V, et al. Thermal stability of sulfonated carbon black[J]. Thermochimica Acta, 2023,728:179593. |
| 28 | Association Standard ESD. For the protection of electrostatic discharge susceptible items⁃packaging materials for ESD sensitive items [S]. New York, 2008, 25. |
| 29 | Koopmans M, Leiviskä MAT, Liu J, et al. Electrical conductivity of doped organic semiconductors limited by carrier⁃carrier interactions[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2020,12(50):56 222⁃56 230. |
| 30 | Laredo E, Bello A, Diaz J, et al. Effect of cold⁃crystallization on the AC and DC conductive properties of polylactide biocomposites with carboxylic or neat large aspect ratio MWCNT[J]. Polymer Composites, 2013,34(1):67⁃76. |
| 31 | Xiao X, Chevali V S, Song P, et al. Enhanced toughness of PLLA/PCL blends using poly(d⁃lactide)⁃poly(ε⁃caprolactone)⁃poly(d⁃lactide) as compatibilizer[J]. Composites Communications, 2020,21:100385. |
| [1] | 胡永祥, 谢纪岭, 李伟铭, 张璐, 汤香港, 吕亿同, 申红望, 鞠冠男. 马来酸酐接枝改性GTR对聚乳酸性能的影响[J]. 中国塑料, 2024, 38(7): 20-24. |
| [2] | 魏佳, 刘凯, 彭丽娟, 田阳阳, 赵琳, 李艳红, 杨佩佩, 李松伟, 陆波. 壳聚糖/聚苯胺⁃氧化石墨烯尼古丁分子印迹复合材料的制备与吸附性能研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2024, 38(7): 32-36. |
| [3] | 王杰, 辛德华, 李晖, 蒋洪石, 周洪福, 赵建国. 纳米黏土与二氧化硅协同改性聚乳酸研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2024, 38(7): 43-48. |
| [4] | 徐琛, 骆博飞, 刘腾腾, 邢晶凯. 成核剂改性聚丙烯研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2024, 38(7): 79-85. |
| [5] | 王珅, 刘宣伯, 张艳芳, 贾雪飞, 祝桂香, 张龙贵. 生物可降解无纺布材料研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2024, 38(7): 86-92. |
| [6] | 刘莹, 孙昊, 杨勇, 姜开宇, 于同敏, 马赛, 祝铁丽. 超声振动对玻璃纤维增强聚酰胺6注塑制件力学性能的影响[J]. 中国塑料, 2024, 38(7): 9-14. |
| [7] | 牛荷, 吕明福, 张宗胤, 徐耀辉, 许巍, 张师军, 郭鹏. 聚乙醇酸加工技术中助剂的应用进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2024, 38(6): 105-110. |
| [8] | 杨莲, 蒋晶, 贾彩宜, 谢悦涵, 王小峰, 李倩. 聚酰胺6微纤增强聚丙烯复合材料制备及化学注塑发泡性能研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2024, 38(6): 12-18. |
| [9] | 曹帅, 姜涛, 刘雄, 王瑛, 李文戈, 吴新锋. MXene导热复合材料的制备研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2024, 38(6): 139-144. |
| [10] | 周紫怡, 王洋样, 孙滔, 蒋伟, 董同力嘎, 云雪艳. 聚(己二酸/对苯二甲酸)⁃丁二醇酯基自发气调薄膜的性能研究及应用[J]. 中国塑料, 2024, 38(6): 31-38. |
| [11] | 董亚鹏, 赵恬娇, 王美珍, 崔文举, 林福华, 王波. 长链脂肪酸钠/芳基酰胺脂肪酸钠复配成核剂对聚丙烯性能影响研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2024, 38(6): 60-65. |
| [12] | 王涵, 梁金华, 高振国, 姜炜, 周昊. 微胶囊型自修复环氧树脂材料的力学性能及修复效率[J]. 中国塑料, 2024, 38(5): 40-46. |
| [13] | 张之琪, 王向东, 刘海明, 陈士宏. 聚酰胺弹性体对生物基聚酰胺56和聚酰胺66共混物的增韧改性及其发泡行为研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2024, 38(5): 55-60. |
| [14] | 孛海娃, 赵中国, 王筹萱, 薛嵘. 高导电、低逾渗PLA/CNTs导电复合材料的结构设计及性能研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2024, 38(4): 13-18. |
| [15] | 赵小红, 卢杏. 淀粉的改性及其对淀粉/PBAT/碳酸钙复合材料结构和性能的影响[J]. 中国塑料, 2024, 38(4): 40-46. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2
京公网安备11010802034965号
京ICP备13020181号-2