京ICP备13020181号-2
© 《China Plastics》
© 《China Plastics》

China Plastics ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (12): 155-166.DOI: 10.19491/j.issn.1001-9278.2022.12.021
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Weimeng, WANG Jie, HU Jing( )
)
Received:2022-09-03
Online:2022-12-26
Published:2022-12-20
CLC Number:
ZHANG Weimeng, WANG Jie, HU Jing. Research progress in effect of pore structure on performance of 3D printed bone tissue scaffolds[J]. China Plastics, 2022, 36(12): 155-166.
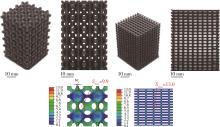
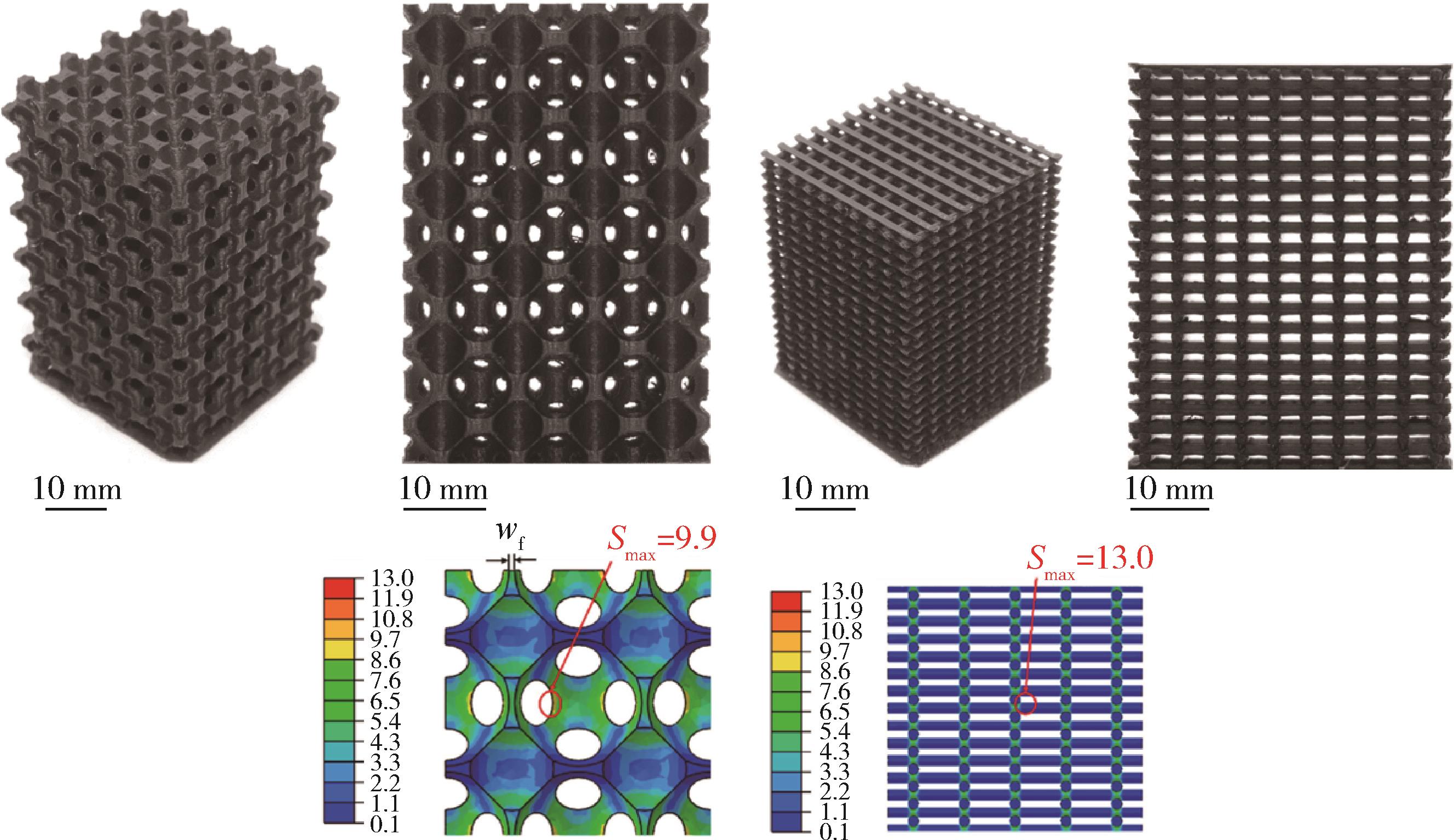
| 1 | Gleadall A, Visscher D, Yang J, et al. Review of additive manufactured tissue engineering scaffolds: relationship between geometry and performance[J]. Burns & Trauma, 2018, 6. |
| 2 | 邵惠锋,贺 永,傅建中.增材制造可降解人工骨的研究进展——从外形定制到性能定制[J].浙江大学学报(工学版),2018,52(06):1 035⁃1 057. |
| SHAO H F, HE Y, FU J Z. Research advance of degradable artificial bone with additive manufacturing: customization from geometric shape to property[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University(Engineering Science),2018,52(06):1 035⁃1 057. | |
| 3 | Entezari A, Roohani I, Li G, et al. Architectural design of 3D printed scaffolds controls the volume and functionality of newly formed bone[J]. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2019, 8(1): 1801353. |
| 4 | 于 强,田 京.构建骨组织工程支架中应用的3D打印技术[J].中国组织工程究,2015,19(30):4 870⁃4 875. |
| YU Q, TIAN J. Application of three⁃dimensional printing technique in manufacturing scaffolds for bone tissue engineering[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research,2015,19(30):4 870⁃4 875. | |
| 5 | 梁浩文,王 月,陈小腾 等.3D打印生物陶瓷人工骨支架的研究进展[J].粉末冶金技术,2022,40(02):100⁃109+117.DOI:10.19591/j.cnki.cn11-1974/tf.2021030040 . |
| LIANG H W, WANG Y, CHEN X T, et al. Progress of 3D printing bioceramic on artificial bone scaffolds[J]. Powder Metallurgy Technology,2022,40(02):100⁃109+117.DOI:10.19591/j.cnki.cn11-1974/tf.2021030040 . | |
| 6 | Hong N, Yang G H, Lee J, et al. 3D bioprinting and its in vivo applications[J]. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater, 2018, 106(1): 444⁃459. |
| 7 | Xu Y, Zhang F, Zhai W, et al. Unraveling of advances in 3D⁃printed polymer⁃based bone scaffolds[J]. Polymers, 2022, 14(3): 566. |
| 8 | Gregor A, Filova E, Novak M, et al. Designing of PLA scaffolds for bone tissue replacement fabricated by ordinary commercial 3D printer[J]. Journal of Biological Engineering, 2017, 11(1): 1⁃21. |
| 9 | Ghayor C, Bhattacharya I, Guerrero J, et al. 3D⁃printed HA⁃based scaffolds for bone regeneration: microporosity, osteoconduction and osteoclastic resorption[J]. Materials, 2022, 15(4): 1 433. |
| 10 | 田 冶,曾庆慧,胡相华 等.3D打印技术及在组织工程领域的研究进展[J].中国医疗器械信息,2015,21(08):7⁃12.DOI:10.15971/j.cnki.cmdi.2015.08.002 . |
| TIAN Y, ZENG Q H, HU X H, et al. The principle of 3D printing technology and its research progress in tissue engineering[J]. China Medical Device Information,2015,21(08):7⁃12.DOI:10.15971/j.cnki.cmdi.2015.08.002 . | |
| 11 | Loh Q L, Choong C. Three⁃dimensional scaffolds for tissue engineering applications: role of porosity and pore size[J]. Tissue Eng Part B Rev, 2013, 19(6): 485⁃502. |
| TIAN Y, ZENG Q H, HU X H, et al. The principle of 3D printing technology and its research progress in tissue engineering[J]. China Medical Device Information,2015,21(08):7⁃12.DOI:10.15971/j.cnki.cmdi.2015.08.002 . | |
| 12 | Rezania N, Asadi⁃Eydivand M, Abolfathi N, et al. Three⁃dimensional printing of polycaprolactone/hydroxyapatite bone tissue engineering scaffolds mechanical properties and biological behavior[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine, 2022, 33(3): 1⁃14. |
| 13 | 马哲一. 骨组织工程支架内微流体流动状态的数值仿真及分析[D].秦皇岛:燕山大学,2009. |
| 14 | 王 凯,郑 爽,潘 肃,等.制备3D打印骨组织工程支架修复骨缺损的特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(34):5 516⁃5 522. |
| WANG K, ZHENG S, PAN S, et al. Preparation of 3D printed bone tissue engineering scaffold[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research,2019,23(34):5 516⁃5 522. | |
| 15 | 付 华. 聚醚醚酮/羟基磷灰石复合粉末的制备及性能研究[D].武汉:武汉工程大学,2015. |
| 16 | 卓 越. 可降解骨骼生物支架结构设计与制备方法研究[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学,2017. |
| 17 | 王 进,葛建飞,郭开今,等.3D打印多孔材料应用于骨缺损修复的研究进展[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2019,12(07):556⁃560. |
| WANG J, GE J F, GUO K J, et al. Research progress of 3D printing porous biomaterials for bone defect repair[J]. Chinese Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery,2019,12(07):556⁃560. | |
| 18 | 党 莹,李 月,李瑞玉,等.骨组织工程支架材料在骨缺损修复及3D打印技术中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(14):2 266⁃2 273. |
| DANG Y, LI Y, LI R Y, et al. Three⁃dimensional printing technology preparation of bone tissue engineering scaffold materials in bone defect repair[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research,2017,21(14):2 266⁃2 273. | |
| 19 | 许晓茗. 基于3D打印技术制备Gel/n⁃HA/PLGA骨组织工程支架的研究[D].泉州:华侨大学,2018. |
| 20 | 赵 帝. 仿生人工骨3D打印流场仿真分析及试件力学性能研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2015. |
| 21 | 孙开瑜. 面向牙槽骨修复的3D打印技术研究[D].杭州:杭州电子科技大学,2018. |
| 22 | 李 洋. 激光增材制造(3D打印)制备生物医用多孔金属工艺及组织性能研究[D].苏州:苏州大学,2015. |
| 23 | 易 涛. 基于3D打印的钛合金骨支架表面微结构的设计制造及性能研究[D].成都:四川大学,2021.DOI:10.27342/d.cnki.gscdu.2021.000618 . |
| 24 | 张继坤,乌日开西·艾依提,阿依古丽·喀斯木,等.3D打印聚醚醚酮复合材料人工骨的成型参数优化[J].西安交通大学学报,2022,56(08):22⁃31. |
| ZHANG J K, WURIKAIXI A, AYIGULI K, et al. Optimization of printing parameters of 3D printed polyetheretherketone composite artificial bone[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University,2022,56(08):22⁃31. | |
| 25 | 张旭婧. 3D同轴打印组织工程骨支架成型工艺与实验研究[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆大学,2017. |
| 26 | 陈艺菲,郑赛男,阙 林.3D打印复合材料骨组织工程支架及其在颌面骨再生中的研究进展[J].山东医药,2022,62(25):83⁃86. |
| CHEN Y F, ZHENG S N, QUE L. Advances in 3D printed composite bone tissue engineering scaffolds and their use in maxillofacial bone regeneration[J]. Shandong Medical Journal,2022,62(25):83⁃86. | |
| 27 | Kelly C N, Miller A T, Hollister S J, et al. Design and structure⁃function characterization of 3D printed synthetic porous biomaterials for tissue engineering[J]. Adv Healthc Mater, 2018, 7(7): e1701095. |
| 28 | Pereira T F, Silva M a C, Oliveira M F, et al. Effect of process parameters on the properties of selective laser sintered Poly(3⁃hydroxybutyrate) scaffolds for bone tissue engineering[J]. Virtual and Physical Prototyping, 2012, 7(4): 275⁃285. |
| 29 | 向声燚. HA/PCL骨组织工程支架3D打印工艺及性能研究[D].北京:北京化工大学,2019.DOI:10.26939/d.cnki.gbhgu.2019.000930 . |
| 30 | 宋春艳,马思佳,钱 明.3D生物打印中细胞活力的研究进展[J].中国生物制品学杂志,2021,34(07):873⁃877.DOI:10.13200/j.cnki.cjb.003384 . |
| SONG C Y, MA S J, QIAN M. Progress in research on cell viability in 3D bioprinting[J]. Chinese Journal of Biologicals,2021,34(07):873⁃877.DOI:10.13200/j.cnki.cjb.003384 . | |
| 31 | Shi J, Yang J, Zhu L, et al. A porous scaffold design method for bone tissue engineering using triply periodic minimal surfaces[J]. Ieee Access, 2018, 6: 1 015⁃1 022. |
| 32 | Bahraminasab M. Challenges on optimization of 3D⁃printed bone scaffolds[J]. Biomed Eng Online, 2020, 19(1): 69. |
| 33 | Domingos M, Intranuovo F, Russo T, et al. he first systematic analysis of 3D rapid prototyped poly (ε⁃caprolactone) scaffolds manufactured through BioCell printing: the effect of pore size and geometry on compressive mechanical behaviour and in vitro hMSC viability[J]. Biofabrication, 2013, 5(4): 045004. |
| 34 | Hung K, Chen M, Lan W, et al. Three⁃dimensional printing of a hybrid bioceramic and biopolymer porous scaffold for promoting bone regeneration potential[J]. Materials, 2022, 15(5): 1971. |
| 35 | Kou X Y, Tan S T. A simple and effective geometric representation for irregular porous structure modeling[J]. Computer⁃Aided Design, 2010, 42(10): 930⁃941. |
| 36 | 杜 岳. 应用于骨科的可控不规则多孔结构的设计与性能研究[D].南京:南京航空航天大学,2020.DOI:10.27239/d.cnki.gnhhu.2020.001388 . |
| 37 | Diez⁃Escudero A, Harlin H, Isaksson P, et al. Porous polylactic acid scaffolds for bone regeneration: A study of additively manufactured triply periodic minimal surfaces and their osteogenic potential[J]. J Tissue Eng, 2020, 11: 2041731420956541. |
| 38 | Montazerian H, Zhianmanesh M, Davoodi E, et al. Longitudinal and radial permeability analysis of additively manufactured porous scaffolds: Effect of pore shape and porosity[J]. Materials & Design, 2017, 122: 146⁃156. |
| 39 | Foroughi A H, Razavi M J. Shape optimization of orthopedic porous scaffolds to enhance mechanical performance[J]. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2022, 128: 105098. |
| 40 | Tang M S, Abdul Kadir A Z, Ngadiman N H A. Simulation analysis of different bone scaffold porous structures for fused deposition modelling fabrication process[J]. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2020, 788(1): 012023. |
| 41 | Adachi T, Osako Y, Tanaka M, et al. Framework for optimal design of porous scaffold microstructure by computational simulation of bone regeneration[J]. Biomaterials, 2006, 27(21): 3 964⁃3 972. |
| 42 | Hollister S J L C Y, Saito E, et al. Engineering craniofacial scaffolds[J]. Orthodontics & craniofacial research, 2005, 8(3): 162⁃173. |
| 43 | Gong B, Cui S, Zhao Y, et al. Strain⁃controlled fatigue behaviors of porous PLA⁃based scaffolds by 3D⁃printing technology[J]. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed, 2017, 28(18): 2 196⁃2 204. |
| 44 | Theodoridis K, Aggelidou E, Vavilis T, et al. Hyaline cartilage next generation implants from adipose⁃tissue⁃derived mesenchymal stem cells: Comparative study on 3D⁃printed polycaprolactone scaffold patterns[J]. Journal of Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine, 2019, 13(2): 342⁃355. |
| 45 | Tang M S, Kadir A Z A, Ngadiman N H A, et al. Simulation analysis of different bone scaffold porous structures for fused deposition modelling fabrication process[C]. 5th International Conference on Mechanical Engineering Research (ICMER), 2019. |
| 46 | Liang H, Wang Y, Chen S, et al. Nano⁃Hydroxyapatite Bone Scaffolds with Different Porous Structures Processed by Digital Light Processing 3D Printing[J]. International journal of bioprinting, 2022, 8(1): 502⁃502. |
| 47 | Liebschner M a K, Wettergreen M. Scaffold pore space modulation through intelligent design of dissolvable microparticles[J]. Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, N J), 2012, 868: 71⁃89. |
| 48 | Cho Y S, Gwak S J, Cho Y S. Fabrication of Polycaprolactone/Nano Hydroxyapatite (PCL/nHA) 3D Scaffold with Enhanced In Vitro Cell Response via Design for Additive Manufacturing (DfAM)[J]. Polymers, 2021, 13(9): 1394. |
| 49 | 王中汉,王辰宇,刘 贺,等.3D打印钛合金孔隙支架骨长入影响因素的分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(52):7 821⁃7 828. |
| WANG Z H, WANG C Y, LIU H, et al. Effects of three⁃dimensional printed porous titanium scaffolds on bone ingrowth[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research,2016,20(52):7 821⁃7 828. | |
| 50 | Qin H, Wei Y, Han J, et al. 3D printed bioceramic scaffolds: Adjusting pore dimension is beneficial for mandibular bone defects repair[J]. Journal of Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine, 2022, 16(4): 409⁃421. |
| 51 | Wang P, Hu J, Ma P X. The engineering of patient⁃specific, anatomically shaped, digits[J]. Biomaterials, 2009, 30(14): 2 735⁃2 740. |
| 52 | Wang Z, Wang C, Li C, et al. Analysis of factors influencing bone ingrowth into three⁃dimensional printed porous metal scaffolds: A review[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 717: 271⁃285. |
| 53 | Wang C, Xu D, Lin L, et al. Large⁃pore⁃size Ti6Al4V scaffolds with different pore structures for vascularized bone regeneration[J]. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl, 2021, 131: 112499. |
| 54 | Narra N, Blanquer S B G, Haimi S P, et al. mu CT based assessment of mechanical deformation of designed PTMC scaffolds[J]. Clinical Hemorheology and Microcirculation, 2015, 60(1): 99⁃108. |
| 55 | Taniguchi N, Fujibayashi S, Takemoto M, et al. Effect of pore size on bone ingrowth into porous titanium implants fabricated by additive manufacturing: An in vivo experiment[J]. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl, 2016, 59: 690⁃701. |
| 56 | Velioglu Z B, Pulat D, Demirbakan B, et al. 3D⁃printed poly(lactic acid) scaffolds for trabecular bone repair and regeneration: scaffold and native bone characterization[J]. Connect Tissue Res, 2019, 60(3): 274⁃282. |
| 57 | Shaunak S, Dhinsa B S, Khan W S. The role of 3D modelling and printing in orthopaedic tissue engineering: a review of the current literature[J]. Current Stem Cell Research & Therapy, 2017, 12(3): 225⁃232. |
| 58 | Karageorgiou V, Kaplan D. Porosity of 3D biomaterial scaffolds and osteogenesis[J]. Biomaterials, 2005, 26(27): 5 474⁃5 491. |
| 59 | Fierz F C, Beckmann F, Huser M, et al. The morphology of anisotropic 3D⁃printed hydroxyapatite scaffolds[J]. Biomaterials, 2008, 29(28): 3 799⁃3 806. |
| 60 | Sudarmadji N, Chua C K, Leong K F. The development of computer⁃aided system for tissue scaffolds (CASTS) system for functionally graded tissue⁃engineering scaffolds[J]. Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, N J), 2012, 868: 111⁃123. |
| 61 | Chang H I, Wang Y. Cell responses to surface and architecture of tissue engineering scaffolds[M]. Regenerative medicine and tissue engineering⁃cells and biomaterials,InTechOpen, 2011. |
| 62 | Egan P F. Integrated design approaches for 3D printed tissue scaffolds: Review and outlook[J]. Materials, 2019, 12(15): 2 355. |
| 63 | Marques A, Miranda G, Silva F, et al. Review on current limits and potentialities of technologies for biomedical ceramic scaffolds production[J]. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B⁃Applied Biomaterials, 2021, 109(3): 377⁃393. |
| 64 | 水恒涛. 应力刺激效应下聚乳酸骨支架的降解行为研究[D].南京:东南大学,2020.DOI:10.27014/d.cnki.gdnau.2020.004258 . |
| 65 | Wang Z, Yao R, Wang D, et al. Structure design and biological evaluation of the mechanical⁃adaptive titanium⁃based porous implants[J]. Materials Technology, 2021, 36(14): 851⁃856. |
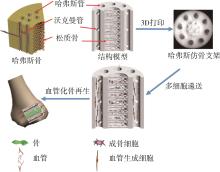
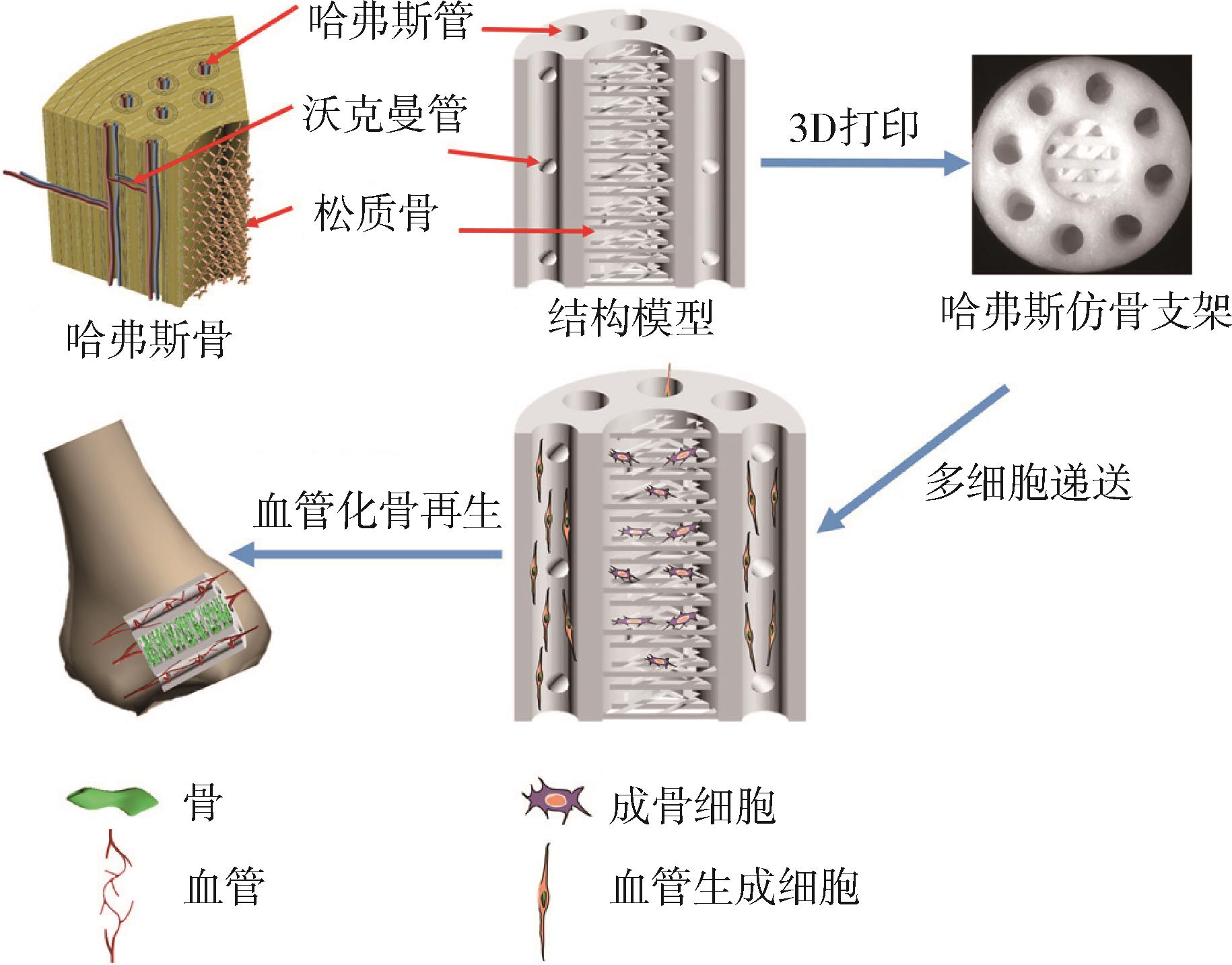
| 66 | Zhang M, Lin R, Wang X, et al. 3D printing of Haversian bone⁃mimicking scaffolds for multicellular delivery in bone regeneration[J]. Science advances, 2020, 6(12): eaaz6725. |
| 67 | Montazerian H, Mohamed M G A, Montazeri M M, et al. Permeability and mechanical properties of gradient porous PDMS scaffolds fabricated by 3D⁃printed sacrificial templates designed with minimal surfaces[J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2019, 96: 149⁃160. |
| 68 | 杨文静,乌日开西·艾依提,王娟,滕 勇.基于3D打印的CPC人工骨支架流道结构设计[J].机械设计与制造,2015(08):30⁃33.DOI:10.19356/j.cnki.1001-3997.2015.08.009 . |
| YANG W J, WURIKAIXI A, WANG J. Design of the structure of channels for CPC artificial bone scaffolds based on 3D printing[J]. Machinery Design & Manufacture,2015(08):30⁃33.DOI:10.19356/j.cnki.1001-3997.2015.08.009 . | |
| 69 | Jensen J, Rolfing J H D, Le D Q S, et al. Surface⁃modified functionalized polycaprolactone scaffolds for bone repair: In vitro and in vivo experiments[J]. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A, 2014, 102(9): 2 993⁃3 003. |
| 70 | Dave K, Gomes V G. Interactions at scaffold interfaces: Effect of surface chemistry, structural attributes and bioaffinity[J]. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl, 2019, 105: 110078. |
| 71 | Stevens M M. Biomaterials for bone tissue engineering[J]. Materials Today, 2008, 11(5): 18⁃25. |
| 72 | Laschke M W, Harder Y, Amon M, et al. Angiogenesis in tissue engineering: breathing life into constructed tissue substitutes[J]. Tissue engineering, 2006, 12(8): 2 093⁃2 104. |
| 73 | Luo Y, Zhai D, Huan Z, et al. Three⁃dimensional printing of hollow⁃struts⁃packed bioceramic scaffolds for bone regeneration[J]. Acs Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(43): 24 377⁃24 383. |
| 74 | 刘 畅,徐 玲.改良同轴3D打印具有空心管道结构的镁黄长石支架[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(34):5 425⁃5 429. |
| LIU C, XU L. Modified coaxial 3D⁃printed akermanite scaffold with hollow⁃pipe structure[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research,2022,26(34):5 425⁃5 429. | |
| 75 | Stratton S, Shelke N B, Hoshino K, et al. Bioactive polymeric scaffolds for tissue engineering[J]. Bioactive materials, 2016, 1(2): 93⁃108. |
| 76 | Yang C, Wang X, Ma B, et al. 3D⁃printed bioactive Ca3SiO5 bone cement scaffolds with nano surface structure for bone regeneration[J]. Acs Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(7): 5 757⁃5 767. |
| 77 | Isaacson N, Lopez⁃Ambrosio K, Chubb L, et al. Compressive properties and failure behavior of photocast hydroxyapatite gyroid scaffolds vary with porosity[J]. Journal of Biomaterials Applications, 2022: 08853282211073904. |
| 78 | Micic M, Antonijevic D, Milutinovic⁃Smiljanic S, et al. Developing a novel resorptive hydroxyapatite⁃based bone substitute for over⁃critical size defect reconstruction: physicochemical and biological characterization and proof of concept in segmental rabbit's ulna reconstruction[J]. Biomedical Engineering⁃Biomedizinische Technik, 2020, 65(4): 491⁃505. |
| 79 | Germain L, Fuentes C A, van Vuure A W, et al. 3D⁃printed biodegradable gyroid scaffolds for tissue engineering applications[J]. Materials & Design, 2018, 151: 113⁃122. |
| 80 | Limmahakhun S, Oloyede A, Sitthiseripratip K, et al. Stiffness and strength tailoring of cobalt chromium graded cellular structures for stress⁃shielding reduction[J]. Materials & Design, 2017, 114: 633⁃641. |
| 81 | Di Luca A, Longoni A, Criscenti G, et al. Toward mimicking the bone structure: design of novel hierarchical scaffolds with a tailored radial porosity gradient[J]. Biofabrication, 2016, 8(4): 045007. |
| 82 | Mustafa K, Oden A, Wennerberg A, et al. The influence of surface topography of ceramic abutments on the attachment and proliferation of human oral fibroblasts[J]. Biomaterials, 2005, 26(4): 373⁃381. |
| 83 | Zhang B G, Myers D E, Wallace G G, et al. Bioactive coatings for orthopaedic implants⁃recent trends in development of implant coatings[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2014, 15(7): 11 878⁃11 921. |
| 84 | Malinauskas M, Rekstyte S, Lukosevicius L, et al. 3D microporous scaffolds manufactured via combination of fused filament fabrication and direct laser writing ablation[J]. Micromachines, 2014, 5(4): 839⁃858. |
| 85 | Bacakova L, Filova E, Parizek M, et al. Modulation of cell adhesion, proliferation and differentiation on materials designed for body implants[J]. Biotechnol Adv, 2011, 29(6): 739⁃767. |
| 86 | Ali D, Sen S. Computational fluid dynamics study of the effects of surface roughness on permeability and fluid flow⁃induced wall shear stress in scaffolds[J]. Annals of Biomedical Engineering, 2018, 46(12): 2 023⁃2 035. |
| 87 | Wang F, Tankus E B, Santarella F, et al. Fabrication and characterization of PCL/HA filament as a 3D printing material using thermal extrusion technology for bone tissue engineering[J]. Polymers, 2022, 14(4): 669. |
| 88 | Yeo A, Wong W J, Khoo H H, et al. Surface modification of PCL⁃TCP scaffolds improve interfacial mechanical interlock and enhance early bone formation: an in vitro and in vivo characterization[J]. J Biomed Mater Res A, 2010, 92(1): 311⁃21. |
| 89 | Murab S, Gruber S M S, Lin C J, et al. Elucidation of bio⁃inspired hydroxyapatie crystallization on oxygen⁃plasma modified 3D printed poly⁃caprolactone scaffolds[J]. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl, 2020, 109: 110529. |
| 90 | Serra T, Ortiz⁃Hernandez M, Engel E, et al. Relevance of PEG in PLA⁃based blends for tissue engineering 3D⁃printed scaffolds[J]. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl, 2014, 38: 55⁃62. |
| 91 | Jeon H, Lee H, Kim G. A surface⁃modified poly(varepsilon⁃caprolactone) scaffold comprising variable nanosized surface⁃roughness using a plasma treatment[J]. Tissue Eng Part C Methods, 2014, 20(12): 951⁃63. |
| 92 | Fonseca D R, Sobreiro⁃Almeida R, Sol P C, et al. Development of non⁃orthogonal 3D⁃printed scaffolds to enhance their osteogenic performance[J]. Biomaterials Science, 2018, 6(6): 1 569⁃1 579. |
| 93 | Gariboldi M I, Best S M. Effect of ceramic scaffold architectural parameters on biological response[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2015, 3: 151. |
| 94 | 施建平. 面向骨植入体3D打印的多孔结构构建研究[D].南京:东南大学,2018. |
| 95 | Zhang L, Yang G, Johnson B N, et al. Three⁃dimensional (3D) printed scaffold and material selection for bone repair[J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2019, 84: 16⁃33. |
| 96 | Söhling N, Neijhoft J, Nienhaus V, et al. 3D⁃printing of hierarchically designed and osteoconductive bone tissue engineering scaffolds[J]. Materials, 2020, 13(8): 1836. |
| 97 | 刘 莹. 结构仿生双孔形多孔Al2O3陶瓷的制备及其性能研究[D].西安:西安理工大学,2014. |
| 98 | Otsuki B, Takemoto M, Fujibayashi S, et al. Pore throat size and connectivity determine bone and tissue ingrowth into porous implants: three⁃dimensional micro⁃CT based structural analyses of porous bioactive titanium implants[J]. Biomaterials, 2006, 27(35): 5 892⁃5 900. |
| 99 | Boccaccio A, Uva A E, Fiorentino M, et al. Geometry design optimization of functionally graded scaffolds for bone tissue engineering: a mechanobiological approach[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(1): e0146935. |
| 100 | Nune K C, Li S, Misra R. Advancements in three⁃dimensional titanium alloy mesh scaffolds fabricated by electron beam melting for biomedical devices: Mechanical and biological aspects[J]. Science China Materials, 2018, 61(4): 455⁃474. |
| 101 | Carrel J P, Wiskott A, Moussa M, et al. A 3D printed TCP/HA structure as a new osteoconductive scaffold for vertical bone augmentation[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2016, 27(1): 55⁃62. |
| 102 | Leber C, Choi H, Bose S, et al. Micromachined Si channel width and tortuosity on human osteoblast cell attachment and proliferation[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 2010, 30(1): 71⁃77. |
| 103 | Dou Y, Huang J, Xia X, et al. A hierarchical scaffold with a highly pore⁃interconnective 3D printed PLGA/n⁃HA framework and an extracellular matrix like gelatin network filler for bone regeneration[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2021, 9(22): 4 488⁃4 501. |
| 104 | Kalita S J, Bose S, Hosick H L, et al. Development of controlled porosity polymer⁃ceramic composite scaffolds via fused deposition modeling[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 2003, 23(5): 611⁃620. |
| 105 | Di Luca A, Szlazak K, Lorenzo⁃Moldero I, et al. Influencing chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stromal cells in scaffolds displaying a structural gradient in pore size[J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2016, 36: 210⁃219. |
| [1] | . Effect of graphite micro-sheets on crystallization and properties of polychlorotrifluoroethylene [J]. , 2023, 37(1): 18-25. |
| [2] | . Applications and performance of medium carbon chain chlorofaffin in PVC products [J]. , 2023, 37(1): 31-37. |
| [3] | . Study on properties of recycled polypropylene for automobile exterior parts [J]. , 2023, 37(1): 112-118. |
| [4] | DONG Youbang, ZHANG Zeqi, YANG Rongjie. Synthesis and characterization of aminopropyl oligomeric silsesquioxane and its amidation products [J]. China Plastics, 2022, 36(8): 1-9. |
| [5] | JIAO Zhiwei, WANG Kechen, ZHANG Yang, YANG Weimin. Performance of PVC/ABS composites filled with carbon black and talc powders based on carbon nano coating deposition [J]. China Plastics, 2022, 36(8): 10-15. |
| [6] | HU Chenguang, SU Hang, FENG Xiaoxin, DING Feng, LI Enshuo, FU Jiawei. Preparation and properties of waste glass⁃fiber⁃reinforced plastic⁃modified asphalt [J]. China Plastics, 2022, 36(8): 119-126. |
| [7] | YANG Yan, WANG Jie, LI Zongyu, WANG Yiming, WANG Yunnan, LI Shuijuan, LEI Liangcai, LI Haiying. A review for synthetic methods of hyperbranched ionic liquid polymers [J]. China Plastics, 2022, 36(8): 159-165. |
| [8] | ZHANG Taozhong, CHEN Xiaolong, HAO Xiaoyu, YU Fujia. Comparison of mechanical properties and interfacial interactions of polypropylene composites filled with talc, calcium carbonate, and barium sulfate [J]. China Plastics, 2022, 36(8): 36-41. |
| [9] | GUO Xiaolei, LUO Jingyun, DING Xin, WANG Yuchen, NIE Minghan, SONG Jiajie, ZHANG Yan’e, HU Jing. Study on modification and foaming behavior of PHBV through chain extension [J]. China Plastics, 2022, 36(8): 73-79. |
| [10] | YU Changyong, XIN Zhong. Effect of α/β complex nucleating agent based on hexahydrophthalate on properties of polypropylene [J]. China Plastics, 2022, 36(7): 121-128. |
| [11] | TAN Liqin, LIU Weiqu, LIANG Liyan, WANG Shuo, FENG Zhiqiang, LIN Jiaming. Preparation and performance of epoxy resin modified with mercaptan polysiloxane [J]. China Plastics, 2022, 36(7): 21-29. |
| [12] | LIU Yi, SUN Wei, QU Guoxing, WANG Ye, YUAN Ning, YANG Shaolin, XU Xia, CHANG Xiaoyi, ZHANG Yufei. Structure and performance analysis of transparent polypropylene special material for thin⁃wall injection molding [J]. China Plastics, 2022, 36(7): 37-43. |
| [13] | XU Jie, ZHONG Jinfu, TONG Xiaoqian, LI Guangfu, FU Dongliang, LI Chengcheng. Preparation and performance of carboxyl⁃terminated tannic acid/gallic acid⁃based epoxy composite [J]. China Plastics, 2022, 36(7): 44-50. |
| [14] | GUO Yuwen, ZENG Bei, GAO Xing, WANG Pan, REN Lianhai. Effect of PET microplastics on performance of co⁃digestion of sewage sludges and food wastes [J]. China Plastics, 2022, 36(7): 51-60. |
| [15] | SHEN Xuemei, ZHU Xiaolong, HU Yanchao, SONG Renyuan, ZHANG Xianfeng, LI Xi. Fabrication and properties of poly(lactic acid))/ibuprofen microspheres through electrostatic spray method [J]. China Plastics, 2022, 36(7): 61-67. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||