京ICP备13020181号-2
© 《China Plastics》
© 《China Plastics》

China Plastics ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (12): 84-90.DOI: 10.19491/j.issn.1001-9278.2023.12.013
• Plastic and Environment • Previous Articles Next Articles
HUO Zhanbin, FU Ye( ), WENG Yunxuan
), WENG Yunxuan
Received:2023-06-21
Online:2023-12-26
Published:2023-12-26
CLC Number:
HUO Zhanbin, FU Ye, WENG Yunxuan. Degradation behaviors of PBAT biodegradable mulch film in farmland soil and simulated soil environments[J]. China Plastics, 2023, 37(12): 84-90.
| 样品 | 降解前 | 农田土壤环境降解60天 | 模拟土壤环境降解90天 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Td,5 %/℃ | Td,max/℃ | 灰分含量/% | Td,5 %/℃ | Td,max/℃ | 灰分含量/% | Td,5 %/℃ | Td,max/℃ | 灰分含量/% | |
| LN⁃1 | 351 | 415 | 10 | 332 | 413 | 36 | 322 | 412 | 27 |
| LN⁃2 | 320 | 415 | 11 | 318 | 413 | 41 | 316 | 412 | 48 |
| LN⁃3 | 348 | 413 | 9 | 319 | 412 | 53 | 300 | 411 | 52 |
| LN⁃4 | 322 | 413 | 9 | 321 | 412 | 36 | 314 | 410 | 33 |
| LN⁃5 | 338 | 412 | 9 | 320 | 408 | 41 | 310 | 408 | 42 |
| LN⁃6 | 331 | 412 | 10 | 323 | 407 | 22 | 323 | 408 | 27 |
| 样品 | 降解前 | 农田土壤环境降解60天 | 模拟土壤环境降解90天 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Td,5 %/℃ | Td,max/℃ | 灰分含量/% | Td,5 %/℃ | Td,max/℃ | 灰分含量/% | Td,5 %/℃ | Td,max/℃ | 灰分含量/% | |
| LN⁃1 | 351 | 415 | 10 | 332 | 413 | 36 | 322 | 412 | 27 |
| LN⁃2 | 320 | 415 | 11 | 318 | 413 | 41 | 316 | 412 | 48 |
| LN⁃3 | 348 | 413 | 9 | 319 | 412 | 53 | 300 | 411 | 52 |
| LN⁃4 | 322 | 413 | 9 | 321 | 412 | 36 | 314 | 410 | 33 |
| LN⁃5 | 338 | 412 | 9 | 320 | 408 | 41 | 310 | 408 | 42 |
| LN⁃6 | 331 | 412 | 10 | 323 | 407 | 22 | 323 | 408 | 27 |
| 样品 | 降解前结晶率/% | 降解30天结晶率/% | 降解60天结晶率/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| LN⁃1 | 12.88 | 18.02 | 23.04 |
| LN⁃2 | 11.00 | 11.36 | 17.32 |
| LN⁃3 | 11.56 | 18.81 | 25.50 |
| LN⁃4 | 10.38 | 13.02 | 29.22 |
| LN⁃5 | 15.88 | 17.27 | 18.86 |
| LN⁃6 | 13.80 | 22.88 | 26.88 |
| 样品 | 降解前结晶率/% | 降解30天结晶率/% | 降解60天结晶率/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| LN⁃1 | 12.88 | 18.02 | 23.04 |
| LN⁃2 | 11.00 | 11.36 | 17.32 |
| LN⁃3 | 11.56 | 18.81 | 25.50 |
| LN⁃4 | 10.38 | 13.02 | 29.22 |
| LN⁃5 | 15.88 | 17.27 | 18.86 |
| LN⁃6 | 13.80 | 22.88 | 26.88 |
| 样品 | 0天 | 30天 | 60天 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn/kDa | PDI | Mn/kDa | PDI | Mn/kDa | PDI | |
| LN⁃1 | 57 | 1.9 | 47 | 2.0 | 40 | 2.0 |
| LN⁃2 | 57 | 1.7 | 44 | 1.9 | 30 | 1.9 |
| LN⁃3 | 48 | 1.9 | 37 | 2.0 | 36 | 2.0 |
| LN⁃4 | 49 | 1.9 | 35 | 2.0 | 31 | 2.0 |
| LN⁃5 | 43 | 1.6 | 32 | 1.7 | 31 | 1.7 |
| LN⁃6 | 42 | 1.7 | 30 | 1.8 | 29 | 1.8 |
| 样品 | 0天 | 30天 | 60天 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn/kDa | PDI | Mn/kDa | PDI | Mn/kDa | PDI | |
| LN⁃1 | 57 | 1.9 | 47 | 2.0 | 40 | 2.0 |
| LN⁃2 | 57 | 1.7 | 44 | 1.9 | 30 | 1.9 |
| LN⁃3 | 48 | 1.9 | 37 | 2.0 | 36 | 2.0 |
| LN⁃4 | 49 | 1.9 | 35 | 2.0 | 31 | 2.0 |
| LN⁃5 | 43 | 1.6 | 32 | 1.7 | 31 | 1.7 |
| LN⁃6 | 42 | 1.7 | 30 | 1.8 | 29 | 1.8 |
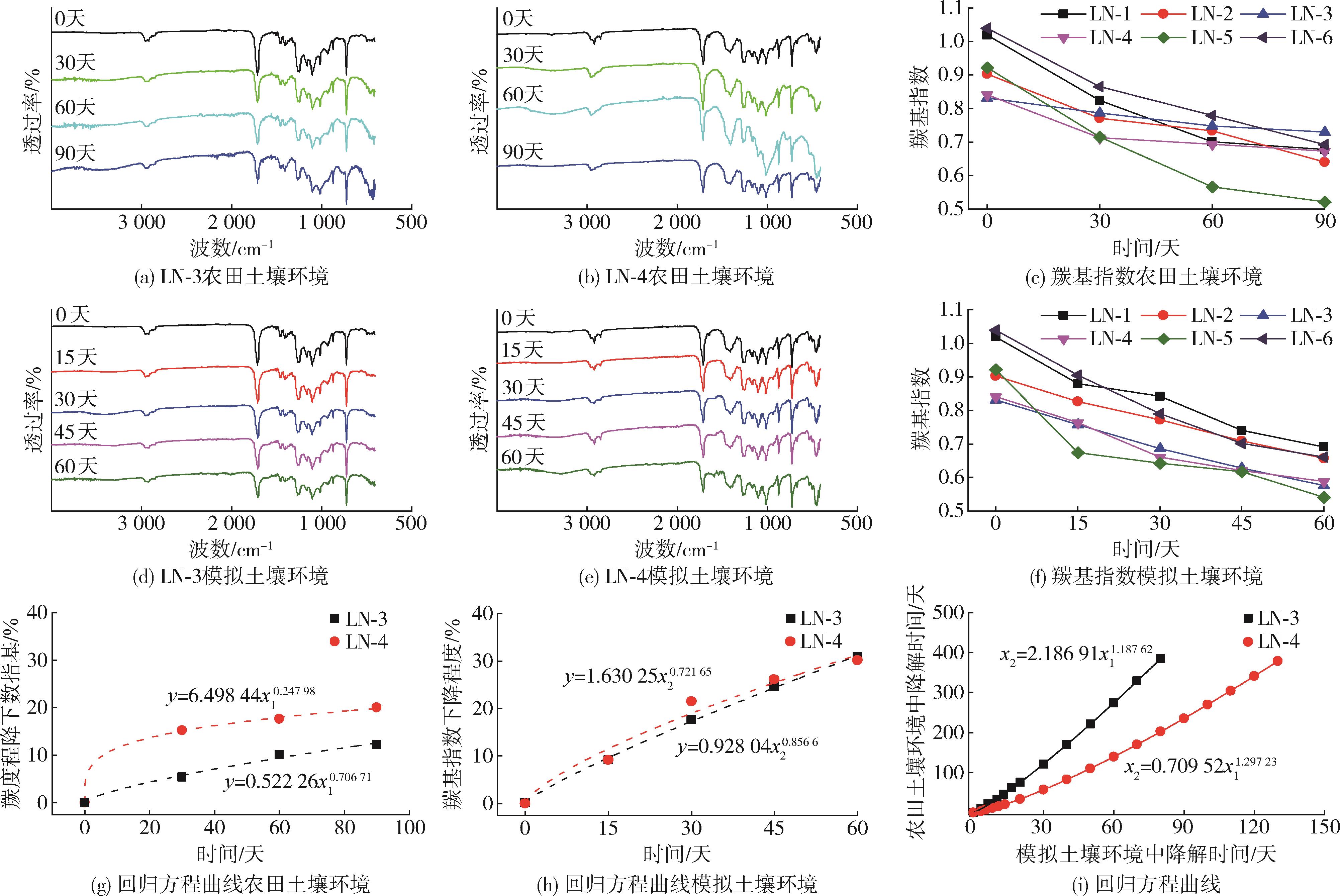
| 环境 | 类型 | LN⁃3 | LN⁃4 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 方程 | R2 | 方程 | R2 | ||
| 农田土壤 | 线性方程 | y=0.138 2t+0.711 4 | 0.969 | y=0.208 1t+3.855 4 | 0.965 |
| 指数方程 | y=100(1-e-0.001 58t ) | 0.969 | y=100(1-e-0.002 99t ) | 0.760 | |
| 幂函数方程 | y=0.522 26t0.706 71 | 0.988 | y=6.498 44t0.247 98 | 0.998 | |
| 模拟土壤 | 线性方程 | y=0.512 5t+0.939 8 | 0.994 | y=0.5145t+1.930 3 | 0.953 |
| 指数方程 | y =100(1-e-0.0062t ) | 0.999 | y=100(1-e-0.006 58t ) | 0.969 | |
| 幂函数方程 | y =0.928 04t0.856 6 | 0.999 | y=1.630 25t0.721 65 | 0.971 | |
| 环境 | 类型 | LN⁃3 | LN⁃4 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 方程 | R2 | 方程 | R2 | ||
| 农田土壤 | 线性方程 | y=0.138 2t+0.711 4 | 0.969 | y=0.208 1t+3.855 4 | 0.965 |
| 指数方程 | y=100(1-e-0.001 58t ) | 0.969 | y=100(1-e-0.002 99t ) | 0.760 | |
| 幂函数方程 | y=0.522 26t0.706 71 | 0.988 | y=6.498 44t0.247 98 | 0.998 | |
| 模拟土壤 | 线性方程 | y=0.512 5t+0.939 8 | 0.994 | y=0.5145t+1.930 3 | 0.953 |
| 指数方程 | y =100(1-e-0.0062t ) | 0.999 | y=100(1-e-0.006 58t ) | 0.969 | |
| 幂函数方程 | y =0.928 04t0.856 6 | 0.999 | y=1.630 25t0.721 65 | 0.971 | |
| 1 | SOMANATHAN H, SATHASIVAM R, SIVARAM S, et al. An update on polyethylene and biodegradable plastic mulch films and their impact on the environment[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 307(3): 135839. |
| 2 | QI Y, BERIOT N, GORT G, et al. Impact of plastic mulch film debris on soil physicochemical and hydrological properties[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 266(3): 115097. |
| 3 | 翁小倩,谢 茵.全生物降解地膜降解性能对土壤温度、豇豆生长及产量的影响[J].农业科技通讯,2022(9):135⁃140. |
| WENG X Q, XIE Y. Effects of biodegradable mulch on soil temperature, cowpea growth and yield[J]. Bulletin of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022(9): 135⁃140. | |
| 4 | ZHANG M M, XUE Y H, JIN T, et al. Effect of long⁃term biodegradable film mulch on soil physicochemical and microbial properties[J]. Toxics, 2022, 10(3): 129. |
| 5 | 张 婷,张彩丽,宋鑫宇,等.PBAT薄膜的制备及应用研究进展[J].中国塑料,2021,35(7):115⁃125. |
| ZHANG T, ZHANG C L, SONG X Y, et al. Research progress in preparation and application of PBAT films[J]. China Plastics, 2021,35(7):115⁃125. | |
| 6 | BAI J, PEI H J, ZHOU X P, et al. Reactive compatibilization and properties of low⁃cost and high⁃performance PBAT/thermoplastic starch blends[J]. European Polymer Journal, 2021, 143(1): 110198. |
| 7 | FU Y, WU G, BIAN X C, et al. Biodegradation behavior of poly(butylene adipate⁃co⁃terephthalate) (PBAT), poly(lactic acid) (PLA), and their blend in freshwater with sediment[J]. Molecules, 2020, 25(17): 3 946. |
| 8 | LIU B, GUAN T H, WU G, et al. Biodegradation behavior of degradable mulch with poly(butylene adipate⁃co⁃terephthalate) (PBAT) and poly(butylene succinate) (PBS) in simulation marine environment[J]. Polymers, 2022, 14(8): 1 515. |
| 9 | WENG Y X, JIN Y J, MENG Q Y, et al. Biodegradation behavior of poly(butylene adipate⁃co⁃terephthalate) (PBAT), poly(lactic acid) (PLA), and their blend under soil conditions[J]. Polymer Testing, 2013, 32(5): 918⁃926. |
| 10 | QIAO R M, HAO C P, LIU J L, et al. Synthesis of novel ultraviolet absorbers and preparation and field application of anti⁃ultraviolet aging PBAT/UVA films[J]. Polymers, 2022, 14(7): 1 434. |
| 11 | DE FALCO F, AVOLIO R, ERRICO M E, et al. Comparison of biodegradable polyesters degradation behavior in sand[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021. 416: 126231. |
| 12 | 朱 捷.松嫩平原旱作农田土壤CO2排放规律及碳足迹研究[D].东北农业大学,2015. |
| [1] | . Synthesis and characterizations of poly(butylene succinate-co-butylene adipate) [J]. , 2023, 37(5): 34-39. |
| [2] | GAO Qiqi, HAO Yanling, CHENG Long, SONG Xiaoshuang, WANG Shihui. Preparation and performance of corn starch/TiO2 nanocomposite films [J]. China Plastics, 2023, 37(2): 45-50. |
| [3] | SUN Wenxiao, YANG Fan, HOU Mengzong, HE Dandan, WU Hui, LIU Qiang, ZHANG Hong. Microplastic pollution and degradation in environment [J]. China Plastics, 2023, 37(11): 117-126. |
| [4] | ZHOU Ziyu, SANG Xiaoming, GENG Xu, CHEN Xinggang. Research progress in thermosetting resins containing Schiff base structure [J]. China Plastics, 2023, 37(11): 163-169. |
| [5] | MA Chao, MA Lanrong, WEI Liao, YIN Huibo, LIN Xiang. A review of modification processing and water⁃soluble degradation ability of polyglycolic acid material [J]. China Plastics, 2022, 36(9): 74-84. |
| [6] | MA Guocheng, HE Zhen, CHEN Shaojun. Research progress in degradability of cellulose acetate [J]. China Plastics, 2022, 36(9): 111-121. |
| [7] | LIN Jianhui, LU Jiahui, WU Xinying, FAN Xueying, DENG Guirong, GAO Liang, MEI Chengfang, YANG Yonggang. Study of uncertainty evaluation in determination of ultimate aerobic biodegradability of degradable materials under controlled composting conditions [J]. China Plastics, 2022, 36(9): 140-147. |
| [8] | WU Xiongjie, ZHU Dongbo, SUN Jiangbo, GAO Longmei, CHU Yu, CHENG Jinsong, XIE Aidi. Study on application performance of polyethylene/CaSO4 nanoparticle composite flexible packaging [J]. China Plastics, 2022, 36(6): 10-15. |
| [9] | JI Feng, GONG Weihua, ZHANG Yan, LUO Shuiyuan, YU Qingyu, ZHU Junqiu, GUO Jiangbin. Preparation of biodegradable PBAT foaming particles by supercritical carbon dioxide autoclave foaming technology [J]. China Plastics, 2022, 36(5): 122-126. |
| [10] | WEI Liao. Research progress in application of water⁃soluble polymer materials for oil and gas field fracturing [J]. China Plastics, 2022, 36(5): 149-157. |
| [11] | LIU Qiang, LU Yahong, WU Hui, MA Yuhao, ZHANG Yupeng, SUN Wenxiao, ZHANG Hong. Microbial degradation of polyethylene plastics [J]. China Plastics, 2022, 36(3): 120-126. |
| [12] | SUI Zhenquan, MAO Jinchao, FAN Jinshi. Preparation and applications of chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) liquid mulch films [J]. China Plastics, 2022, 36(3): 21-25. |
| [13] | JIN Qingping, YI Jianming, GAO Yonghong, CAO Nannan, DENG Siyuan. Effect on mechanical properties of glass⁃fiber⁃reinforcement polymer bars exposure to alkaline solution under natural ambient temperature [J]. China Plastics, 2022, 36(2): 89-95. |
| [14] | HE Xuetao, ZHANG Yi, MO Zhenyu, LI Changjin, WANG Shuo, YANG Weimin, LI Haoyi. Preparation process of PBAT fiber membrane by melt differential electrospinning [J]. China Plastics, 2022, 36(12): 1-5. |
| [15] | LI Wanlong, YANG Weimin, LAN Tianjie, LI Haoyi, DING Yumei, QIU Yonghong. Research progress in supercritical fluid application in plastic processing [J]. China Plastics, 2022, 36(11): 112-117. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||